Everyone is afraid of tick bites, because everyone knows about the possible dangerous consequences such a brief encounter with a blood-sucking insect. Besides discomfort, a tick bite threatens to infect viral infection- tick-borne encephalitis, the outcome of which is very sad.
What is this infection - tick-borne encephalitis virus? How is the disease caused by it manifested? Is it possible to cure this disease and what complications threaten the sick? What is the prevention of tick-borne encephalitis?
What to do when the tick is attributed
If infected ticks are assigned, the likelihood of human infection increases from the time the parasite is shed. As soon as the tick is assigned, it is necessary to remove it as soon as possible. During all handling of ticks, protect yourself as much as possible with rubber gloves. Turn the checkbox on alcohol disinfection and wait about five minutes. Then use special pliers or tweezers. We will catch the tick where it is in close contact with the skin and remove the wobble motion. The infected area is disinfected again.
What is tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral natural focal infection that is transmitted after tick bites and affects mainly the central nervous system. The causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis belongs to the Flavivirus family of viruses, which are transmitted by arthropods.
This disease has many clinical manifestations. Scientists have long tried to study the disease, but only in the first half of the 20th century (in 1935) they were able to identify the causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis. A little later, it was possible to fully describe the virus, the diseases it causes, and how the human body reacts to it.
We eliminate ticking by immersing the solution disinfectant and inserting it into the toilet. We never pinch nails, shoot them or throw them in the trash! The incubation time is about 14 days of the phase - lung symptoms influenza - articular and muscle pain, fever, nausea. In some people, the disease may end in this phase and complete healing. a phase characterized by high fever, severe headaches, lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, muscle stiffness in the neck, muscle tremors, paralysis, disturbances in sleep, memory and concentration, and general disorientation. The relaxation period is about 14 days. . Tests for tick-borne encephalitis refer to clear, uncompromising speech.
 This virus has the following features:
This virus has the following features:
- reproduces in carriers, the reservoir in nature is a tick;
- tick-borne encephalitis virus is tropic or, in other words, tends to the nervous tissue;
- active reproduction begins in the spring-summer period from the moment of “awakening” of ticks and tick-borne encephalitis;
- the virus does not live long without a host, it is quickly destroyed by ultraviolet radiation;
- when heated to 60 ° C, it collapses in 10 minutes, boiling kills the causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis in just two minutes;
- he does not like chlorine-containing solutions and lysol.
In comparison, 83% of people go to Austria for an effective prophylactic substance. Last year the number of ticks was very high. Tetecular encephalitis - infection viral origin, affecting the brain and brain. The tick-borne encephalitis virus is transmitted, in particular, by ticks, or can be obtained by ingestion of undertreated cows, goats or sheep's milk or dairy products.
This period lasts from a week to fourteen days. The first stage of the disease is similar to a mild flu and ends after a few days without any further consequences. If the disease enters the second phase, the virus can attack the central nervous system and leave lasting effects.
How is tick-borne encephalitis transmitted?
The main reservoir and source of infection are ixodid ticks. How does the tick-borne encephalitis virus enter the body of an insect? 5–6 days after the bite of an infected animal in a natural focus, the pathogen penetrates into all organs of the tick and concentrates mainly in the reproductive and digestive systems, salivary glands. There, the virus remains for the entire life cycle of the insect, and this is from two to four years. And all this time after a tick bite of an animal or a person, tick-borne encephalitis is transmitted.
Infection can occur after several tens of minutes
Nearly 80% of respondents are unaware of the severity possible infections. Cellular encephalitis can be infected two hours after a tick. If you are away from home for several hours, you should look into it. The current check may not result in the detection of all tics, but it will reduce the likelihood of a longer sneeze, says the epidemiologist.
Encephalitis has several phases of symptoms
A clear sign of meningoencephalitis is stiff neck muscles where the chin cannot be raised on the chest, which is a signal for an immediate visit to the hospital, Skoda adds. The Czech Republic has the worst results for tick-borne encephalitis in the entire European Union. This results in 25% of infections, which is an extremely high number.

Infect, maybe, absolutely every resident of the area where there are outbreaks of infection. The statistics are disappointing for a person.
- Depending on the region, the number of infected ticks ranges from 1–3% to 15–20%.
