Inflammation of the brain is accompanied by the destruction of nerve tissue and disruption of the functioning of the nervous system. Usually encephalitis of the brain is infectious. The disease manifests itself independently or as a result of a previous illness. Recovery depends on the timeliness of seeking medical help.
Characteristics and causes of pathology
The concept includes a number of inflammatory diseases of the brain. Inflammation of the brain develops as a result of the penetration of the pathogen into the human body or due to allergic phenomena. The main reason for the development of the disease is neuroinfection.
Microbes and viruses interfere with the activity of nerve fibers, neurons and blood vessels, adversely affecting the functioning of the nervous system. Signs of intoxication appear, the shell and certain parts of the brain are affected.
Depending on the affected area, Meningitis is accompanied by inflammation of the cerebral cortex, which develops as a result of hypothermia, penetration of fungi, viruses, bacteria. Encephalitis is a severe condition in which the brain becomes inflamed. The disease is characterized by severe course and high mortality.
Encephalitis can be primary or secondary. The source of infection in the primary form is usually insects. An infected individual bites a person, then the virus spreads through the bloodstream to the brain and other organs. This form is manifested due to the rabies virus (from the bite of an infected dog), herpes, influenza, Coxsackie. Microbial encephalitis is formed as a result of, for example, syphilis.
Based on the causes of the primary form of the disease, epidemic, tick-borne, herpes, mosquito, viral encephalitis are isolated.
DTP vaccination, smallpox and rabies vaccines can cause the development of encephalitis.
Since vaccination can cause brain pathology in infants, a thorough examination of newborns by a pediatrician and neuropathologist is necessary.
Secondary encephalitis is formed as a complication of another disease: toxoplasmosis, malaria, measles, rubella. You can get infected by airborne droplets or by eating contaminated food.
Risk factors
There are several factors that increase the risk of pathology:
- children's age up to 1 year, the elderly;
- the presence of the herpes simplex virus;
- reduced immune status;
- the summer-autumn period, when insect carriers of neuroinfection are most active.
Based on the location of the pathogen, subcortical, cerebellar, mesencephalic, stem encephalitis is distinguished.
Types of disease
Each type of pathology is characterized by certain signs and a special course of the pathological process.
Epidemic
Another name is lethargic. Diagnosed in both children and adults. Symptoms are manifested in a sharp increase in temperature, intense headaches, soreness of the articular tissue.
The patient has confusion, delusions, hallucinations. Later, strabismus, shortness of breath, excessive sweating are added.
pincer
The frequency of detection of this species increases in spring and summer, when infected ticks are most active.
When it enters the body, the infection enters the brain through the bloodstream. A person begins to be afraid of bright light, pain in the head increases, vomiting develops. Numbness of the limbs occurs, muscle structures are paralyzed.
mosquito
Another name for the species is Japanese. Infected mosquitoes carry the virus. The disease is accompanied by high body temperature, vomiting, confusion. Fixed, convulsive seizures. The species is characterized by a high mortality rate.
influenza
It develops as a complication of the flu. Manifested by nausea, pain in the head, weight loss, weakness. The disease often introduces the victim into a coma.
Koreva
Since measles is a childhood disease, this type of encephalitis is inherent in children. Inflammation of the brain begins to develop several days after measles.
The patient is weakening, febrile, disturbed by epileptic seizures. The disease damages the nerves of the skull, causing paralysis, myelitis.
windpox
Progresses due to chicken pox. The disease is more often diagnosed in childhood. The child becomes weak, becomes drowsy. Gradually, coordination of movements is disturbed, paralysis of the arms and legs develops, epileptic seizures develop.
herpetic
The herpes virus infects the cerebral cortex. This type progresses slowly, leading to impaired consciousness, excruciating headache, and chaotic movements of the limbs.
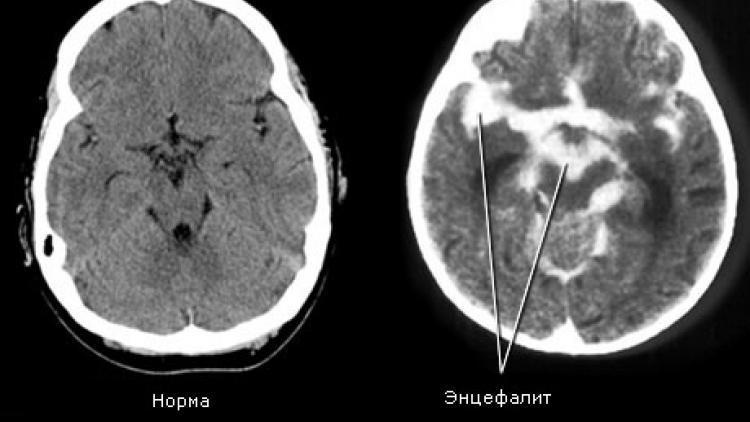
Signs of the disease
Symptoms of encephalitis are differentiated depending on the causative agent of the disease and its location. There are also general manifestations of pathology. Like other diseases of an infectious nature, encephalitis affects an increase in body temperature, indigestion, and disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the respiratory tract.
