The brain is the most important organ responsible for the functioning of the nervous system and other organs. Since newborn babies develop rapidly, this process must be closely monitored. Ultrasound detects abnormalities and abnormalities in the state of the brain, the doctor can give a complete assessment of the blood flow and vessels.
In some children, disorders can be associated with a variety of factors, and if they are detected at an early age, there is a chance to correct the situation.
What is an ultrasound of the brain

The method of examining the brain with ultrasound began to be practiced not so long ago, but quickly gained popularity. The doctor conducts research using a special apparatus, and can obtain information not only about the vessels, but also examine in detail the ventricles of the brain and even the structure of the skull.
An ultrasound of the brain in newborns is performed before the fontanel is overgrown. There are no other similar methods for examining children at an early age. There is no need to be afraid that ultrasound will harm the baby. The occurrence of unpleasant consequences after the application of the procedure was not recorded, but there are positive results. Timely noticed complications of the brain using neurosonography can be stopped by prescribing appropriate treatment.
Indications for research

Research of this kind is carried out not for all newborns, but only for those who have indications for this. Usually, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan if there was a problem childbirth and the child could be injured. They successfully detect various anomalies if they are suspected. This research method allows you to detect brain tumors.
It is easier to study newborns through the fontanelle, and after it is overgrown, you will not be able to see anything. It is for this reason that it is impossible to delay if ultrasound is shown, because lost time can cost the child's health or life. The doctor conducts an ultrasound scan only up to one year as prescribed by a neurologist, but sometimes this procedure is offered to be performed for all newborns, even if there is no reason to carry it out.
It is imperative to do an ultrasound of the brain for children for the following indications:
- Birth injury;
- Intrauterine diseases;
- Prematurity;
- Too much weight;
- Obvious anomalies and defects.
A neuropathologist may order a study for a child if there are signs of diseases associated with neurology.
Preparing a baby for an ultrasound
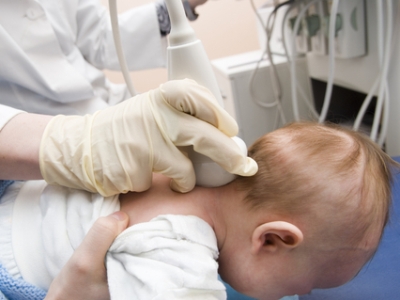
Neurosonography is performed through the fontanelles of the newborn. Usually, the child has only one left - the largest, while the rest are delayed. Since the remaining fontanelle will only heal by the end of the first year of life, the study should be carried out as early as possible. The child does not need to prepare for an ultrasound of the brain. Moreover, the baby can do anything at the time of the procedure: sleep and stay awake. The decoding will be accurate and will show the state of the ventricles of the brain.
But if you also need to do a newborn examination of the brain vessels, do not feed him for about a couple of hours before the procedure. This is the only recommendation, as there are no longer any special requirements for an ultrasound scan of a newborn.
How the research is done
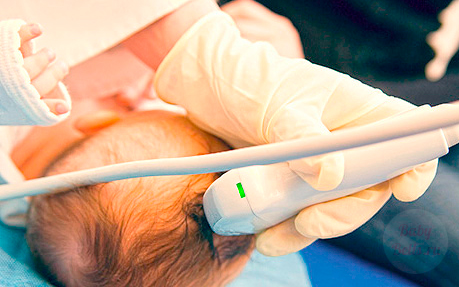
Brain examinations in newborns are easy to do. This method does not require special behavior from the baby, the main thing is that he be as few months old as possible, and the fontanel is not yet overgrown. If the first decryption shows an alarming result, ultrasound can be repeated to monitor the dynamics of development and treatment.
For children in a critical situation, this method is a real salvation. For such newborns, ultrasound is done almost daily, without any harm. Unlike X-ray, ultrasound is harmless.
The doctor conducts the examination only through the soft area of the head. As a rule, this is a large fontanelle, but the anterior or other areas that have not yet had time to tighten and harden are also suitable. The screen displays data by which the doctor determines the state of the brain structures. Since immobility is not necessary, the child can be turned as it should. If you need to look at the back of the head, you can safely bend your head, while the procedure will not be disturbed.
The interpretation of the ultrasound scan is compared with specific norms, so the doctor who conducts the ultrasound can say for sure if the child has abnormalities.Decoding the results

The final result of the study of the brain is of great importance. In order for the interpretation of the ultrasound scan to be accurate, it is necessary to conduct a study on high-quality and modern equipment, and a highly qualified doctor should evaluate the results. It only depends on this how correct the result will be.
An inexperienced specialist may miss something important, and since the procedure can only be carried out for several months, until the child is one year old, such mistakes can be fraught with dangerous consequences. It is better to play it safe and do another ultrasound with another doctor, if there is any doubt that the result of the decryption is incomplete.
This research method allows you to detect:
- Cysts. Their detection is a common result of ultrasound. In fact, these bubbles are harmless to the newborn, the baby has no symptoms and the doctor notices them quite by accident. Typically, a cyst can disappear as imperceptibly as it appeared. After a few months, do a second ultrasound; most likely, there will be no cyst anymore;
- Cysts due to hemorrhage. This type of education is also harmless and goes away by itself. If the decryption shows the presence of such a cyst, you should not be afraid;
- Arachnoid cysts. This type is dangerous for the baby's brain, because it is a defect. Bubbles of fluid spread throughout the brain, do not disappear over time, and can grow in size. If the test result showed these cysts, the doctor will prescribe treatment, but the state of the brain will have to be constantly monitored. It is worth noting that there are no early symptoms;
- Intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus. With these diseases, ultrasound is necessary. This is especially true for neglected forms;
- Ventricular hemorrhage. Premature babies often suffer from this problem;
- Deciphering an ultrasound scan of the brain will show how severe a form of pathology is in a newborn. In especially dangerous cases Hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain in newborns can cause serious disorders and threaten the life of the child.
These are not all the problems that an ultrasound of the brain in a baby can show, but if the transcript of an ultrasound of the brain was done correctly, the result will show how to proceed. It may be necessary to observe the baby for several more months to make sure that there is no threat.
Pros and cons of brain ultrasound
The advantages of an ultrasound scan of the baby's brain are obvious. Firstly, this procedure is inexpensive and accessible to almost everyone. Secondly, it does not require preparation. The child does not feel pain during the process, he does not need to be anesthetized or perform any other manipulations.
The main advantage of brain ultrasound is the rapid receipt of research results. The decryption shows all the necessary information, moreover, this method of examining soft tissues is considered the only possible one.
The most dangerous brain diseases in infants are easy to detect using this procedure, but it is worth remembering that even an ultrasound machine cannot guarantee anything. This is one of the disadvantages of the method, although otherwise it is irreplaceable. You can confirm or deny the diagnosis by going through an additional examination.
Another advantage of ultrasound is the ability to monitor the course of the disease, the dynamics of its development, or, conversely, cure.
The harmlessness of the method allows you to use it for as many months in a row as needed, until the child is one year old. This leads to another drawback - the inability to do an ultrasound scan for an adult or a child whose fontanel is tightened with bone tissue. In general, this technique has no equal, and it is used all over the world.

