In this article, we will consider the norm of blood acid base balance.
Analysis of the acid-base state of blood and its gases is of great importance in the diagnosis of diseases in surgery, anesthesiology and resuscitation, and also plays an equally important role in treatment. Each modern laboratory contains a special blood sample. If you want to monitor the main parameters in the blood, the data on them can be obtained from an electrolyte analyzer.
Any changes in the acid-base state of the blood indicate the development of a certain pathological process. Studies of the gas composition of blood are used, as a rule, when there is a suspicion of the presence of respiratory diseases in a person or in case of metabolic disorders. The results of repeated studies allow tracking the dynamics and assessing the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
But for this you need to know the rate of acid-base balance.
What does this study show?
Blood is one of the basic substances of the human body. It constantly circulates through it, supplying oxygen to all tissues and cells. In addition, she is directly involved in the elimination of toxins and harmful compounds from the body. Blood renewal is also an ongoing process. It is important to understand that a blood test for acid base balance is such an analysis, based on the results of which a specialist can assess the work of the body as a whole.
The most clinically significant indicator is the pH level. This value should be stable. If it deviates to a smaller or larger side, the specialist may suspect violations in the processes that are responsible for the formation of such an indicator.
The rate of acid base balance in adults differs from that in children.
When the acid-base balance is disturbed, a person experiences very rapid aging. Along with this, there is a significant weakening of the body's protective barriers, as a result of which various diseases develop. With untimely therapy, serious pathologies can occur, which often do not respond to treatment.

Indicators
In addition to pH, the main indicators of blood acid base balance are:
- pCO2 - this value characterizes the partial voltage of carbon dioxide in the blood. It is determined in the absence of air access. Based on this indicator, we can talk about the degree of functioning of the respiratory organs.
- PaO2 is a value that characterizes the partial pressure of oxygen, which is present in a gaseous medium balanced with blood.
- PAO2 - which is present in the alveolar air.
- ТСО2 is an indicator that characterizes the general level of carbon dioxide, that is, all its forms and states.
- AB is an indicator of true bicarbonate. A deviation of this value in one direction or another is observed with respiratory disorders.
- SB is an indicator of standard bicarbonate. Allows you to assess the severity of metabolic disorders.
- BE is an indicator of excess or deficiency of non-carboxylic acids. This value shows the volume of a strong base that is required to normalize the pH values.
- BE-ecf - the amount of excess or deficiency of bases, which is calculated for the extracellular fluid.
- BB - is the sum of bicarbonate ions and protein anions.
- CaO2 is the level of oxygen capacity of the blood.
- CtO2 is a value that reflects the actual oxygen content in the blood.
- DA-aO2 is a value on the basis of which it is possible to assess the diffusion capacity of the lungs and the volume of shunt blood flow.
- SpO2 is an indicator that characterizes the ratio of total and oxygenated hemoglobin fractions.
If you suspect the occurrence of certain pathological processes in the body, the doctor prescribes a laboratory analysis to study the acid-base balance.
Indications for the purpose of the study
The doctor should be consulted when certain alarming symptoms appear, which indicate a dysfunction of the digestive system, liver, kidneys and lungs, as well as with frequent exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. Especially if, at the same time, a person experiences rapid aging, which externally manifests itself in the form of the appearance of early wrinkles, flabbiness of the skin, this indicates deviations of indicators from the norm of blood acid base balance.

Purpose of the analysis
The study of the gas composition is assigned for the following purposes:
- Detection of various pathologies at the earliest stages of their development.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of a previously established therapeutic regimen.
When evaluating the results of the study, the specialist can also judge the general condition of the patient's body.
Preparing for the study
When prescribing an acid base balance analysis, the specialist explains to the patient some of the rules that must be followed before passing the biological material. The doctor is obliged to inform the patient that during this analysis, in most cases, puncture of the artery is performed. The patient should be prepared for the appearance of uncomfortable or painful sensations in the area of the puncture of the blood vessel. Before sampling the biomaterial, the patient is recommended to rest for 30 minutes. Stable physical condition is the key to obtaining the most informative results, especially for people suffering from severe respiratory failure. Correction of the diet and diet before the study is not required.
Biomaterial sampling rules
To study the acid-base balance, blood is needed:
- Venous. Norms of acid base balance of venous blood Ph 7.26-7.36.
- Lymph - 7.35-7.40.
- Arterial. Norms of acid base balance of arterial blood Ph 7.35-7.45.
- Intercellular fluid - 7.26-7.38.
- Capillary. Norms of acid base balance of capillary blood Ph 7.35-7.44.
- Intra-articular fluid - 7.3.
Arterial blood is the most suitable biological material for the study of gas composition. This is due to the fact that its study makes it possible to fully assess the degree of functioning of the organs of the respiratory system.

Types of receipt:
- Puncture of the radial artery. This technique is considered to be the simplest. After its implementation, the probability of hematoma formation is less than 2%. A puncture of the radial artery should not be performed with severe atherosclerosis in this area, as well as with a negative Allen test. The latter is done as follows: the patient needs to squeeze and unclench the brush several times until its skin turns pale, after which the vessel is squeezed. If normal skin color is restored in less than 5 seconds, this can be considered normal. A longer shade restoration process indicates impaired blood flow.
- Puncture of the femoral artery. The disadvantages of this technique are the high risk of blood loss, thrombosis, occlusion of a blood vessel, ischemia of the hand, and various complications of an infectious nature. Taking biomaterial is not carried out in the presence of a vascular prosthesis in this area, taking anticoagulants, with aneurysms and thrombosis of a local nature. The complexity of this method of conducting the study lies in the fact that it is not always possible to puncture the artery at the first attempt.
The level of carbon dioxide, which is the end product of metabolic processes in tissues, is somewhat higher in venous blood than in arterial blood. In this case, the volume of oxygen, on the contrary, is lower. If you conduct a study of the acid base balance of venous blood, it is possible to assess the indicators of systemic metabolism. The collection of biological material is extremely rarely performed from peripheral vessels, since the result of such a study is not considered clinically significant.
