Unfortunately, traumatic brain injury is by no means considered a rarity in modern medicine. And it's no secret that such conditions can be extremely dangerous. And today, many people are interested in questions about how to treat a concussion. What are the symptoms of this injury? What is the first aid technique in this case?
What is concussion?
A concussion is a mild form of traumatic brain injury. According to statistics, more than 80% of head injuries result in a concussion. Most often, such a condition is not a threat to the health and life of a person, especially if he was provided with qualified medical care on time. Serious pathological changes during concussion are most often absent - they can only be detected at the cellular or even subcellular level.
Main causes of concussion
Surely almost everyone knows that the main cause of a concussion is a bruise to the head. Such an injury is associated with a fall or blow. Sometimes the reason is a sharp change in the position of the body in space.
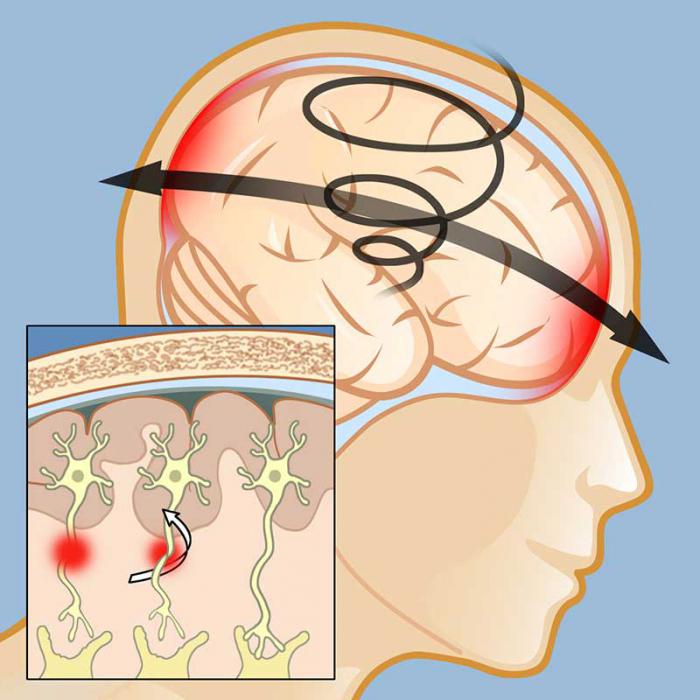
Often, a concussion is caused by a fall from a height, an industrial injury, a traffic accident, etc. Some sports, including all types of martial arts, as well as football, motorcycling, etc., can also be attributed to risk factors.
In any case, no one is immune from falling, and therefore concussion. Therefore, it is so important to know about the main symptoms of such a condition, about the first aid technique, since sometimes it can save a person's life.
The main symptoms of a concussion
Before you learn how to treat a concussion, you should familiarize yourself with the main symptoms of this condition. Quite often, a severe bruise of the head is accompanied by a short-term loss of consciousness. After the victim comes to, he may feel severe nausea. In about 70% of cases, it is followed by a single vomiting.
In any case, a head injury (regardless of severity) requires an urgent examination by a specialist. Only a doctor knows exactly how to diagnose and treat a concussion.
Age features of the clinical picture

