In medicine, to study the functions of the brain, a diagnostic procedure is used - electroencephalography (EEG). A harmless and affordable method is often used in pediatric neurology.
What is the research. How is the procedure carried out? Do I need to prepare for it? What is EchoEG and EchoES? When are these methods used? Let's look into these issues
What is an EEG
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is designed to determine the state of the brain in children and adults. The method is based on the registration of impulses that create and transmit neurons. The joint activity of these cells forms the bioelectrical activity of the cerebral cortex, which is recorded by the apparatus.
The electrodes record the signals and transmit them to the apparatus. A computer program analyzes and processes information according to age and time of day.
Indicators are recorded in the form of a curve similar to a cardiogram. Electroencephalography in children is a safe way to obtain information about the functioning of the brain at any age. EEG data allows the doctor to detect the cause of the disease in the child in order to prescribe the correct treatment.
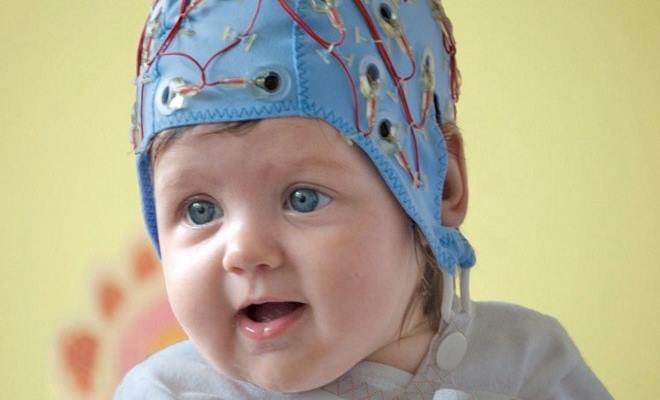
Who does an EEG
An encephalogram for a child is prescribed by a neurologist and a neurophysiologist. The procedure is done at any age - from birth to 18 years.
It is shown to do an EEG in the following cases:
- head injury;
- prolonged crying for no apparent reason;
- sleep disturbance of the baby - drowsiness or insomnia;
- unstable blood pressure in adolescents;
- convulsions of unknown origin;
- vegetative crises;
- irritability;
- rapid depletion of a physical resource;
- sleepwalking - night walking in an unconscious state;
- loss of consciousness;
- fainting;
- speech delay in children;
- convulsions at elevated temperature;
- EEG is done to children with stuttering.

Neurologists prescribe a study in this way in violation of consciousness and vegetovascular crises with fainting.
What does a doctor see on an EEG?
An encephalogram of the child's brain reveals the consistency of brain structures during sleep and wakefulness.
What does the EEG show:
- The stage of brain maturity in young children;
- ischemia and hypoxia of cerebral vessels;
- diagnosis of the severity of the disease;
- evaluation of the effectiveness of anticonvulsants;
- identification of the cause of the convulsive syndrome;
- the presence in the brain of a focus of convulsive activity;
- localization of damage.
EEG reveals meningitis, encephalitis against the background of herpes and other infectious diseases. The procedure reveals concussion and brain contusion.
EEG detects cerebral palsy, epilepsy. Thanks to the study, the doctor determines the cause of the lag in speech skills, memory loss.
How to prepare a child for an EEG
No specific preparation is required for the study. For the procedure of the encephalogram of the child's brain, they are prepared in advance by simple actions. To improve the contacts of the sensor with the hair, wash your hair the day before.
Infants EEG is carried out during sleep. Before the session, the child is fed. For children after 1 year, the procedure is done in a state of wakefulness. In order for the baby to behave calmly, the parents psychologically prepare the child the night before.
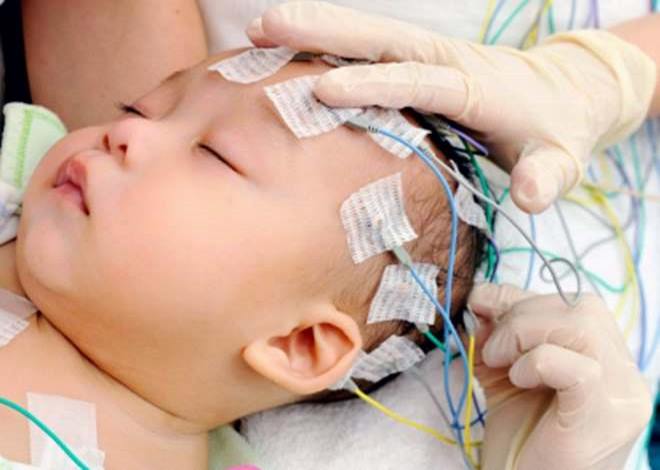
Tips for parents:
- Talk about diagnostics as a fun game of astronauts. During the procedure, a cap with sensors is put on the head, which represents the spacesuit. It is useful to show the baby a picture of an astronaut.
- Take your favorite toys with you to the examination, with which the baby will feel protected.
- An hour before the procedure, the baby is fed.
Before the session, hairpins and jewelry are removed from the baby’s head and her hair is loosened. Important! Parents should be aware that the examination is not done during fever, cough or nasal congestion.
How is an EEG test performed?