In most cases, this analysis is carried out by puncturing the pulmonary artery. When taking blood, if it is made from a vessel of the limb, the tourniquet, as a rule, is not applied. This is due to the fact that against the background of changes in local blood circulation, the study results are significantly distorted and become uninformative. If biomaterial is taken through a catheter inserted into a central vein, the specialist should avoid the channel through which glucose and electrolytes are injected. Blood acid base balance in this case can also be considered uninformative due to falsely increased indicators.
In terms of gas content, the capillary connective liquid tissue is close to the arterial one. However, clinicians consider her research the least informative. Capillary blood sampling is carried out, as a rule, in cases where it is necessary to assess the main indicators of the acid-base balance of blood in newborn babies.
So, what is the acid-base balance rate?

Interpretation of results
The norm of blood acid base balance is of interest to many. First of all, experts analyze the pH level. This is due to the fact that this value is the main one among all clinically significant ones. Deciphering the norm of blood acid base balance in adults is carried out by such doctors as a hematologist and a therapist. A normal result is considered if this indicator is in the range of 7.37-7.44. With a slight deviation to a smaller or larger side, it is customary to talk about certain disorders in the functioning of the body. If this indicator rises or falls significantly, the person is usually fatal.
In children, a pediatrician and a hematologist are involved in the interpretation of blood acid base balance. The result of the norm for babies is values from 7.30 to 7.37.
The norms of acid base balance in newborns are presented in the table.

In addition, diagnostically important indicators are:
- Partial stress of carbon dioxide. In this case, arterial blood is most often taken. The norm of acid base balance for children can be considered from 27 to 39 mm Hg. Art., for women - from 31 to 44 mm Hg. Art., for men - from 34 to 49 mm Hg. Art. If venous blood acted as biological material, such indicators will be 5-6 units higher, which is not a deviation.
- Standard bicarbonates. The norm of acid base balance for whole arterial blood is 17 to 24 mmol / l, for venous plasma - from 21 to 30 mmol / l. With a decrease in these indicators, it is customary to talk about the development of acidosis, with an increase - alkalosis.
Now it is clear what an ACS is. The meaning of the norm is described above.
Factors that have a negative impact on acid base balance
If, in the process of interpreting a blood test for acid-base balance, a specialist discovers certain deviations, he is obliged to clarify whether the patient passed the biological material in a calm state, and also to determine what other factors could cause distortion of the results.

The main indicators of this study can be negatively affected by:
- unbalanced diet, excessive consumption of fast food;
- living in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- prolonged state of stress;
- smoking;
- wrong daily routine.
In the presence of such factors, a specialist may prescribe a repeated study and blood acid base balance in children and adults.
Determination of the acid-base state on your own
It is extremely important to understand that the information content of the study in a specialized laboratory is as high as possible. It is carried out using modern automated analyzers of blood gases, electrolytes, glucose and acid base balance. If, for certain reasons, the patient often needs to take biological material, he can purchase a special device and use it to regularly assess the pH values.
The principle of operation of this device is as follows: the device has two electrodes that are placed in a drop of blood. This creates an electromotive force. After analysis, the pH meter (within one minute) gives accurate results. Such a device can be digital or analog. Analog models are considered outdated, so they are rarely used by patients in practice. Digital pH meters are the most modern devices with a user-friendly interface, built-in memory and a system of prompts, so there is no need to record the research results on paper every time.
Pharmacies and medical equipment stores sell portable and stationary devices. Thus, a person can install a pH meter at home. There are mobile versions of this device.
It is not difficult to decipher the blood acid base balance rate.

Alkalosis and acidosis
It is customary to talk about such conditions in cases when, when decoding acid base balance, the doctor discovers abnormalities. Alkalosis is a disease characterized by elevated levels of key indicators. This condition leads to the following consequences:
- violation of the processes of food digestion;
- deficiency of minerals;
- the entry into the blood of a large volume of toxic compounds.
Over time, this pathological process begins to progress. Lack of treatment leads to pathologies of the digestive tract, severe allergic reactions, dermatological problems. In addition, if a person has chronic diseases, against the background of alkalosis, they begin to rapidly become complicated. The reasons for the increase in pH are:
- malfunctions of the heart and blood vessels;
- prolonged stressful situations;
- diseases in which there are frequent episodes of vomiting;
- overweight;
- unbalanced diet.
If, during the study of acid base balance, a deviation of the indicators is revealed in the lower direction, this indicates acidosis. This condition is considered very life-threatening, and this threat lies in the fact that in the initial stages the disease is not accompanied by alarming symptoms. As the progression progresses, the following phenomena occur:
- increased blood sugar;
- episodes of lack of air;
- nausea;
- state of shock.
If the analysis indicators are significantly reduced, the blood is acidified. In case of delayed treatment, a lethal outcome is inevitable.
We examined the decoding and norms of blood acid base balance in children and adults.
Acid-base condition prices
- Study of the level of carboxyhemoglobin in the blood 500 rubles.
- Study of the level of methemoglobin in the blood 500 rubles.
- KShchS 1100 rubles.
Study of the acid-base state (ACS) or acid-base state (CBS) is important in the diagnosis and treatment of various emergency conditions, including surgical ones.
Acidity and alkalinity are understood as the concentration of free hydrogen ions (H +) in a solution, i.e. blood pH. For the efficient course of vital processes, the concentration of free hydrogen ions (H +) must be within strict limits. In fact, the study of acid base balance includes, along with measuring pH, the determination of physiologically important gases present in the blood (oxygen - О 2 and carbon dioxide - СО 2) and about 20 other parameters. All these indicators and their values are closely interrelated with each other.
Patients in the intensive care unit and operating unit may experience significant changes in these parameters within short periods of time. Acid-base balance studies, unlike all other types of laboratory tests, are performed on arterial blood samples.