- Any animal can be a natural reservoir of infection: hedgehogs, moles, chipmunks, squirrels and voles, and about 130 other species of mammals.
- According to epidemiology, tick-borne encephalitis is distributed from Central Europe to Eastern Russia.
- Some species of birds are also among the possible carriers - hazel grouse, finches, blackbirds.
- There are known cases of infection with human tick-borne encephalitis after drinking milk from tick-infected domestic animals.
- The first peak of the disease is recorded in May-June, the second - at the end of summer.
Ways of transmission of tick-borne encephalitis: transmissible, during the bite of an infected tick, and alimentary - after eating infected foods.
This disease not only attacks adults but also children. They just carry their symptoms much more easily than mature people. In the case of children, the disease is more mild and usually does not have permanent effects. The average hospital stay is 10 days.
The biggest one is the misleading information that says it's best to rub the mites with oil or cream. This is especially dangerous because the tick eliminates potentially infected saliva from the bloodstream. Many people also turn the tick clockwise. The bite device is not threaded, and thus a mechanism like this can cause the body of the tick to unintentionally tear off the head.
The action of the tick-borne encephalitis virus in the human body
The place of frequent localization of the causative agent of the disease in the body of an insect is the digestive system, reproductive apparatus and salivary glands. How does the tick-borne encephalitis virus behave after it enters the human body? The pathogenesis of tick-borne encephalitis can be described as follows.
The calendar is already spring, although it does not indicate the weather. Spring is really time to do this year. We don't know when, but we know whether or not at least hope that spring will come and that day will come as soon as possible. It will be warm outside, and we will pull short trousers out of the briefcase with short sleeves. We put sneakers or sandals at our feet and finally go on a trip to nature.
Unfortunately, walking through the forest is not as safe as it seems. Someone could say that there is nothing worse in the forest than a child stumbles upon a root and rubs his knee. Broken or fractured knee doesn't mean any tragedy, that's a fact. It is also stated here that if a child gets a tic, he will go to him with a doctor, where the parasite will be pulled out and the problem will be over. But nowhere is it written that a tick caught by you or anyone else will not be infected with ticklish encephalitis.

 During the course of the disease is conditionally divided into several periods. The initial phase proceeds without visible clinical manifestations. Next comes the phase neurological changes. It is characterized by typical clinical manifestations of the disease with the defeat of all departments nervous system.
During the course of the disease is conditionally divided into several periods. The initial phase proceeds without visible clinical manifestations. Next comes the phase neurological changes. It is characterized by typical clinical manifestations of the disease with the defeat of all departments nervous system.
And it's not "fun" anymore. So let's say something closer to this disease. Ticking encephalitis, also called ticking or tickling, is one of the infectious diseases of viral origin. As one of the names suggests, it affects the brain and the brain. Sure, their virus transmits tics, but it can also be transmitted by mosquitoes. There is also a risk of disease if we use poorly processed cow's, goat's or sheep's milk.
As has been said, the risk is to live in nature. Such a stay is especially dangerous if we are not properly protected. It's about using a normal and ordinary thing like proper clothes. This means long trousers, long sleeves, high boots. On the other hand, it would seem that few could afford to get up like this on a hot day. Probably the best and effective solution is a repellant. Another risk factor that unfortunately cannot be stopped or affected can be age.
The outcome of tick-borne encephalitis, it happens in three main options:
- recovery with a gradual long-term recovery;
- the transition of the disease to a chronic form;
- death of a person infected with tick-borne encephalitis.
The first signs of tick-borne encephalitis
The first days are the easiest and at the same time dangerous in the development of the disease. Lungs - since there are no clinical manifestations of the disease yet, there is no hint of infection. Dangerous - because due to lack of obvious signs you can miss the time and encephalitis will develop with full force.
For patients over the age of sixty, the disease usually worsens and becomes more complicated. Palliative illness may also occur. The most common cases ending in death occur between the elderly. Cellular encephalitis is detected by taking a blood sample. If in the blood for the virus, disease-causing, antibodies are detected, the patient is usually diagnosed with the disease. However, the presence of these antibodies does not always have to mean tick-borne encephalitis because they can show up in the blood after a recent vaccination or if someone is infected with other related viruses.
