The study of the state of the brain is required not only for adults: in some cases, diagnosis is necessary for young children, including newborns. An event such as neurosonography, or ultrasound of the brain, is safe for health and does not require anesthesia. During the procedure, the child does not experience pain or discomfort. Details about what it is - neurosonography, and in what cases it is required, will be discussed in this article.
What is neurosonography?
Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the brain in children, which can be performed from birth up to 12 months. The procedure is necessary if there is a suspicion of a pathology of brain development. It is carried out while the child has a large or small fontanel open - ultrasound is not able to pass through the hard bones of the skull structures.
Indications for NSG are:
- Non-standard, disproportionate head shape;
- Convulsions, epileptic seizures, abnormalities in the work of the nervous system;
- Blood poisoning;
- Past viral diseases and complications associated with them;
- Hyperactivity of the baby and inappropriate behavior;
- genetic abnormalities;
- oxygen starvation of the brain;
Why oxygen starvation is dangerous for a child explains gynecologist Raisa Zanitullina:
- Suspicion of the presence of a tumor disease;
- Skull injuries;
- Hormonal disruptions that can be caused by dysfunction of the pituitary gland;
- Non-standard formation of individual parts of the body;
- Suspicion of encephalitis, meningitis, cerebral palsy, ischemia;
- Developmental and growth retardation;
- Hemorrhage in the eyeball;

- Infection of the fetus in the womb;
- Chromosomal pathologies detected during pregnancy;
- Mother taking alcohol or drugs during pregnancy;
- Premature birth;
- Frequent regurgitation;
- The difference between the Rh factors in the newborn and mother;
- Difficult childbirth;
- The birth of a child as a result of a caesarean section.
Neurosonography of newborns does not harm the child's body and can be performed in all cases, unless the fontanel is overgrown in the child: when it becomes ossified, it will be impossible to get an idea of the state of the brain structures using this method and you will have to resort to MRI.
Also, for children whose fontanel has already closed, transcranial neurosonography can be performed. This technique makes it possible to study the state of the brain directly through the bones of the skull. Transcranial ultrasound diagnostics is less informative than classical neurosonography, but still allows the specialist to clarify the diagnosis.
How the diagnosis is carried out and what the diagnosis is being studied, the neurologist Marina Aleksandrovna Krasnova tells:
This method is expressed in the fact that the sensor of the device is applied to different parts of the skull, however, the main information is obtained by installing it in the temporal bone region - a thinner bone is located here, which contributes to the passage of ultrasonic waves.
This type of research is often combined with dopplerography. In this case, the specialist receives not only an image of the brain structures, but also information about their size, as well as the speed of blood flow in the tissues.
Pathologies that NSG can detect
Examination of the child's brain using ultrasound allows you to identify various abnormalities, since this method visualizes all the structures of the organ, its ventricles, choroid plexuses.
With the help of NSG, such pathologies and deviations are detected, such as:
- Choroid plexus cysts, which tend to appear and then disappear on their own;
- Subependymal cysts located near the ventricles of the brain and resulting from hemorrhage or impaired blood supply in this area;
- Arachnoid cysts. Such formations indicate the pathology of the development of the so-called arachnoid membrane, which covers the entire brain;
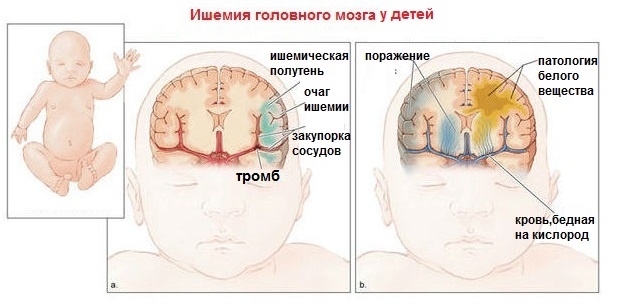
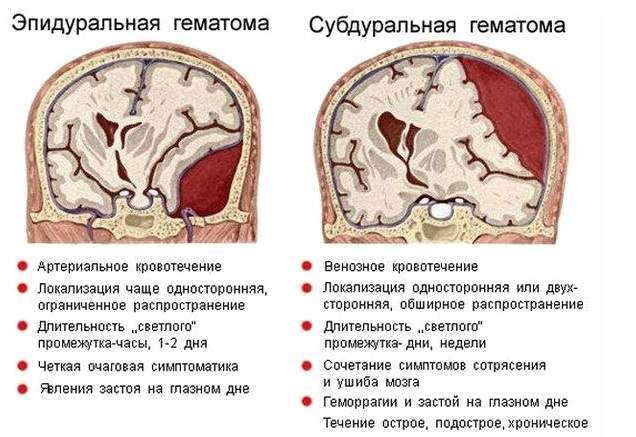
- Hematomas of organ tissues;
- Increased intracranial pressure. This pathology indicates the presence of tumors, hematomas or cysts, or is the result of excessive accumulation of fluid in the spaces of the brain;
- Tumor neoplasms;
- Meningitis;
- Hemorrhages in the ventricles of the brain. A similar deviation is most often observed in premature babies born before 34 weeks of gestation. The earlier the date of birth, the more extensive is the hemorrhage;
- Intracerebral, or parenchymal, hemorrhage. A similar phenomenon occurs with infectious lesions of the brain, birth injuries, acute lack of oxygen;
- Malformations of the brain.