For the normal functioning of all cells in the body, oxygen (O 2) is needed. The decisive role in the transport of oxygen to the tissues belongs to the hemoglobin contained in erythrocytes. The term "hemoglobin" means several forms of hemoglobin that are present in human blood, both in normal conditions and in pathology. More than 98% of the oxygen absorbed by the lungs from the inhaled air is carried to the cells of the body in the form of oxyhemoglobin. Normally, small amounts of hemoglobin fractions are present in the blood, which are not capable of carrying O 2 - dyshemoglobins (sulfhemoglobin, methemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin).
Methemoglobin is constantly formed as a result of the normal metabolism of cells in the body. Methemoglobin contains ferric iron and is not capable of transporting oxygen! With the formation of significant amounts of methemoglobin, the transport function of blood is sharply impaired. The body has a mechanism for regulating the level of methemoglobin in the blood, which maintains the proportion of this fraction not higher than 1.0-1.5% of the total hemoglobin.
Carboxyhemoglobin- a strong compound of hemoglobin (Hb) and carbon monoxide (CO). Carboxyhemoglobin is formed very quickly because carbon monoxide is about 200 times more capable of attaching to hemoglobin than oxygen. Carboxyhemoglobin is unable to carry oxygen to the tissues of the body, therefore, in case of poisoning with carbon monoxide, a person can quickly die. In large quantities, carboxyhemoglobin is formed during carbon monoxide poisoning, and in small quantities it is always present in the blood of all smokers and residents of large cities.
Indications:
Acid-base balance analysis is required
· To make a diagnosis blood gas analysis is an integral part of the diagnosis of respiratory failure and primary hyperventilation. It also detects metabolic acidosis and alkalosis.
· To assess the severity of the disease
· To monitor the effectiveness of treatment this analysis is very important for the selection of oxygen (O 2) therapy for patients with chronic respiratory failure type 2 and for the optimization of ventilator settings.
An increase in methemoglobin (FMetHb) in the blood develops when:
Poisoning with nitrites, nitrates, nitroso compounds, aniline, sulfonamides, acetanilide, chlorides, bromides, etc.
· Hereditary deficiency of NADH-methemoglobin reductase: low activity of the enzyme manifests itself in early childhood. As a rule, this disease has no clinical consequences, manifesting itself as a minor cosmetic defect.
The presence of abnormal variants of hemoglobin, designated as hemoglobin M
An increase in carboxyhemoglobin (FCOHb) in the blood develops when:
· Carbon monoxide poisoning. At the level of FCOHb above 30%, severe headaches, general weakness, vomiting, shortness of breath, tachycardia are noted, and at a level of 50%, convulsions, coma; above 70%, respiratory failure occurs and death is possible.
Methodology:
Determination of blood gases, acid-base status, oximetry parameters are carried out on an ABL 800 FLEX analyzer manufactured by RADIOMETR, Denmark, determination of up to 50 parameters.
A decrease or increase in one indicator - blood pH - indicates acidosis or alkalosis, but does not give an exhaustive answer to the question of which component of acid-base balance is disturbed: respiratory or metabolic.
If, however, two indicators are interpreted (pH and pCO 2), then the determination of the priority of acid base balance disturbance becomes possible (Table 1).
Table 1. Determination of the priority of acid-base balance disorder
|
arterial blood pH (norm 7.35 - 7.45) |
рС0 2 (norm 35 -45 mm Hg) | Primary violation |
| Reduced | Increased | Respiratory acidosis |
| Reduced | Norm or reduced | Metabolic acidosis |
| Promoted | Increased or normal | Metabolic alkalosis |
| Increased | Reduced | Respiratory alkalosis |
| Norm | Downgraded |
Mixed form respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis |
| Norm | Increased |
Mixed form respiratory acidosis and metabolic alkalosis |
Acid-base blood homeostasis is characterized by the following indicators:
pH is an indicator of active blood reaction; in total reflects the functional state of the respiratory and metabolic components and changes if the capabilities of all buffer systems are exceeded (normally 7.35 - 7.45).
pCO 2 (mm Hg) - the tension of carbon dioxide in the blood; the only respiratory indicator COH, reflecting the functional state of the respiratory system, changing with its pathology and as a result of compensatory reactions during metabolic shifts (normally 35-45 mm Hg in arterial blood).
AB (mmol / l) - true bicarbonates of blood (aktual bikarbonate); the concentration of carbonic acid ions, HC0 3 - in the physical state of blood in the bloodstream, that is, determined without contact with air at a temperature of 38 ° C (normally 21.8-27.2 mmol / l).
SB (mmol / l) - standard bicarbonate (standard bikar-bonate); concentration of bicarbonate ions (HC0 3 -, measured under standard conditions: pCO 2 - 5.3 kPa (40 mm Hg), at a temperature of 38 ° C and full saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen. Characterizes the displacement of ions of the bicarbonate system.
This indicator is considered more valuable in the diagnostic sense than true bicarbonate, since it reflects only metabolic changes (normally 21.6-26.9 mmol / l).
BB (mmol / l) - buffer base of blood; the total concentration of buffer ions bicarbonates, proteins, hemoglobin in fully oxygenated blood. The diagnostic value of this indicator is small, because it changes depending on pCO 2, hemoglobin concentration (normally 43.7-53.5 mmol / l).
BE (mmol / L) - excess or lack of buffer bases (base excess). It characterizes the shift of ions of all buffer systems and indicates the nature of violations of acid-base homeostasis. A negative BE value reflects a base deficiency or an excess of acids. With metabolic shifts in blood COH, the BE shift will be more pronounced than with respiratory disorders (normally BE = -3 - + 3 mmol / l).