Incubation period tick-borne encephalitis sometimes reaches 21 days, but on average lasts from 10 days to two weeks. If the virus enters through contaminated products, it is shortened and is only a few days (no more than 7).
Approximately in 15% of cases, after a short incubation period, prodromal phenomena are observed, but they are nonspecific, it is difficult to suspect this particular disease from them.
Tick-borne encephalitis should be treated in a hospital and the patient should be in the care of professionals. Upon admission to the hospital a short time infusion is given. At least in part, it relieves pain and the nasal organism, which is dehydrated due to frequent vomiting. There is another blood sample that shows what substances are in the body and what is missing. Upon completion of these studies, cerebrospinal fluid is taken, which is the most optimal informant regarding the disease.
Based on this sample, the appropriate treatment is initiated. Throughout the treatment, the patient should be silent on the bed, limit physical activity and not interfere mentally. If a person does not do this, the condition may worsen and the hospital will stay longer. In some cases, spontaneous recovery may occur, but death and complications are also at risk.

The first signs of tick-borne encephalitis appear:
- weakness and fatigue;
- various options sleep disorders;
- a feeling of numbness of the skin of the face or torso may develop;
- one of the frequent signs of tick-borne encephalitis are various types of radicular pain, in other words, unrelated pains appear along the nerves extending from spinal cord- in the arms, legs, in the area of the shoulders and other departments;
- already at this stage of tick-borne encephalitis are possible mental disorders when absolutely healthy person starts behaving strangely.
Symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis
From the moment the tick-borne encephalitis virus enters the bloodstream, the symptoms of the disease become more pronounced.
The best way to prevent this insidious disease is self capitalization. This vaccination can take place not only before the tick season, but throughout the year. The vaccine may be given in three or four doses and does not start working until two weeks after the second dose. Three years will protect us from this vaccination. Unfortunately, everyone has to pay for it out of their own pocket. Another precaution is to wear appropriate clothing and footwear already mentioned in nature. This prevents ticks from biting into the skin and swallowing.
This parasite is able to take over any part of the body, but especially where the skin is exposed, such as between the legs and shoes. Then they move into the raw, warm body of the body. If, however, the tick does not find a place within a certain time, he or she will let go or die. Repellent should be used before being in wild nature. If the tick is human, it should be removed as soon as possible. We use rubber gloves during removal. We should never pull nails out of our noses, sunbathe or break a basket.

 During the examination of a person, the doctor detects the following changes in the condition:
During the examination of a person, the doctor detects the following changes in the condition:
- v acute period tick-borne encephalitis face, skin of the neck and body reddened, eyes injected (hyperemic);
- blood pressure decreases, the heartbeat becomes rare, changes appear on the cardiogram, indicating a conduction disorder;
- during the height of tick-borne encephalitis, breathing quickens and shortness of breath appears at rest, sometimes doctors register signs of developing pneumonia;
- the tongue is covered with a white coating, as in a lesion digestive system, there is bloating and constipation.
Forms of tick-borne encephalitis
Depending on the location of the pathogen in the central nervous system of a person, various symptoms the course of the disease. An experienced manifestation specialist can guess which area of the nervous system has been attacked by the virus.
Need to dip it disinfectant solution and put it in the toilet. If a tick is infected, the infection specifically determines the time during which the parasite has been lost. Tetecular encephalitis is one of the diseases in which it is not good to rely on alternative medicine or healing powers. Therefore, in case of illness, contact your doctor immediately, who will know best how to help.
Ticking encephalitis is an infectious disease of the brain and skin of the brain. It is caused by a virus that is most often transmitted by a tick bite. The number of patients with tick-borne encephalitis is increasing every year. The disease occurs mainly during a stay in nature.
There is various forms tick-borne encephalitis.

Diagnostics
Diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis, as a rule, is delayed due to a blurred initial clinical picture. Patients in the first days of the disease complain of general symptoms Therefore, the doctor directs the person for general clinical examinations.
