Despite the advances in modern medicine, traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains one of the most severe and complex pathologies in neurology. Even seemingly minor injuries (concussion) can lead to long-term disorders of the nervous system, and often bad amenable to traditional therapy. Severe TBIs (brain contusion, diffuse axonal twisting) sometimes lead to the patient's death or severe disability.
TBI remains one of the main causes of disability in the population
Statistics show that in recent years, the incidence of craniocerebral injuries has a steady upward trend, especially in young people. Moreover, the proportion of severe injuries to the skull and brain has significantly increased, the consequences of which are post-traumatic encephalopathy, impaired intelligence, cerebrospinal fluid hypertension.
Pathogenesis of TBI
Traumatic brain injury is most often the result of mechanical impact on the head and neck area. The most common situations are: traffic accidents, hit by a hard object, falling from a height, less often the cause is head compression or sudden acceleration of the human body.
Thus, the following main causes of brain damage during trauma can be distinguished:
- Local violation of the structure of tissues with a sharp impact with a heavy object (impact, fall).
- Diffuse damage to brain tissue, for example, due to acceleration.
- Compression of intracranial structures.
As a result of the damaging factor, a cascade of pathological reactions is triggered, leading to a disruption in the interaction of intracerebral structures, and in severe injuries, organic changes in brain tissue with progressive edema. Scientists have proposed several theories of the pathogenesis of brain injury: displacement of the brain inside the skull, changes at the molecular level, the mechanism of a counterstrike, and others. The whole complex of pathological changes is called traumatic brain disease.
TBI classification
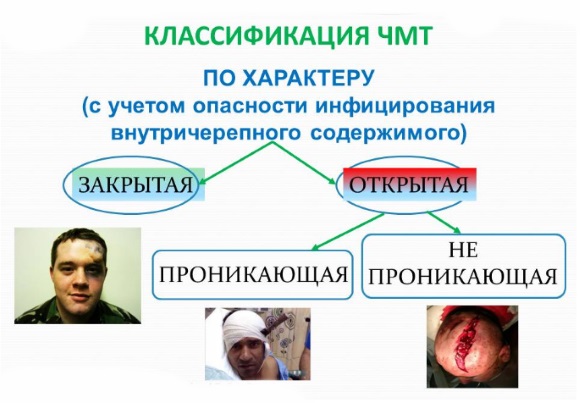
All types of TBI are usually divided into closed and open
According to the features of the damage to the soft tissues of the head and bones of the skull, traumatic brain injury can be open or closed.
A closed skull injury is characterized by a lack of communication between the intracranial cavity and the external environment. Moreover, even the presence of cracks or bone fractures does not violate the closed space of the cranium. The presence of damage to the soft tissues of the head (wounds, abrasions) with preserved integrity of the bone tissue allows such a head injury to be considered closed.
In turn, open TBI is a head injury in which there is a communication between the cranial cavity and the external environment. If at the same time there is a violation of the integrity of the dura mater, then such head injuries are penetrating, in other cases, non-penetrating damage is diagnosed.
In modern neurology, traumatic brain injury is classified as follows:
- Brain concussion.
- Brain contusion (mild, moderate, severe).
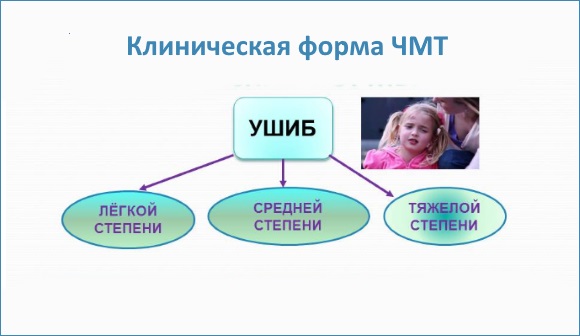
One of the types of traumatic brain injury is contusion
- Compression of intracranial structures.
A concussion is considered a relatively mild type of head injury. The more severe ones include contusion and compression of the brain, which can additionally be aggravated by fractures of the skull bones, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral edema, and intracranial hematoma. The latter, depending on the location, happens: intracerebral, epidural, subdural, intraventricular.