AR - anionic difference. The clinical application of the AR indicator is based on the assumption that any solution, including plasma, must be electrically neutral, i.e. the sum of the cations is equal to the sum of the anions. Plasma contains one main measurable cation Na + and two main measurable anions CI - and HCO 3 -. The contribution of other unmeasured anions (HA) and cations (NA) is small (Table 2). It follows from this that the sum of measurable and unmeasured anions is equal to the sum of measurable and unmeasured cations:
HA + (CI - + HCO s -) = HK + Na +
Table 2.
Using the data in the table, you can calculate the AR:
AR = HA - NC = 23 - 11 = 12 meq / l
AR = HA - HK = Na + - (CI - + HCO3 -)
In cases of an increase in H +, the disparity between the concentrations of cations and anions measured in plasma will go beyond the normal range of 9 - 13 meq / l.
AR can be useful in identifying the etiology of metabolic acidosis.
As a rule, the more ARs, the easier it is to determine the cause of the acidosis.
High AR is characteristic of lactic acidosis caused by anaerobic glycolysis. Diabetic ketoacidosis and uremia are also associated with an increase in AR. If the level of lactate, ketone and creatinine is normal with a high AR, it is most likely that the cause of acidosis is the intake of toxic substances (methanol, paraldehyde, ethanol, ethylene glycol, drugs). A high plasma salicylate level is accompanied by a significant increase in AR.
Classification of acid-base balance disorders
1. Simple violations:
Acidosis:
- metabolic
- respiratory
Alkalosis:
- metabolic
- respiratory
2.Mixed offenses:
2.1 Unidirectional: metabolic and respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
2.2 Multidirectional:
Metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
- metabolic alkalosis and respiratory acidosis
By the degree of compensation:
1. Compensated.
The pH values remain within the normal range (pH = 7.35 - 7.45), the content of bicarbonates and CO 2 changes depending on the direction of metabolic and respiratory shifts.
2. Subcompensated.
In addition to changes in the content of bicarbonates and CO 2, pH also changes, but within insignificant limits of + 0.04 (pH = 7.31 - 7.49)
3. Uncompensated.
PH< 7,30 - некомпенсированный ацидоз;
PH> 7.50 - uncompensated alkalosis.
Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis results from a significant decrease in the level of bicarbonate in the body.
Causes:
1. Increase in the production of non-volatile acids.
Enhanced production of acidic metabolites (so-called keto acids - (3-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate) is one of the characteristic features of uncontrolled or poorly controlled insulin-dependent diabetes. In this condition, called diabetic ketoacidosis, the amount of bicarbonate in the blood is significantly reduced due to its use to neutralize excess acids.
In cells that are largely deprived of oxygen and, therefore, cannot metabolize (oxidize) glucose, lactate accumulates. Such a significant accumulation of lactate in the blood in quantities sufficient for the development of metabolic acidosis occurs when tissues are inadequately perfused with blood, and therefore insufficiently oxygenated.
The most striking cause of lactic acidosis in violation of tissue perfusion is hypovolemic shock. In addition, lactic acidosis can occur with renal or hepatic failure, diabetes, sepsis, and leukemia.
2. Increased loss of bases.
Bicarbonate is secreted into the small intestine for digestion and absorbed in the lower gastrointestinal tract. If reabsorption does not occur, it is lost in feces.
Any diseases of the digestive tract (for example, severe diarrhea) can lead to the loss of bicarbonate from the body in quantities sufficient for the development of metabolic acidosis.
Also, the loss of bicarbonate can be associated with renal failure (proximal tubular acidosis - renal acidosis type II). Deterioration of Na + reabsorption leads to the appearance of an alkaline urine reaction. In addition, proximal tubular acidosis is characterized by a decrease in serum urates, phosphates and potassium, glucosuria and aminoaciduria.
With the help of the AR value, it is possible to distinguish the loss of HCO3 - with diarrhea from the loss of HCO3 - caused by renal tubular acidosis tab. 3.
Table 3. Anionic difference according to (P. Marino, 1998)
3. Increased intake of acids from the outside.
Abuse of acidic foods, ingestion of hydrochloric acid, administration of large quantities of old canned blood
4.Reducing the excretion of H + ions through the kidneys.
Under normal conditions, the kidneys excrete H + in the form of titratable acid (phosphates, sulfates) and ammonia. This mechanism can be impaired in kidney disease, adrenal insufficiency, distal renal tubular acidosis, and hyperaldosteronism. With renal failure, a decrease in the number of functioning nephrons, adequate filtration and excretion of H + are absent.
In type I renal acidosis (distal tubular acidosis), H + secretion in the distal tubules is impaired. Since the excretion of H + in the distal tubules depends on the exchange of Na +, a decrease in fluid volume promotes an increase in acidosis. Through the same mechanism associated with a decrease in Na + supply to the renal tubules, adrenaline insufficiency and selective hypoaldosteronism also lead to a deterioration in H + excretion. In this case, metabolic acidosis is combined with other forms of electrolyte metabolism disorders: hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, hypercalcemia.
Compensatory reactions
A decrease in the level of HCO 3 - in blood plasma (metabolic acidosis), which occurs primarily, is compensated by an increase in pulmonary ventilation and a decrease in pCO 2, while the ratio pCO 2 / HCO 3 remains unchanged.
The increase in acid content is buffered with a bicarbonate buffer:
НС1 + H 2 C0 3 / NaHC0 3 ↔ Na Сl + H 2 C0 3
C0 2 + H 2 O
Diagnostic criteria:
1. At lowered pH, normal or lowered pCO 2 level indicates primary metabolic acidosis;
2. At normal pH, a low pCO 2 level indicates a mixed form of respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis;
3. At a normal pH value, a normal pCO 2 level may indicate that the acid-base balance values are within the normal range, but the possibility of mixed metabolic alkalosis / acidosis is not excluded.
In these cases, the AR is determined and by this indicator the changes in acid-base balance are judged.
4. Deficiency of bases - AB, BE, BB, SB.
Clinical forms of acidosis
Lactate acidosis
Etiopathogenesis.