The carrier is just a few ticks
Encephalitis can only be caused by ticks infected with the virus. The frequency of infected ticks varies by region. Risks are especially deciduous or mixed forests at lower elevations. V Czech Republic a large number of diseases are reported from southern parts Bohemia and Šumava, from all over Prague, Brno and Bruntal, Plze and Opava. Infested mites occur profusely along watercourses and surrounding waterways. In our country, mainly in the basins of the Vltava, Sazava, Berounka, Labe and Dyje and around the Vranov dam.
 What can be found in general analysis blood? The level of blood neutrophils rises and the ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) accelerates. You can already suspect brain damage. Along with this, there is a decrease in glucose in the blood test, and protein appears in the urine. But on the basis of only these tests, it is still difficult to conclude that there is any disease.
What can be found in general analysis blood? The level of blood neutrophils rises and the ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) accelerates. You can already suspect brain damage. Along with this, there is a decrease in glucose in the blood test, and protein appears in the urine. But on the basis of only these tests, it is still difficult to conclude that there is any disease.
Tetecular encephalitis is a seasonal disease
The virus survives for a long time and multiplies in the so-called reservoirs. These are the most common small rodents. A tick that burns from a formation rodent becomes a carrier of the virus. This is due to the activity and number of ticks in the wild, as well as the weather and the number of rodents in the previous year. Ticks occur naturally from April to October. Most big number- At the beginning of June. Then they gradually decrease until September, when the second peak. Between one and five ticks in 100 are reported to be infected during outbreaks.
Other research methods help to finally determine the diagnosis.
- The virological method for detecting tick-borne encephalitis is the detection or isolation of a virus from the blood or cerebrospinal fluid during the first week of illness, followed by infection of laboratory mice.
- More accurate and faster serological blood tests RSK, ELISA, RPHA, take paired blood sera of a sick person with an interval of 2-3 weeks.
It is important to fully collect information about the development of the disease before starting the examination. Already at this stage, the diagnosis can be assumed.
Even a bite with infected ticks should not cause encephalitis. Only 30 to 40 percent of those infected will experience the disease. This period lasts from 7 to 14 days. The disease itself usually occurs in two stages. Headaches, fatigue, fever, nausea, muscle and joint pain are reported first. The symptoms may resemble a small flu. Patients are often considered mild summer colds that pass.
The next stage is severe headaches and fever
This is usually followed by a period of 1 to 2 weeks without symptoms. Added nausea and vomiting. Symptoms of nervous system damage include stiff neck muscles, muscle tremors, nerve palsy, dizziness, sleep disturbances, memory disturbances, and disorientation. Such acute condition lasts 2 to 3 weeks. Then the condition gradually improves.
Consequences of tick-borne encephalitis
Recovery from tick-borne encephalitis can be lengthy for several months.
 The European form of the disease is an exception, the cure occurs quickly without minimal residual effects, but late initiation of treatment can complicate the disease and in 1-2% of cases leads to death.
The European form of the disease is an exception, the cure occurs quickly without minimal residual effects, but late initiation of treatment can complicate the disease and in 1-2% of cases leads to death.
As for other forms of the disease, the prognosis here is not so favorable. The fight against the consequences sometimes lasts from three weeks to four months.
The consequences of tick-borne encephalitis in humans include all kinds of neurological and psychiatric complications. They are observed in 10-20% of cases. For example, if during the course of the disease a person had a decrease in immunity, this will lead to persistent paresis and paralysis.
met in practice lightning forms tick-borne encephalitis, leading to fatal complications during the first days of the onset of the disease. The number of deaths ranges from 1 to 25% depending on the variant. The Far Eastern type of the disease is accompanied by the maximum number of irreversible consequences and deaths.
In addition to the severe course and unusual forms of the disease, there are complications of tick-borne encephalitis affecting other organs and systems:
- pneumonia;
- heart failure.
Sometimes there is a relapsing course of the disease.
Treatment
Tick-borne encephalitis is one of the most serious illnesses, its course is not easy and is almost always accompanied by numerous symptoms. Treatment of tick-borne encephalitis is complicated by the lack of drugs that could affect the pathogen. That is, there are no specific drugs that can kill this virus.