The course of craniocerebral injury
Any traumatic brain injury has three periods in its development: acute, intermediate and long-term consequences.
First period characterized by the development of pathological changes in the brain tissue immediately after exposure to a damaging factor. Symptoms depend on the degree of changes occurring in the brain, edema of brain structures, the presence or absence of other injuries (concomitant injury), the initial somatic status of the patient. Its duration is at least two weeks or more.
In the interim there is a restoration of damage to the nervous tissue, and, accordingly, the lost functions. Also, compensatory and adaptive mechanisms in the body are turned on, which contributes to the adaptation of the patient in the presence of severe damage to the central nervous system. The duration of this period with a concussion and slight injury of the brain is up to six months, with more severe injuries - about a year.
Final period head injury - restorative. Depending on the severity of the injury, it can last a year or two or more than two years. As a rule, during the first two years after injury, most patients develop post-traumatic encephalopathy, which requires treatment in neurology. With the correct treatment approach, the restoration or adaptation of the central nervous system occurs.
Symptoms
The symptoms of traumatic brain injury largely depend on the degree of brain damage, the presence of focal changes and edema, and concomitant encephalopathy. An important criterion for the severity of TBI is the patient's state of consciousness, the presence of focal and cerebral symptoms.
Brain concussion
This type of head injury is referred to as a minor brain injury. Its characteristic features are:
- Loss of consciousness for a short time (seconds, several minutes).
- A state of mild stunnedness after injury.
- The presence of diffuse headache.
- Nausea, rarely single vomiting.
- Sometimes retrograde amnesia, less often anterograde.
With a concussion of the brain, the fact of impairment of consciousness occurs in almost all cases and can vary from its complete loss to a state of "clouding" in the head, slight stunning. Examination of the patient reveals diffuse symptoms: nystagmus, sluggishness in the reaction of the pupils to light, asymmetry of reflexes, pathological reflexes (Marinescu, Rossolimo, Babinsky). Again, against the background of the existing encephalopathy, these signs are persistent, and with a concussion they disappear within 3-5 days. Violations of autonomic innervation - frequent consequences of a concussion, usually there is an instability of blood pressure, sweating, a feeling of "heat" in the body, cold extremities.

Concussion symptoms depending on the severity
Brain contusion
This type of head injury is characterized by focal damage to the structures of the brain. Often, a contusion of the brain is accompanied by fractures of the bones of the skull, hemorrhages under the lining of the brain, and rapidly increasing edema. Subsequently, this often leads to post-traumatic encephalopathy.
Symptoms may differ depending on the degree of damage (mild, moderate, or severe). For a mild brain injury, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- Loss of consciousness (tens of minutes).
- Nausea, sometimes repeated vomiting.
- Amnesia, retrograde or anterograde.
- Diffuse headache, dizziness.
In the neurological status, diffuse or focal symptoms are determined. Most patients have skull fractures, subarachnoid hemorrhage.
With moderate to severe brain contusion, the severity of symptoms is much higher. In this case, the duration of loss of consciousness can be several hours, and in severe cases, several weeks. For such injuries, the characteristic signs are focal changes: impaired oculomotor function, damage to cranial nerves, sensory, movement disorders (paresis, paralysis).
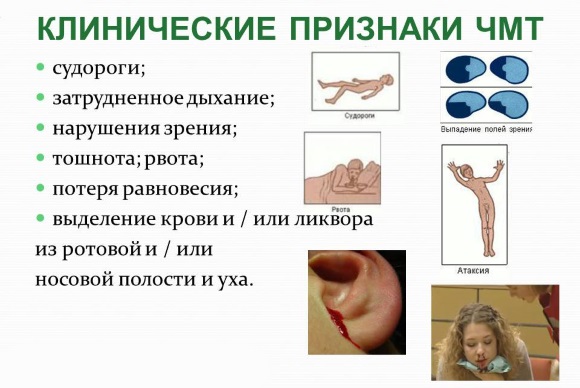
Traumatic brain injury symptoms
In severe TBI, stem disorders occur, which is caused by edema of the brain structures: fluctuations in blood pressure, abnormal breathing rhythms, impaired thermoregulation, muscle tone. The meningeal signs are determined (stiffness of the occipital muscles, Kernig's, Brudzinsky's symptoms). Severe head trauma can be accompanied by a seizure disorder.