1. Decrease in tissue oxygenation - tissue hypoxia. The greatest importance is attached to circulatory disorders (cardiogenic, septic, hypovolemic shock). The presence of all forms of hypoxia theoretically contributes to the development of lactic acidosis. Cardiac arrest is accompanied by anaerobic metabolism and lactic acidosis;
2. Dysfunctions of the liver reduce its ability to convert lactic acid into glucose and glycogen.
3. Lack of thiamine (vitamin B1) in alcohol abuse patients leads to inhibition of pyruvate oxidation in mitochondria and contributes to the accumulation of lactic acid.
4. Increase in the dextrorotatory isomer of lactic acid (D-lactate acidosis) undetectable by standard laboratory techniques. This isomer is formed by the action of microorganisms that break down glucose in the intestine. Most often occurs in patients after extensive operations on the intestines, with dysbiosis, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Apparently, this is the most common acid base balance disorder, but it is often not diagnosed (P. Marino, 1998);
5. The possibility of lactic acidosis with prolonged infusion of adrenaline and other vasoconstrictor agents is not excluded.
6. Lactic acidosis can develop in cases of sodium nitroprusside use, during the metabolism of which cyanides are formed that can disrupt the processes of oxidative phosphorylation.
Diagnostics of the lactic acidosis:
Presence of metabolic acidosis associated with increased AR;
Pronounced deficiency of bases;
AR> 30 meq / l, while there are no other causes of acidosis (ketoacidosis, renal failure, administration of toxic substances);
The level of lactic acid in the venous blood exceeds 2 meq / l. This indicator reflects the intensity of the formation of lactate in the tissues.
Treatment:
Elimination of the cause of lactic acidosis.
Sodium bicarbonate administration shown at pH<7,2, содержании НСОз - <15 ммоль/л. Расчет примерной дозы натрия бикарбоната можно провести по следующей формуле:
HCO3 deficiency - (mmol) = 0.3 * body weight (kg) * BE = ml 8.5% soda solution
For 3% soda: BE * 0.8 * body weight
For 4% soda: BE * 0.6 * body weight
For 5% soda: BE * 0.5 * body weight
First, half of the detected HCO3 deficiency is eliminated by intravenous administration of the solution for 30 minutes. Then, under the control of the HCO3 content in the blood serum, the correction is continued for 4-6 hours.
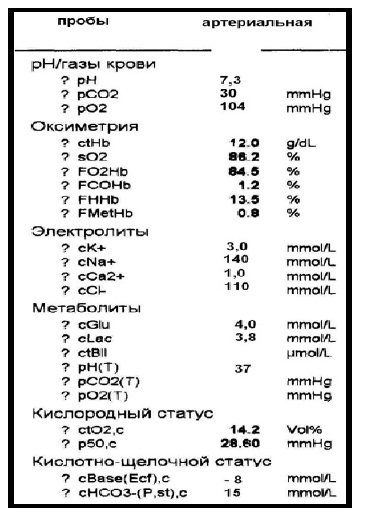
In this case, the pH is below normal - referred to as uncompensated acidosis. Next, we estimate the gas composition of the blood: the pO 2 level for arterial blood is slightly increased, but the pCO 2 is reduced. Given the deficiency of bases and increased lactate, it can be concluded that this is metabolic lactic acidosis, in which immediate compensation in the form of hyperventilation is included.
Ketoacidosis
Etiopathogenesis
In conditions of a pronounced insulin deficiency, the flow of glucose into muscles and adipose tissue is blocked, the level of glucose in cells decreases, and tissues experience “energy hunger”. This leads to hypersecretion of counterinsular hormones - growth hormone, glucagon, cortisol, adrenaline. Under the influence of these hormones, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and lipolysis are stimulated. As a result of lipolysis, fats are broken down into free fatty acids, which become a source of energy and ketone bodies. In conditions of insulin deficiency, excessive formation of ketone bodies occurs, and ketoacidosis develops.
Diagnostics
Clinical symptoms:
Weakness, thirst, nausea;
Diabetic precoma;
Diabetic coma.
Laboratory data:
Hyperglycemia
Glucosuria
Metabolic acidosis (decreased pH, HCO3, pCO 2, severe base deficiency)
Acetone in plasma
Acetonuria
Plasma hyperosmolarity> 300 mOsm / L
Treatment
The initial dose of insulin is 10 IU IV. The subsequent infusion of insulin in isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution is carried out at a rate of 0.1 U / kg / hour.
Deficiency of extracellular and intracellular fluid in ketoacidosis can reach 10% of body weight. Treatment should begin with the introduction of isotonic solutions containing Na + and CI -. The danger of over-administration of crystalloids lies not only in volume overload, but also in an imbalance in sodium and glucose concentrations. Therefore, dynamic control of these substances is necessary and, if necessary, timely correction.
Loss of K + in ketoacidosis reaches 200 - 700 mmol and continues as the acidosis is eliminated. When correcting hypokalemia, it is necessary to take into account not only the deficit, but also the need. The formula for calculating the K + deficit is presented:
Potassium deficiency (mmol) = patient weight (kg) x 0.2 x (4.5 - K + plasma)
The introduction of sodium bicarbonate is recommended when the pH drops.< 7,2 и снижении АД сист ниже 90 мм рт.ст., для предупреждения дальнейших электролитных нарушений и гемолиза. Но введение раствора соды должно быть более осторожным, чем при лактат-ацидозе, рекомендуется вводить 1/2 расчетной дозы.
Alcoholic ketoacidosis
Causes:
The transformation of ethanol into acetaldehyde during metabolism in the liver with the formation of NAD-H, which promotes the production of ketone bodies;
Concomitant starvation, accompanied by increased ketogenesis and ketonemia;
Dehydration leading to oliguria and decreased urinary excretion of ketone bodies.
Diagnostics.