The procedure is done in a sound and light proof room. A hat is put on the child's head, on which sensors are pinned. Using wires, the electrodes are connected to the apparatus. The sensors are pre-lubricated with gel to avoid an air cushion. Clip-on earrings are put on the earlobes.
Babies during the procedure lie on the changing table or mother's arms.
Older children go through a more complex procedure. For this patient is placed on the couch. In the reclining position, the head cannot be bent.
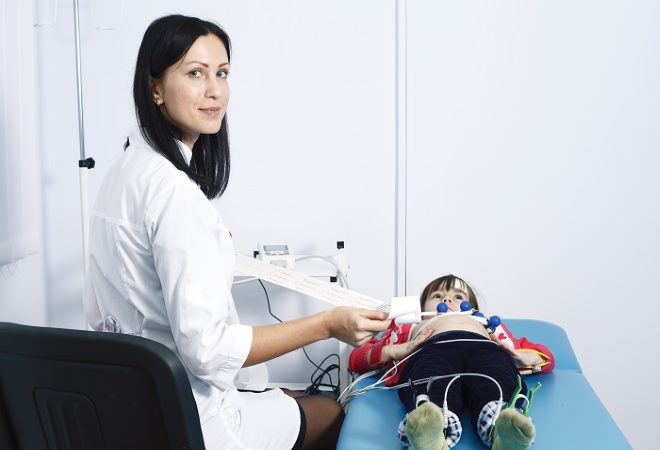
During the session, provocative tests are used:
- First, a background recording of the bioelectrical activity of neurons is made for 15 minutes.
- The child is asked to open and close his eyes several times at intervals. The test is necessary to study the brain at rest and the transition to activity.
- The next exercise is hyperventilation. The child takes a deep breath and exhale 2-3 times intermittently. The test reveals a latent tumor, epilepsy and a stressful state of the nervous system.
- Another provocative test is photostimulation. The procedure is performed using an electric light bulb. The closed eyes of the child are illuminated with flashes of light several times. Light load on vision reveals epilepsy, the degree of activity of speech and psychomotor development of children.
The procedure lasts half an hour. If provocative tests do not reveal pathology, an EEG with sleep deprivation is performed.
For this, the child is woken up several hours earlier than usual. If a paroxysmal state of the brain or a deep sleep disorder is suspected, a night EEG is done.
EEG interpretation
4 types of rhythms are recorded on the tape. The EEG is deciphered by a doctor. A "bad" EEG during seizures is indicated by frequent electrical discharges of high amplitude. At the end of the attack, bioelectric activity decreases. Outside of convulsions, the apparatus fixes foci of increased convulsive activity.
In other brain pathologies, focal or diffuse changes are recorded on the tape. In tumors and strokes, a slow rhythm is noted with a predominance of beta waves. Diffuse changes are noted with encephalitis, meningitis, concussion or brain injury.
After injury, the frequency of the alpha rhythm increases. With dementia, this indicator is completely absent. If diffuse beta rhythms are detected, this indicates a concussion.
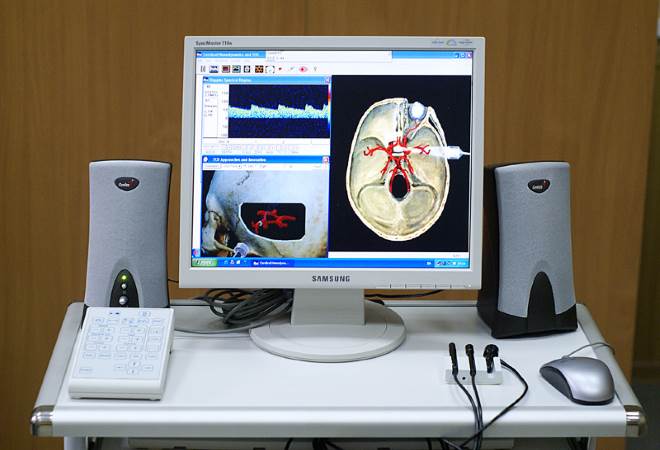
What is EchoEG
Echoencephalography of the brain (Echoeg) is an ultrasound examination using expert-class equipment with an advanced computer program.
The advantages of Echoeg are that it reveals pathology not only in the depths of the brain, but also near the bones of the skull:
- intracranial hematoma;
- intracranial pressure;
- degree of hydrocephalus;
- brain tumors;
- abscess.
The informativeness of the method is equal to magnetic resonance imaging and replaces it in case of contraindications to the latter.
What is the EchoES method
Echoencephaloscopy (Echoes) is an ultrasound scan of brain structures. The study is based on echolocation. The method allows you to receive signals from the ventricles of the brain. It is resorted to in case of suspicion of hypertension syndrome.
The need for the method arises with such a brain pathology:
- perinatal encephalopathy that developed during gestation or during childbirth;
- attention deficit disorder;
- stuttering;
- traumatic brain injury;
- sleep disturbance:
- increased activity;
- enuresis.

No preparation is required before the study. The method is harmless, therefore it is used in children and pregnant women.
An electroencephalogram is necessary to detect or exclude brain pathology. The procedure can be done several times without harming a child of any age. In severe brain pathology, in addition to the EEG, an improved study of Echoeg and Echoes is used.