Severe brain contusions are almost always combined with fractures of the cranial bones, often the base of the skull, traumatic hemorrhages, and edema of the brain tissues. Outwardly, the "glasses symptom" is sometimes determined - a sign of a fracture of the front of the skull, liquorrhea from the nose or ears.
Traumatic brain injury of severe degree almost always leaves consequences in the form of post-traumatic encephalopathy. Symptoms regress after a few months, and residual effects may be persistent, sometimes for life.
Compression of the brain
This type of traumatic brain injury is especially severe and often leads to the death of the patient in the absence of medical care. Compression of the brain by an intracranial hematoma (epi-, subdural, or intracerebral) leads to a displacement of the stem structures and, as a consequence, disruption of vital functions. This type of injury can be an independent pathology or be combined with other types of brain damage (for example, brain contusion).
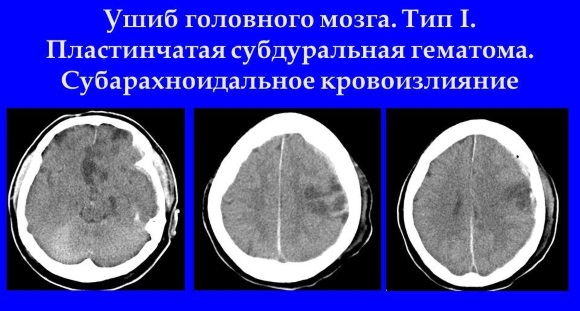
Compression of the brain may be due to intracranial hematoma
A gradual increase in the severity of cerebral, focal symptoms, signs of cerebral edema with dislocation (displacement) of cerebral structures is characteristic. The onset of compression symptoms is often preceded by the so-called "light gap" after the injury, when the patient feels good for a while. It is especially common in children.
Complications of TBI
Traumatic brain disease can have both early and long-term consequences. Early complications of traumatic brain injury include:
- Cerebral edema.
- Displacement of the median stem structures.
- Secondary intracranial hemorrhages (hematomas, subarachnoid hemorrhage).
- Secondary inflammatory process (meningitis, encephalitis).
- Extracranial inflammation (pneumonia, bedsores, sepsis).
- Respiratory failure.
Long-term consequences are largely due to the severity of the traumatic brain injury. The most common are:
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy (asthenia, headaches, autonomic disorders).
- Persistent focal disorders (paresis, paralysis, impaired vision, hearing, speech).
- Epileptic syndrome.
- Mental disorders.
Diagnostics

Methods for diagnosing craniocerebral trauma
The diagnosis of "traumatic brain injury" is established in neurology on the basis of a primary examination by a doctor, anamnesis data and patient complaints. Additional examination methods are required.
At a minimum, an X-ray of the skull is required in case of a concussion; for more severe injuries, a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is required.
In a hospital, a neurologist or neurosurgeon also prescribes general clinical and biochemical blood tests, ECG. If there is a suspicion of combined traumatic injuries, R-graphy of the chest, extremities, ultrasound of the abdominal organs. According to the indications in neurology, a lumbar puncture is performed, which helps to identify subarachnoid hemorrhage, secondary purulent meningitis.
Treatment
Any traumatic brain injury requires observation and treatment in stationary conditions (neurosurgery, neurology, traumatology). In exceptional cases, outpatient treatment of a mild concussion of the brain is allowed, but only after preliminary diagnosis and examination by a neurosurgeon or neurologist. Therapy of a mild degree of brain damage involves the appointment of bed rest for at least a week, the elimination of autonomic dysfunction, the appointment of nootropics, sedatives, and the normalization of blood pressure.