 When prescribing treatment, they are guided by the principle of symptom relief. Therefore, funds are mainly prescribed to maintain the body:
When prescribing treatment, they are guided by the principle of symptom relief. Therefore, funds are mainly prescribed to maintain the body:
- apply hormonal preparations or glucocorticosteroids as an anti-shock treatment for tick-borne encephalitis and to combat respiratory failure;
- magnesium preparations and sedative drugs are prescribed to relieve seizures;
- for detoxification, isotonic solution and glucose are used;
- after the acute phase of tick-borne encephalitis subsides, B vitamins and antihistamines are used.
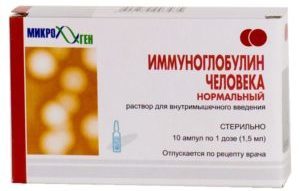 Human immunoglobulin is also used against tick-borne encephalitis. It is obtained from the blood plasma of donors. The timely administration of this medicine contributes to the mild course of the disease and a quick recovery.
Human immunoglobulin is also used against tick-borne encephalitis. It is obtained from the blood plasma of donors. The timely administration of this medicine contributes to the mild course of the disease and a quick recovery.
Immunoglobulin is used according to the following scheme:
- prescribe the drug from 3 to 12 ml for first three days;
- in the case of a severe course of the disease, immunoglobulin is used twice a day with an interval of 12 hours, 6–12 ml, after three days the drug is used only 1 time;
- if the body temperature has risen again - the medicine is prescribed again in the same dose.
Disease prevention
Prevention of tick-borne encephalitis is nonspecific and specific. The first reduces the likelihood of contact with the carrier of the infection:
- in order not to get infected with tick-borne encephalitis, you need to reduce the likelihood of ticks being sucked during walks in nature from April to June, that is, use repellents;
- when working outdoors in the foci of the spread of infection, it is recommended even in summer time wear closed clothing, cover open areas of the body as much as possible;
- after returning from the forest, you must carefully examine the clothes and ask someone close to examine the body;
- a non-specific measure for the prevention of tick-borne encephalitis in one's own area is mowing tall grass in spring and summer, using chemicals to repel ticks.
 What to do if a tick is found on the body after a walk? It is necessary to remove it as soon as possible, so the likelihood of the causative agent of the disease entering the human blood will decrease. It is recommended not to throw the insect away, but to bring it to the laboratory and analyze it for tick-borne encephalitis. In a hospital or paid laboratory, a blood-sucking insect is examined for the presence of a pathogen. The method of infecting laboratory animals with a virus isolated from a tick is used. Even a small fragment is enough to make a diagnosis. They also use more fast way insect research - PCR diagnostics. If the presence of the pathogen in the tick is established, the person is urgently sent to emergency prophylaxis diseases.
What to do if a tick is found on the body after a walk? It is necessary to remove it as soon as possible, so the likelihood of the causative agent of the disease entering the human blood will decrease. It is recommended not to throw the insect away, but to bring it to the laboratory and analyze it for tick-borne encephalitis. In a hospital or paid laboratory, a blood-sucking insect is examined for the presence of a pathogen. The method of infecting laboratory animals with a virus isolated from a tick is used. Even a small fragment is enough to make a diagnosis. They also use more fast way insect research - PCR diagnostics. If the presence of the pathogen in the tick is established, the person is urgently sent to emergency prophylaxis diseases.
There are two main ways to protect a person from the development of an ailment: in an emergency and in a planned manner.
- Emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis is carried out after contact with a tick. It can be started even before the fact that the infection of the insect is established. Immunoglobulin is used in a standard dose - 3 ml for adults, and for children 1.5 ml intramuscularly. The drug is prescribed as preventive treatment encephalitis to all unvaccinated against infection. 10 days after the first dose, the drug is administered again, but in a double dose.
- Planned specific prophylaxis tick-borne encephalitis is the use of a vaccine against a pathogen. It is used by everyone living in an area with high rates of morbidity. Vaccination can be done according to epidemic indications a month before the spring season of awakening ticks.
 Scheduled to vaccinate against tick-borne encephalitis, not only residents of infected areas, but also visitors, in case of a business trip to a dangerous, from the point of view of morbidity, zone.
Scheduled to vaccinate against tick-borne encephalitis, not only residents of infected areas, but also visitors, in case of a business trip to a dangerous, from the point of view of morbidity, zone.