Alcoholic ketoacidosis usually develops 1 to 3 days after excessive drinking. Typically, glucose and ketone levels do not rise very high.
Treatment.
Shown in / in the introduction of isotonic sodium chloride solution and 5% glucose.
Glucose inhibits the formation of ketone bodies in the liver, and saline solutions increase their excretion in the urine. Correction of potassium is carried out according to its content in blood serum. sodium bicarbonate is applicable only if pH< 7,2 и снижении АД сист ниже 90 мм рт.ст..

Interpretation of the assay begins with pH. In this case, the pH is below normal and is referred to as uncompensated acidosis. Next, we evaluate the gas composition of the blood: the pO 2 level for venous blood is normal, however, it is impossible to conclude about the presence of hypoxemia, for this it is necessary to determine the pO 2 in arterial blood. But taking into account the normal level of lactate, we can conclude that there is no O 2 deficiency, there is aerobic glycolysis. The genesis of acidosis is metabolic and this conclusion can be made by the level of base deficiency.
The decrease in bicarbonate levels may be associated with metabolic acidosis or advanced renal failure, this can be said based on history and clinical data.
Metabolic alkalosis
Causes:
Loss of non-volatile acids
Severe and prolonged vomiting of gastric juice (it is acidic) leads to the loss of HCI from the body. These are the causes of metabolic alkalosis associated with pyloric stenosis, a condition in which the movement of gastric contents into the small intestine is difficult.
Loss of H + ions
Hypokalemia increases proximal tubular reabsorption of HCO3 and increases distal tubular H + secretion. An increase in albdosterone levels increases the secretion of H +.
Excessive administration of sodium bicarbonate.
In this case, alkalosis develops with the uncontrolled administration of bicarbonate, citrate, lactate or acetate.
Compensatory mechanisms:
An increase in the content of HCO3 - in the blood plasma (metabolic alkalosis), occurring primarily, is compensated by a decrease in pulmonary ventilation andan increase in pCO 2. As a rule, pronounced respiratory acidosis is not is developing. However, with severe metabolic alkalosis, there is a risk of hypoventilation and hypercapnia.
NaOH + H 2 C0 3 / NaHC0 3 ↔ 2NaHC0 3 + H 2 O
Diagnostics.
HCO3 in arterial blood is more than 25 mmol / l, in venous blood - more than 30 mmol / l;
PH is higher than normal;
РСО2 is normal or increased, in the most severe cases it can be decreased;
With hypochloremic alkalosis - СI less than 100 mmol / l;
Hypokalemia is common.
Treatment.
1. Elimination of the root cause of alkalosis;
2. Replenishment of the deficit: CI deficiency (mol / l) = 0.27 * body weight (kg) * (100 - actual CI content)
The required volume of isotonic sodium chloride solution can be determined by the formula: NaСI (l) = СI / 154 deficit, where 154 is the СI content (mol / l) in 1 liter of 0.9% sodium chloride solution;
3.In case of losses of HCI, an intravenous HCI solution is necessary. A prerequisite for its appointment is a normal fluid content in the body and a normal concentration of K + in the blood serum. The hydrogen deficiency is determined by the following formula:
Deficiency Н + = 0.5 * body weight (kg) *
(actual HC0 3 content - desired HC0 3 content)
1 liter of 0.1 normal solution HC0 3 contains 100 mmol H +. the rate of introduction of the HCl solution is 0.2 mmol / kg / h.
The maximum daily dose of HCI solution = 100 mmol.
Ph blood, its norm for a healthy person is clearly marked, is an important laboratory analysis. Ph is the level of acid-base balance, an important indicator of human blood health. This is the concentration of hydrogen in the body. If its content does not exceed the norm, then all systems and organs work in the required mode. In case of imbalance, a failure occurs: it can lead to the development of serious pathological processes that can even threaten life. When the acid-base balance can be disturbed, what consequences can this have?
What is the Ph level and its norm
This indicator indicates the health of the body and normal immunity. Therefore, it is advisable to maintain the acid-base balance and regularly undergo analysis for its level. Only if the body has a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals, it will not quickly age and hurt.
These indicators can be negatively affected by:
- improper nutrition;
- unfavorable ecological situation;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- constant stress;
- wrong daily routine.
These factors cause the blood test to show a low Ph. Some of them can be influenced by a person. For example, you can balance your diet, monitor the quality of products.
If the acid-base balance is disturbed, then problems such as:
- disruption of the digestive system;
- deterioration of the lungs and kidneys, which purify the air and substances entering the body;
- the main regulatory body - the liver - begins to work poorly;
- chronic pathologies develop.
All this negatively affects the appearance of a person. He begins to age quickly.
If hydrogen ions are in the body in a normal amount, then the body is in order. The lungs, liver and kidneys are responsible for the acid-base state. These organs remove toxic substances and maintain the required concentration of acids and alkalis. It is very important to monitor its level in order to notice the development of serious diseases in time.
How is human blood Ph and abnormalities determined?
In the process of undergoing a preventive examination, doctors usually recommend that the patient determine the acidity of the blood. This will help the specialist assess the state of human health and identify pathology. The hydrogen content is also determined at home. Anyone can buy a special device for this.
Laboratory research is carried out using the electrometric method. Capillary blood is used for research. It contains a stable acid-base environment. Therefore, accurate information can be obtained without errors. The amount of hydrogen is determined by special glass electrodes. It also takes into account how much carbon dioxide is in the blood cells.
Determination of Ph in laboratory conditions will provide more information, and specialists can decipher the result. If it is not possible to visit the hospital, you can buy a special device at the pharmacy that will show the state of the blood.
Alkalosis
This condition leads to disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
Its reasons are:
- prolonged vomiting, with which stomach acid comes out;
- abuse of foods high in alkaline compounds;
- constant stress;
- overweight;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system.
You can get rid of the problem only by eliminating the reasons that influenced the Ph.