It is immediately worth noting that the clinical picture largely depends on the age factor, which must certainly be taken into account during the diagnosis. For example, a concussion in a child of infancy and preschool age is rarely accompanied by loss of consciousness. The main symptoms include nausea, vomiting, severe pallor of the skin, drowsiness.
Most often, loss of consciousness occurs in adolescents and adults. But in elderly patients, symptoms such as disorientation in time or space, as well as throbbing headaches, which are especially intense in hypertensive patients, are observed.
Concussion: the severity of the condition
Of course, further treatment depends on the severity of the injury. So how serious can a concussion be? The severity in this case is determined very conditionally, and it depends on the accompanying symptoms:
- With a slight concussion, loss of consciousness is either absent or does not last very long, and patients, as a rule, feel relatively well.
- The average degree of severity is often accompanied by a slight bruise of the brain. Loss of consciousness can last up to 15 minutes, and the victim clearly shows symptoms of injury.
- A severe concussion is accompanied by a prolonged loss of consciousness, sometimes up to a coma. Often, such an injury is accompanied by the formation of hematomas in various parts of the brain. This leads to compression and disruption of the work of certain nerve centers.
Again, it is worth noting that this system is highly inaccurate. To make a more accurate diagnosis, a doctor's examination and some additional examinations are needed.
First aid for suspected injury or concussion
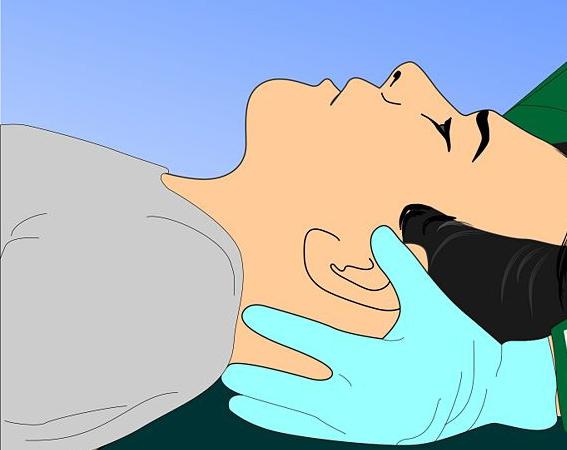
Of course, first aid for a concussion is extremely important. And to begin with, an ambulance brigade must be called to the place. At the same time, the victim is recommended to be placed in a comfortable horizontal position. If there is no suspicion of injury to the spine, neck or thigh bones, then it is best for the patient to lie on his right side, turning his head and bending his knees. This posture will protect a person from possible suffocation caused by tongue slipping, saliva, blood or vomit entering the respiratory system.
Modern diagnostic methods
There are no skull fractures in concussion. The information received from witnesses of the incident is extremely important for the doctor, since every little thing matters here. For example, a specialist needs to know what kind of injury caused the concussion, what symptoms appeared in the first minutes, how long the victim was unconscious, etc. In addition, it is necessary to inform the doctor about other facts, for example, about the presence of psychological problems, alcohol consumption , drugs, medicines, etc.
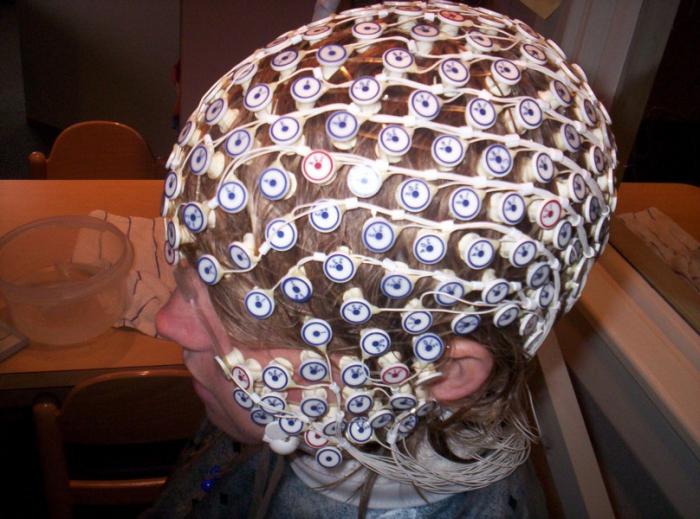
Naturally, after a visual inspection, additional studies are carried out. In particular, ophthalmography, Doppler ultrasound, electroencephalography, and otoneurological examination can be informative. But with computed and magnetic resonance imaging, deviations, as a rule, are not detected.
Concussion: treatment
At the first suspicion of an injury, an ambulance should be called. In some cases, the victim may feel relatively well, refusing medical attention. In no case should this be done - only a specialist can determine whether a concussion has really taken place.

Treatment, of course, depends on the severity of the injury. With a slight injury, the patient can be discharged from the hospital after 2-3 days. First of all, you need to restore the normal functioning of the nervous system. For this purpose, patients are prescribed nootropic drugs for concussion: Encephabol, Picamilon, Nootropil, etc. In addition, it is necessary to stop the pain - anesthetic drugs in this case are selected individually.
If necessary, the patient is given sedatives, for example, Corvalol, Valocordin, tincture of valerian or motherwort. Sometimes conduct vascular therapy aimed at normalizing blood circulation. In some cases, it is necessary to take diuretics (if edema is suspected). In any case, only a doctor knows how to treat a concussion. And it is strictly forbidden to do this on your own, at home.
Potential short-term consequences and post-traumatic care
Some side effects are possible after a concussion. For example, many patients complain of recurrent headaches that can be relieved with analgesics. Sometimes there is constant nausea, which is accompanied by vomiting. Short-term effects of a concussion include bouts of dizziness. Also, after an injury, people often complain of problems with concentration, as well as difficulties in performing any ordinary and familiar activities (reading, tying shoelaces, etc.).

In most cases, these disorders go away on their own after 7-14 days. However, proper care and adherence to certain rules is what people with a diagnosis of concussion need. Treatment continues after discharge from the hospital. What is it?
In order for the body to recover faster, the patient is recommended to observe bed rest. Calmness, lack of stress and physical activity is what will help a person recover faster. That is why doctors forbid victims to listen to loud music, read, watch TV for a long time, play sports, etc. The minimum amount of external stimuli will help a person recover much faster. If, after two weeks, the symptoms have not disappeared, it is worth visiting the doctor again and undergoing some additional research.
Possible Complications
Unfortunately, in some cases, concussion, even with treatment, can lead to one or another complication. In particular, vasomotor disorders often occur, which include general persistent fatigue, problems with concentration, headaches and dizziness, which are aggravated by physical exertion. As well as frequent and strong flushes of blood to the head, abruptly replaced by a general pallor of the skin.
Moreover, concussion can also affect the psychological state. Often, injuries lead to emotional lability, increased irritability, a sharp change in emotions, clouding of consciousness, and neuroses. Psychoses are much less common, accompanied by hallucinations and delusions. In the risk group in this case, professional athletes, especially boxers, who receive blows to the head and, accordingly, concussions of varying severity almost constantly. Often in such cases dementia and other disorders develop.