Today there are two main versions of vaccines: tissue-inactivated and live, but attenuated. They are used twice with repeated revaccination. But none of the available drugs protect against tick-borne encephalitis for a long time.
Is the tick-borne encephalitis virus dangerous today during the active development of the preventive branch of medicine? More long years the causative agent of the disease will be classified life threatening person. There are all prerequisites for this - great amount animal carriers in nature, their distribution over a large area, lack of specific treatment all forms of illness. From all this, only one correct conclusion follows - it is necessary to carry out timely prevention of tick-borne encephalitis through vaccination.
Encephalitis caused by the ixodid tick is dangerous. Basic source of infection- tick saliva, when it enters human blood, vital damage occurs important organs: brain (spinal) cord, central nervous system. What forms of encephalitis are distinguished, how the virus affects the body, with what symptoms you should immediately consult a doctor, we will consider in more detail in this article.
Forms of tick-borne encephalitis
The disease develops in stages. First to 3-7 days When the virus enters the body, it is in the incubation stage. The infection is focal, the peak of the outbreak falls on Aug. Sept month. It is during this period of the year that the tick is most active. With a decrease in immunity, the disease begins to progress rapidly, passing from one form to another.
There are 4 periods (forms) of encephalitis:
- feverish, primary initial stage encephalitis. Symptoms are bright, like with the flu: fever, chills, fever, toxicosis, aching bones. After 8-10 days, the symptoms subside, become less pronounced. Sick, on time passed the course treatment begins to improve.
- Meningeal, replaces the primary febrile form. The virus, if not eliminated in time, quickly penetrates into the bloodstream, affecting the nervous system and meninges. Symptoms appear in the form of headaches, vomiting, a sharp increase in temperature, muscle stiffness in the back of the head.
- encephalitic leads to brain damage. In addition to the above symptoms, the patient has pronounced mental disorders, consciousness, there may be convulsions and paralysis. The condition is critical, requiring urgent hospitalization of the patient. Available fatal outcome.
- Polio, leads to damage to neurons in the spinal cord, muscle paralysis. The patient remains disabled, even if the doctors still manage to save his life.
Incubation period of tick-borne encephalitis in humans
The duration of the incubation period is 8-30 days. Depending on the state of immunity, the number of days may vary slightly.
During this period, the virus is introduced into the blood, healthy cells are damaged, they mutate, spread throughout all vital systems:
- liver transplant;
- blood vessels, spleen;
- lymph nodes;
- spinal cord;
- cervical spine;
- soft tissues of the brain;
- cerebellum.
Tick-borne encephalitis is dangerous, leading to damage to the nervous and motor systems. Primary symptoms just begin to appear already in the incubation period.
Symptoms
It is with the onset of the incubation period that the primary symptoms of inflammation become pronounced.
Diagnosing an ailment to doctors is not difficult:

As the virus progresses by about 8-10 day crashes the cardiovascular system. Signs are showing bronchitis (cough, chills). You may suspect pneumonia.
It is in children because of the unstable weak immunity symptoms are most pronounced. The incubation period is not long. quickly, through 10-12 days turns into a more severe meningeal form. The kids start complaining headaches, nausea, vomiting, chills.
There are signs of meningitis:
- high temperature;
- violations psyche;
- since morning dizziness;
- sharp pain in the head;
- in blood increased level ESR, leukocytes.
On the 10-12 knocks acute manifestations encephalitis pass, become more lethargic. The process proceeds rather sparingly, but there are primary signs of paralysis, atrophy of the muscles of the neck and upper limbs(hanging of the head and arms along the body due to the absence of tendon reflexes). Disorders of activity become more pronounced heart and respiratory organs.
signs
Clinically, tick-borne encephalitis can manifest itself in different ways:
- Spreading through the blood, paralyzes the muscles of the neck, limbs.
- In the upper and lower sections there is weakness, hanging down with whips of exhausted arms and legs. The patient is feverish, shivering, there is a feeling of weakness, overwork, aches all over the body.
- Integuments of the skin and oral mucosa at acute course encephalitis hyperemic.
- Often there is paralysis, numbness (numbness) of the limbs, a feeling of stupor, tinnitus.
Severe condition. Possible coma, loss and confusion, fever. directly depend on the places of localization of tick suction.