Usually, breathing exercises and various solutions are prescribed to increase the level. It is impossible to independently engage in treatment, drugs and their dosage should be prescribed only by a doctor.
Acidosis
A mild form of acidosis in adults can be detected only after passing the test.
A progressive problem can make itself felt:
- signs of diabetes;
- lack of oxygen in the body and the ensuing consequences;
- constant nausea and vomiting;
- breathing disorders;
- a shock state in the presence of other pathologies of a chronic form.
A severe course of acidosis requires immediate medical attention, as this condition can be life threatening. You can eliminate the symptoms of the disease by drinking a glass of water and soda.
How to normalize acidity
You can control your acid-base environment using the following rules:
- Adhere to the principles of good nutrition. There are certain foods that can help keep acid and alkali levels normal. These are vegetables, fruits, some cereals, nuts, dried fruits, as well as mineral water.
- Garlic, potato juice and some types of medicinal herbs (chamomile, mint) help to normalize Ph.
- It is necessary to give up fatty, fried and smoked foods, drink less caffeinated and alcohol-containing liquids, stop smoking. All this leads to the accumulation of substances harmful to the body, and their deposition on the walls of blood vessels.
- To eliminate the negative effects of these products, it is necessary to cleanse the body.
It is useful to use special alkaline water, which enriches the body with ions, helps to strengthen the immune system and remove toxins and toxins from the body. You can make tea from this water or use it in the preparation of first courses. If drugs are prescribed to increase the acid-alkaline environment, then between taking them and drinking water, it is necessary to take a break of several hours.
In addition, it is worth leading a healthy lifestyle, normalizing physical activity, and not forgetting about full periods of sleep and rest.
The acid-base balance or pH of the blood has an important function in the body. If there are deviations from the norm in one direction or another, then this will have serious consequences for human health. pH of human blood has the name of the pH value, as it has a translation from the Latin "power of hydrogen".
If we talk about the normal pH in the blood, then it varies depending on the vessels. For veins, it can be in the range from 7.32-7.42, if we talk about arteries, then here it varies from 7.376-7.43.
In medical practice, conditions when the pH of the blood is below 6.8 or above 7.8 are considered fatal to humans.
If this indicator is normal, then the required amount of hydrogen ions is in the blood. Then all systems of the body, such as the respiratory and urinary systems, work normally and help to remove metabolic products from the body.
Signs of a serious abnormality in blood pH are:
- Disorders in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pathologies in the functioning of the respiratory system (respiratory arrhythmia, etc.), kidneys.
- Hemangioma of the liver and other abnormalities.
In this case, a person can be diagnosed with a chronic disease and his appearance will worsen.
Effects of pH on health
This procedure is prescribed to patients who have identified certain deviations. How is a blood test for pH taken? It is preferable to use arterial blood for the procedure, which is considered pure and gives the most accurate result. A blood pH test involves identifying the level of hydrogen and total acidity in the body.
This study on acid-base balance is carried out on an empty stomach, and blood is taken from the capillaries. The laboratory analysis procedure is carried out using an electrometric method. This requires glass pH electrodes. The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is measured, as well as the amount of hydrogen ions.
Deciphering a blood test for pH is carried out by a laboratory assistant who is a specialist in his field.
With the help of this procedure, the following can be said about human health:
- The result of 7.4 indicates that the balance is slightly alkaline and the person's condition is normal.
- If the pH in the blood is high, then there is a lot of alkali in the body, from which a condition called alkalosis develops.
- If the level is much lower than normal, then this condition is called "acidic blood" and indicates an increase in acidity. In medical terms, this pathology is called acidosis.
Any abnormality must be treated carefully. Both oxidation and alkalization of blood have a bad effect on the human body. Therefore, it is necessary to drink special drugs that restore the normal balance in the blood.
The most common causes of alkalosis are:
- With stress and depression, alkalosis can develop.
- May appear as a result of heart and vascular diseases ..
- If the patient is obese.
- If the patient has previously had prolonged vomiting, as a result of which he has lost a lot of acid.
- If a person often eats dairy products, as well as some vegetables and fruits.
With alkalosis, metabolic dysfunction is observed, as a result of which the digestion of food is significantly impaired and toxins enter the blood.
As a result, the patient has the following anomalies:
- Allergies, allergic vasculitis.
- Various skin conditions can occur.
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Various pathological conditions of the liver.
Such diseases, most often, become chronic and often have periods of exacerbation.
This disease is noted more often than alkalosis. Aciodosis can be caused by alcoholism or complications of diabetes mellitus.
Usually, this disease does not have pronounced symptoms. But in some cases, you can observe:
- Constant heartburn.
- Regular nausea.
- And in some cases, vomiting.
- All the symptoms of diabetes.
- Increased fatigue and weakness.
- Respiratory problems and a noticeable lack of oxygen.
As a result of the fact that oxygen is supplied in insufficient quantities to tissues and organs, a shortage of trace elements such as magnesium, potassium in the blood and sodium may develop, which will lead to abnormal conditions:
- Obesity.
- Formations of tumors.
- Weakness of the body.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Kidney and liver problems.
- Bones become brittle.
- Diabetes may develop.
- Pain in the veins, joints, muscles.
- Immunity decreases.
Many patients have a question: how to determine blood pH at home? To do this, a special device is bought at the pharmacy, with the help of which a puncture is made and the required amount of blood is taken. This device analyzes the data using a microprocessor and outputs the result in digital form to the display.
 PH meter for blood
PH meter for blood
But in any case, you cannot diagnose yourself on your own, so you need to contact any medical institution in order to carry out this procedure in a special laboratory.
The acid-base balance of the body can be abnormal depending on several factors:
- If the city has a bad environment.
- A person's exposure to stress.
- Irregular and improper diet.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Frequent alcohol consumption.
- Work and rest regimes do not coincide.