Vomiting, photophobia, seizures of epilepsy appear, headache increases. Patients have impaired consciousness, a person may fall into a coma. There are problems with psychomotor and sensory perception of reality: physical hyperactivity, misunderstanding of the parameters and shapes of objects.

Encephalitis can be asymptomatic, fulminant or abortive. The asymptomatic course is accompanied by a slight pain in the head, slight dizziness. Abortive forms cause symptoms of colds or stomach infections.
The most dangerous form is fulminant, which progresses in a few hours. The temperature rises sharply, the person falls into a coma. Death is recorded as a result of heart failure.
Possible Complications
Inflammation of the brain in a mild form passes without significant complications. Treatment of a severe disease can take several years. The consequences of cerebral encephalitis do not develop in all people, they depend on the individual characteristics of the body.
The most dangerous situation is when the patient does not feel painful symptoms, while the virus spreads through the structure of the brain. In this case, irreversible complications develop:
- chronic fatigue;
- personality changes;
- inability to concentrate;
- amnesia, which over time leads to problems with short-term memory;
- violation of motor activity;
- mental disorders;
- loss of sensitivity.
Degenerative processes in the brain structures lead to disability and death.
Diagnostic methods
The dominant diagnostic method is a puncture, during which a specialist takes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) sampling. The biological material is examined, it reveals lymphocytic pleocytosis, protein concentration.
In the blood test, a high number of leukocytes is detected, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases. Epileptic activity is fixed. During magnetic resonance imaging, pathological changes in the brain are recorded. In the study of the fundus, stagnation of the optic nerve is determined.
The disease is diagnosed on the basis of the results obtained during bacteriological and serological tests. Virological identification is very difficult.
Methods of therapy
If signs of pain are found, an ambulance must be called immediately. The patient is placed in the infectious department. The outcome of treatment depends on the speed of therapeutic measures. Often the patient needs the help of a resuscitator.
Treatment of encephalitis includes etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic methods.
Etiotropic treatment
Eliminates the causes of inflammation of the brain, one of which is the penetration of an infectious agent. To eliminate the infection, antibacterial drugs, antiviral agents and human immunoglobulin, which is necessary for tick-borne encephalitis, are used.
Antibiotics are used for bacterial encephalitis and are administered intravenously. Among antiviral drugs, Acyclovir, Cycloferon, Viferon, Proteflazid are distinguished.
Pathogenetic treatment
It is based on the use of medicines that restore damaged brain structures. Such medicines include:
- hormonal agents;
- anti-edematous drugs - Mannitol, Diakarb, Furosemide;
- antihistamines - Suprastin, Loratadin, Zodak, Tavegil;
- infusions that correct metabolic processes - Dextran, Trisol, potassium;
- angioprotectors - Cavinton, Instenon;
- antihypoxants - Cytochrome, Mexidol, Actovegin;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Ksefokam, Nurofen.
The patient is given vitamin preparations, drugs that correct the work of the heart and organs of the respiratory tract.
Symptomatic treatment
Eliminates manifestations of individual symptoms resulting from encephalitis. Doctors prescribe anticonvulsant, antipyretic, antipsychotic drugs. It is necessary to take funds that activate the work of the neuromuscular apparatus (Neuromidin) and reduce muscle tone (Sirdalud).
Note! Epilepsy attacks can stay with a person forever, which requires taking anticonvulsants for the rest of their lives.
Physiotherapeutic measures are shown to the victim: massage, acupuncture, physiotherapy exercises, electrical stimulation. The patient should be engaged with a psychotherapist, speech therapist.
At the initial stage, encephalitis does not manifest itself with characteristic symptoms, the signs are similar to a cold. Therefore, a person goes to the doctor late, when the brain cells are already destroyed. Emergency medical care can save the patient.