Course and forecast
In spite of severe course illness, in primary latent phase when making timely curative measures forecast positive. The patient quickly improves and recovers.
It should be understood that the further the spread of the virus through the blood, the worse the situation becomes. Defeat meninges, joints inevitably leads to serious consequences. Patients often go to the doctor with meningeal form of encephalitis when headaches, photophobia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness are present.
Particularly severe course of the disease with meningoencephalitic form diseases when there is an overexcitation of psychomotor, hallucinations, seizures of epilepsy.
At focal brain injury breathing is disturbed, reflexes are asymmetric and inhibited. Musculature of muscles, facial expressions are subject to paralysis. There is a cerebellar subcortical syndrome against the background of epileptic seizures. Possible loss of consciousness, coma.
prodromal syndrome present in the polio form of the disease. The cells of the spinal cord are irritated. There is numbness and weakness in the limbs. Clearly violated motor functions at the patient. A wave of fever in the first 3-4 days during the incubation period is replaced by flaccid paresis in the neck, shoulders, and chest.
At this current disease, the head begins to hang on the chest, involuntarily throws back along with the arms. Posture becomes stooped, hunched. There are all signs of polio, leading to the end 2-3 weeks development of the disease to complete atrophy of muscles, then nerves and trunks.
If in the first 7 days a wave of fever proceeds relatively easily and meningeal symptoms are moderately expressed, then with the advent of the second wave the temperature rises sharply, lethargy, lethargy and, most importantly, damage to the trunks, endings, cells of the nervous system. A new phase of the disease begins, the longest and most severe.
In the periphery of the blood, the number of lymphocytes, sugar and protein is exceeded. The flow is progressing. As the nervous system is damaged, hyperkinetic or epileptic syndromes appear. Muscle groups are prone to paresis, heart contractions become spontaneous. Irradiation of infection in the brain complicates the course of the disease. The forecast becomes unfavorable.
If not taken Urgent measures on hospitalization of the patient, the lethal outcome becomes obvious.
Diagnostics
First, the patient will be visually examined by the doctor, complaints will be heard, and information about the last places of stay, where tick infection may have occurred. Further, the patient is redirected to take tests if tick-borne encephalitis is suspected.
The complex of diagnostic measures includes:
- conducting PCR for the presence of antigens in the blood;
- take cerebrospinal fluid for analysis;
- examination ELISA reactions to antigen susceptibility;
- analysis blood composition for the presence of immunoglobulin.
Treatment
First of all, it is carried out body detoxification, at cardiovascular disorders – resuscitation therapy.
Treatment of encephalitis- complex, by injection of immunoglobulin in the first 3-4 days. It is important to prevent swelling from a tick bite in the head area.
In order to normalize blood circulation, improve the trophism of nerve tissues and fibers, it is prescribed antiviral therapy by injection of interferon, intronamixin, cycloferon. When detoxifying the body, you can not do without antipyretic, anti-inflammatory drugs.
To eliminate symptoms, medication is indicated by prescribing:

Encephalitis- a complex infectious disease and the appointment of treatment, the choice of the correct tactics of the therapy regimen should be dealt with only by a competent specialist, an infectious disease specialist. The patient needs rest, inpatient treatment with the exclusion of all provocative stimuli.
Encephalitis is fraught with serious complications, so the treatment course is carried out under close supervision. doctor's supervision for the body's response to the drugs administered. In the absence of improvement, the doctor will select other means and methods of treatment to eliminate all unpleasant symptoms. Usually the course of treatment 3-5 days.
If there is no improvement, then urgent resuscitation methods of treatment are possible to eliminate the symptoms of the disease through the joint actions of doctors: infectious disease specialist, surgeon, therapist, cardiologist.
Self-treatment,picking out tick and more cutting out the resulting tumor on the head, in any other place is unacceptable. Wrong treatment folk remedies in the form of poultices, lotions can only aggravate the situation.
Patients are subject to urgent hospitalization if tick-borne encephalitis is suspected, they need bed rest and peace, the appointment of a sparing diet. Even after graduation treatment course the patient remains under medical supervision. After 3-4 months, it is subject to re-examination, and so, perhaps up to 3 years, until the foci of infection, possible with encephalitis, are completely eliminated.