Acid-base balance is a very important indicator of human health. If even slight deviations in the pH of the blood from the norm are detected, then this can lead to the destruction of cells in the body, enzymes lose their basic functions, as a result of which even death may follow. Therefore, it is important to prevent this pathology in time. The pH of a person's blood is a very important indicator for his life, so you always need to be aware of what kind you have, because the slightest deviation from the norm can lead to death.
Have questions? Ask them to us on Vkontakte
Share your experience on this issue Cancel reply
If you find an error in the text, select it and press Shift + Enter or click here and we will try to quickly correct the error.
Sign up to our newsletter
Thank you for your message. We will fix the bug shortly.
Indicators of KOS - acid-base state - reflect the close relationship between acid-base, oxygen and water-electrolyte exchanges. An imbalance in one of them always entails sharp disturbances in the other two and in the normal course of physiological reactions of homeostasis in general.
In order to understand the significance of CBS regulation, let us consider a simple example.
Hypoxia is accompanied by violations of the CBS and water-electrolyte balance of the following nature: - the main cation of the extracellular fluid enters the cells in an excessive amount, and with each mmol of Na, 6 ml of H2O is introduced into the cell, which entails cell outflow and, at the same time, artificial hypovolemia ... This, in turn, causes an increase in plasma osmolality and leads to an increase in secretion with a decrease in urine output.
A decrease in the volume of circulating blood is accompanied by increased secretion and retention of Na and fluid in the body. That is, the compensatory mechanisms of the body, destabilized by hypoxia, not only fail, but also prevent the removal of excess fluid from the body. As a result of the redistribution of water in the body, a false "hypoxic hypovolemia" occurs due to the outflow of cells. In this case, the therapeutic measures of clinicians are aimed at eliminating hypoxia. Transfusion of fluids to the patient to replenish the circulating blood volume against the background of severe hypoxia can only make the patient's condition worse by increasing the cellular and intraorganic outflow.
blood pH
Gives information about the content of H + ions in the blood.
Normal: in arterial blood pH = 7.36-7.42, in venous blood pH = 7.26-7.36, in capillary blood pH = 7.35-7.44. It should be borne in mind that a normal pH value does not always indicate the absence of violations of CBS, since in this case compensated acidosis cannot be ruled out.
PCO2 of whole blood
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Normal: in arterial blood 35-45 mm Hg. Art., in venous blood - 46-58 mm Hg. Art. An increase or decrease in pCO2 in comparison with the normal level is a sign of respiratory impairment of CBS.
Whole blood buffer bases (BB)
This is the sum of the anions of all weak acids, the main of which are bicarbonates and anions of proteins in the blood completely saturated with O2. The norm is 42-52 mmol / l. This indicator does not change with pCO2 shifts. Therefore, the VV value can be used to judge the presence of non-respiratory disorders of the CBS associated with a change in the content of non-volatile acids in the blood.
Normal Buffer Bases (NBB)
Normal buffer bases (NBB) - the sum of all basic (anionic) buffers in the patient's blood, but reduced to standard conditions (pH = 7.38; pCO2 = 40 mm Hg; 38 ° C; HbO2 = 100%).
Offset buffering bases
The offset of the buffer bases (BE - base excess) in relation to standard conditions.
BE = BB - NBB.
The permissible displacement limit is ± 2.0 mmol / L. The indicator changes in case of non-respiratory disorders of CBS. If there is a deficiency of buffer bases due to their binding with non-volatile acids - negative BE. In alkalosis, buffering bases increase due to a decrease in non-volatile acids - positive BE.
Topical blood bicarbonate
Actual bicarbonate of blood (AB - Actual bicarbonate) reflects the concentration of bicarbonates (HCO3-) in blood plasma under physiological conditions. Normally, it is 21-26 mmol / l.
Standard bicarbonate
Standard bicarbonate (SB - Standart bicarbonate) - the concentration of bicarbonate in blood plasma, reduced to standard conditions. Normally, it is 20-26 mmol / l. By the difference between standard and actual bicarbonates, as well as by pCO2, one can judge about the presence of respiratory disorders of the CBS by the fact that the main part of HCO3- ions is transferred in the form of carbon dioxide. Moreover, if SB = AB, there are no violations; if SB> AB -; if SB< АВ - .
Total CO2 content
Normally, it is 52-73% or 23-53 mmol / l.

PO2 - partial pressure of oxygen
It is an indicator of tissue oxygen supply. Normally, it is 38-40 mm Hg in venous blood. Art., in arterial blood - 80-108 mm Hg. Art. A decrease in this indicator indicates a lack of oxygen in the tissues - hypoxia. However, cases have been described when pO2 remained within the normal range or was higher than the normal value in a number of pathological conditions of the organism (pronounced).
It is used as an indicator of the presence or absence of hypoxia in patients. Lactate is a cleavage intermediate. Its complete oxidation occurs when the body is sufficiently saturated with oxygen through conversion to pyruvate and further, by resynthesis of glycogen in the liver or decomposition to CO2 and H2O. Normally, the content of lactate in arterial blood does not exceed 1 mmol / l, and in venous blood - no more than 2 mmol / l. In the absence of severe diabetes in a patient, an increase in lactate in the blood - hyperlactatacidemia, is interpreted as an indicator of oxygen deficiency in the body.
The content of residual (residual - R) anions in the blood
This indicator is informative for assessing the violation of CBS caused by the accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products in the body. Residual anions include the anions of non-volatile (organic and inorganic) acids.
The normal concentration of R-anions leaves, on average, 12 mmol / l. A significant correlation was noted between lactate and R-anions in the blood. Therefore, if it is impossible to determine lactic acid in the laboratory, the R-anions can serve as a reliable criterion in assessing the lactate content. The increase in R-anions corresponds to an increase in the lactate content in the blood and, in combination with other indicators of CBS, allows us to confirm hypoxia as a cause of metabolic disorders.
Laboratory indicators of the acid-base state of the blood was last modified: October 23rd, 2017 by Maria Saletskaya