Considering what neurosonography shows, this method can be called highly informative. In addition, the diagnostic procedure does not harm the baby and can be performed as many times as needed. NSG does not cause the child absolutely no discomfort: if it is carried out while the baby is sleeping, he does not always wake up during the study. Carrying out this event is possible even if the child is in intensive care.
The procedure can be done at 1, 3 and 6 months for monitoring: not all pathologies appear immediately, and it is important to track their appearance in time. Often this diagnostic method is used for prevention purposes, especially if there are risk factors.
Preparation and course of the diagnostic procedure
Neurosonography of the brain does not require special preparation. It is recommended to drink and feed the baby so that he does not have cause for concern.
During the procedure, the mother can be next to the child and, if the specialist needs to clarify some data, answer questions that arise. The duration of the diagnosis is about 10-15 minutes.
Painless and safe ultrasound transducer used for examination
During the NSG, the specialist uses a special ultrasonic sensor, which is pre-applied with a gel for better gliding over the head. This remedy is hypoallergenic. It also improves the sensor signal by eliminating air between the device and the head surface.
The head of the child throughout the study should be fixed in one position.
All indicators read by the device are displayed on the monitor. In the first month of life, an examination is possible through the occipital or lateral fontanelles, then through the anterior one.
Survey results
During the neurosonography of the brain of newborns, the specialist receives the information necessary to assess the state of the brain.
The norms look like this:
- New growths are not revealed;
- Brain structures are symmetrical;
- The cerebellum is symmetrical and has a trapezoid shape;
A snapshot of the diagnosis of the brain of a newborn
- Vascular plexuses are characterized by homogeneity;
- The ventricles of the brain are homogeneous and symmetrical;
- The furrows and convolutions of the organ are clearly visualized;
- No fluid was found in the gap between the hemispheres.
The results obtained during the NSG are transmitted to the neurologist, who deciphers and determines the presence and nature of the pathology. Having identified the severity, he decides whether treatment is necessary or observation is sufficient.
When deciphering the data obtained, the specialist is guided by indicators of the normal size of the main anatomical structures of the brain.
Table 1. Norms of neurosonography of newborns and children under one year old
| Anatomical education | Norm indicators for newborns | Normal indicators for children aged 1-3 months |
| Lateral ventricles of the brain | Front horns - 1.5 mm (0.5 mm deviation is allowed up or down); Occipital horns - from 1 to 1.5 cm; Body - up to 4 mm. |
Anterior horns - up to 2 mm; Occipital horns - up to 1.5 cm; Body - 3 mm (permissible deviations of 1 mm up or down) |
| third ventricle | 4.5 mm (tolerances of 0.5 mm are allowed) | 5 mm |
| The gap between the hemispheres of the brain | 2 mm | 2 mm |
| big cistern | no more than 6 mm | 3 to 5 mm |
| subarachnoid space | 2 to 3 mm | no more than 2 mm |
The course of therapy is prescribed based on what caused the violation of brain structures.
Table 2. Identified pathologies and approaches to treatment
| Identified pathology | The essence of the state | Treatment approach |
| Hemorrhages in the ventricles of the brain | Depression of the central nervous system | Symptomatic therapy, if necessary, bypass surgery |
| Neoplasms in the cranial cavity | Tumors of the brain or tissues | Surgical treatment, normalization of intracranial pressure, elimination of symptoms of hypoxia |
| Thickening of the membranes of the brain, pathological changes in the tissues of the organ | Meningitis | Antibacterial therapy, elimination of the consequences of intoxication |
| Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain | Hydrocephalus | Conservative or surgical treatment depending on the patient's condition |
| Hemorrhages in the substance of the brain | cerebral palsy, developmental delay | Normalization of blood flow, stabilization of pressure indicators. In some cases, surgery is possible |
| Choroid plexus cysts | The presence of cysts in the form of small vesicles | Medical supervision, since cysts of this type do not require treatment and resolve on their own |
| Arachnoid cysts | Deviations in the development of a mental and neurological nature | When the cyst grows, surgery is performed |
What pathologies can be detected during the study, the doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Natalya Vladimirovna Remizova tells:
NSG is an effective diagnostic procedure that examines the state of the brain of newborns and children under one year old. Ultrasound allows the specialist to establish a diagnosis and prevent serious complications, while harming the health of the child is not caused. If any deviations appear, you should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe a diagnosis of this type.

