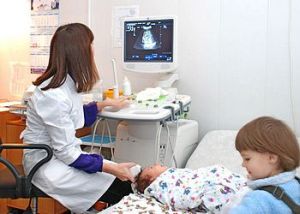
Neurosonography () is a diagnostic procedure that consists in examining the brain of a newborn baby using an ultrasound machine.
This study is carried out either for prevention, or on the recommendation of a neonatologist after the initial examination of the child, which is carried out in the first three weeks of his life.
The transducer of the ultrasound machine sends high-frequency waves to the brain, examining its structure and convolutions. The structure of the brain is reflected from these waves. As a result, an image appears on the monitor. The study is absolutely safe, does not cause discomfort and pain, does not require special preparation and anesthesia.
Until what age is the study done?
Neurosonography of newborns is performed from birth to twelve months, in the event that doctors suspect a pathology in the development of the baby's brain.
Ultrasound makes it possible to assess the state of the brain and its structures, which helps to make a diagnosis.
If the fontanel is already overgrown, then specialists conduct a transcranial ultrasound examination, it is somewhat more expensive.
What anomalies can be detected by the procedure
The study will help to "see" such pathologies:
Indications for research
As mentioned above, the indication for neurosonography is the doctor's suspicion of pathology during the development of the brain. The reasons for such conclusions may be:

Suitable for everyone
The undoubted advantage of this procedure is that it can be done to all babies, it does not cause any harm. There is only one necessary condition for an effective procedure - this is not an overgrown fontanel
The advantage of neurosonography over other studies of the brain is obvious. After all, for example, to conduct - And - examinations, complete immobility is required, which is almost impossible to achieve from a small child, any movement washes away the picture, so specialists have to resort to anesthesia.
When performing an ultrasound, anesthesia is not needed, there is no radiation exposure for the child, the procedure can be repeated as many times as necessary for an accurate diagnosis or confirmation that the pathology has disappeared.
How to prepare for a diagnosis
 There are no special rules for preparing for this type of ultrasound examination. The most important thing is that the baby does not act up, does not turn his head, does not cry, so, of course, it will be more difficult for a specialist. Every mother knows what it takes to make her child happy.
There are no special rules for preparing for this type of ultrasound examination. The most important thing is that the baby does not act up, does not turn his head, does not cry, so, of course, it will be more difficult for a specialist. Every mother knows what it takes to make her child happy.
Before the procedure, it is better to feed the baby, put on a clean diaper.
You can take toys, a pacifier, a bottle with you to calm the little patient in case he becomes naughty.
The course of the procedure
The procedure is not difficult, it will not cause any special difficulties. Mom spreads a diaper on the couch, puts the baby on her back, her task is to entertain the baby.
The doctor brings the sensor to the open fontanelles and begins the study from this part. That is why an open fontanel is so important. The fact is that the dense, thickened bones of the cranium do not allow ultrasonic waves to "penetrate" inside.
Then the specialist examines other areas that "pass" ultrasonic pulses. He translates the sensor to a thin temporal bone, and then examines the anterolateral fontanel, which is located on the line leading from the ear to the temple in front; this is followed by an examination of the posterolateral fontanelle, this is a line from the ear to the temple from behind and a large occipital foramen, it is located directly under the back of the head.
All these zones make it possible to study the posterior, as well as the central parts of the brain, which are located at some distance from the large fontanel.
What are the features
If in the course of the study some kind of violation of the work and development of the brain was revealed, then there is no need to immediately panic. results and 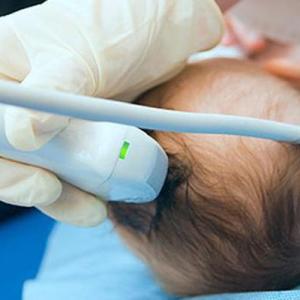 the conclusion must be shown to the neurologist who "leads" the child, he will prescribe the appropriate treatment, which may not be aggressive at all.
the conclusion must be shown to the neurologist who "leads" the child, he will prescribe the appropriate treatment, which may not be aggressive at all.
Be sure to in the presence of pathologies at the doctor's appointment, you need to ask about the advisability of vaccination.
For some diseases or deviations in neurology, vaccinations are not recommended, as they can only aggravate the situation, and a medical exemption may be required for a certain time.
About the results, their interpretation and norms
In conclusion, the specialist indicates the symmetry of the structure of the brain, its echostructure, the sensitivity of the pattern of convolutions and furrows. The examination protocol outlines the state of the subcortical zones, periventricular zones, the state and size of the ventricles, choroid plexuses, and cerebellar stem structures.
Only a doctor can make a correct description and decipher the results of the examination. All indicators are interconnected, and in one case, a slight deviation from the norm will not be critical due to the relationship of certain indicators, and in the other, it can be an alarming bell.
Reliable information and comprehensive answers to questions about the condition of the baby would be more appropriate to get from a neurologist. The doctor of ultrasound diagnostics is engaged in the interpretation of the results of the study.
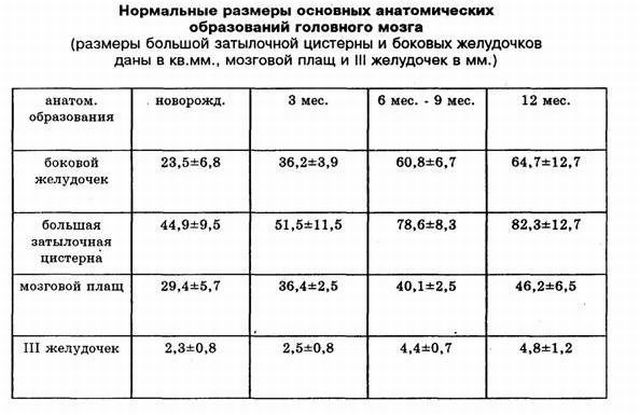
In the table of developmental norms, depending on age, which neurosonography will help to identify