Treatment of patients with TBI should be carried out in a hospital setting
For more serious injuries, the following measures are included in the therapy:
- Maintaining vital body functions: breathing at an optimal level (mechanical ventilation if necessary), correcting blood pressure numbers to ensure sufficient brain perfusion. To increase blood pressure, colloidal solutions and sympathomimetics are injected intravenously. High blood pressure values are corrected by the appointment of antihypertensive drugs.
- Fighting cerebral edema. For this, osmotic diuretics (mannitol) are used. Elimination of cerebrospinal fluid hypertension is achieved by drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways.
- In the presence of hemorrhagic complications, hemostatics (aminocaproic acid) are used.
- To improve microcirculation in the affected tissues and prevent secondary ischemia, antiplatelet agents, vasoactive agents (trental, cavinton), calcium channel blockers are prescribed.
- Elimination of hyperthermia is achieved by the introduction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipsychotics, artificial hypothermia, the introduction of antipsychotics.
- Antibiotic therapy for the prevention of secondary purulent complications. It is especially indicated for open injuries of the skull and brain.
Surgical treatment is mandatory in the case of rapidly increasing edema and compression of the brain by an intracranial hematoma. It is shown when the volume of the latter is more than 30 cm³, as well as signs of dislocation of the middle structures. Modern techniques for eliminating hematomas are minimally invasive intervention using endoscopic equipment.
Rehabilitation

Rehabilitation plan for patients with TBI is drawn up individually
The consequences of a head injury can vary greatly depending on the severity of the damage to the structures of the brain. It can be a mild asthenic syndrome after a concussion, or post-traumatic encephalopathy with focal neurological disorders, cerebrospinal fluid circulation.
Therefore, the plan of rehabilitation measures is drawn up for each patient strictly individually.
If the treatment is carried out in a neurology or rehabilitation center, it includes several main points:
- Drug therapy. Nootropics (Phenotropil, Encephabol, Ceraxon, Cerebrolysin), adaptogens (tincture of ginseng, Eleutherococcus, Leuzea and others), multivitamin complexes, B vitamins (neuroirubin, milgamma). After severe TBI, anticonvulsants (depakin, carbamazepine) are prescribed.
- Physiotherapy treatment. Darsonval, magnetotherapy, IRT; general strengthening massage, as well as aimed at restoring movements in the paretic limbs.
- Psychotherapy. Here the help of a psychologist is needed, both individual psychotherapeutic sessions and group sessions are held. The help of a psychologist is especially necessary for children who have suffered severe head injuries.

Patient in consultation with a psychotherapist
- Kinesotherapy. This includes various types of physical activity, exercise therapy, exercises in the pool, elements of sports.
After completing the main course of rehabilitation in neurology, a spa treatment is recommended. It is better to take it in a specialized sanatorium for people with diseases of the central nervous system. If necessary, cosmetic operations are performed to restore post-traumatic defects of the face and head.
Rehabilitation after traumatic brain injury is especially difficult for people with intellectual and mnestic disorders. Such consequences are sometimes observed after severe head injuries.
In this case, the treatment of traumatic encephalopathy is carried out in specialized centers or neurology under the supervision of a psychiatrist.
Even after mild TBI, post-traumatic encephalopathy can be felt by depression, dyssomnia, decreased performance, and chronic fatigue. In such cases, the appointment of antidepressants is required, with increased anxiety - daytime tranquilizers.

Post-traumatic encephalopathy may develop after traumatic brain injury
A full-fledged complex of rehabilitation measures helps not only restore the patient's health, but also return him to a full-fledged social life, restore professional skills. After severe injuries with persistent dysfunctions of the nervous system, a disability group is established by the decision of the MSEC. To register it, you need to contact the district clinic with an extract from neurosurgery or neurology.
What remedy for headaches, migraines and stress is not yet known to many doctors ?!
- Are you having occasional or regular headaches?
- Pressing and squeezing your head, eyes, or "hits with a sledgehammer" on the back of your head, knocks on your temples?
- Do you sometimes feel sick and dizzy when you have a headache?
- Everything starts to annoy, it becomes impossible to work!
- Do you splash your irritability on loved ones and colleagues?

