A concussion occurs only with an aggressive mechanical impact on the head - for example, this can happen when a person falls and hits his head on the floor. Doctors still cannot give an exact definition of the mechanism for the development of concussion symptoms, because even with computed tomography, doctors do not see any pathological changes in the tissues and cortex of the organ. It is assumed that such an aggressive mechanical impact on the cranium leads to disturbances in the functioning of the nerve cells of the brain, which provokes malnutrition of the tissues of the organ and disorder in communication between the brain centers.
Classification of concussion
In medicine, the term "concussion" means a mild form of traumatic brain injury with a short-term loss of consciousness.
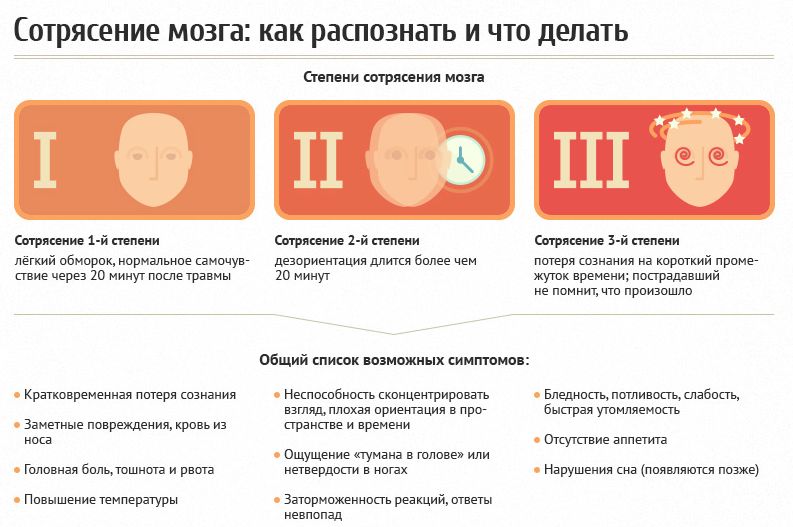
Depending on what symptoms of the condition in question are observed in a person and with what intensity they proceed, the classification of concussion will also depend. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish between two degrees of severity of the course of the condition in question:
- mild concussion. At the same time, no serious disturbances in the structure and functioning of the brain will be noted even after a thorough examination of the patient, and the classic symptoms of this condition disappear in a maximum of 14 days (often in a shorter period).
- severe concussion. Accompanied by ruptures of some blood vessels, the formation of a hematoma in the organ, the classic symptoms of the condition in question do not disappear for a month or more.
In some sources, there are 3 degrees of severity of concussion:
From a blow to the head, a person can lose consciousness - this condition can be short-term and long-term. But most often the person remains conscious and makes the following complaints:
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- general weakness.
In the first hours after injury, the patient may complain of throbbing pain in the occipital region, nausea. But at the same time, the body temperature remains within the normal range, there is no loss of consciousness. Examining the patient visually, you can determine the increased pallor of the skin, rapid breathing, too fast heartbeat, urge to vomit.
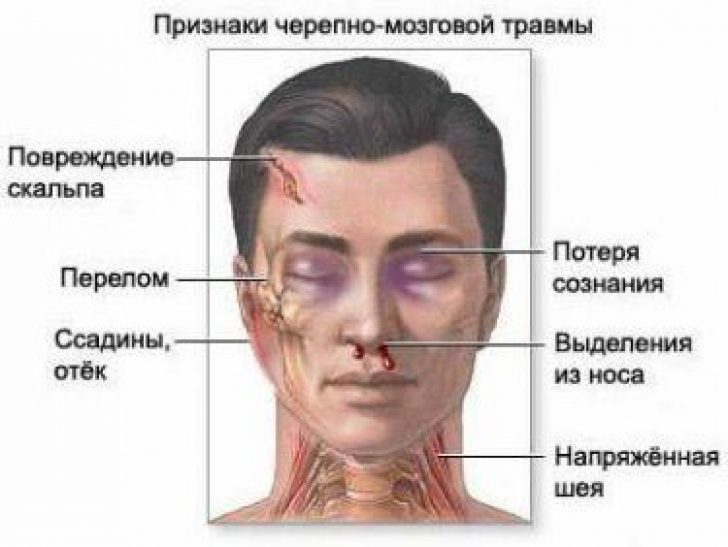
Note:these signs of concussion, which occur in the first hours after the injury, disappear after a few days, some patients notice a significant improvement in their state of health the very next day.
In this condition, the activity of the nerve cells of the brain is disrupted, which affects the functioning of the organs of vision - there may be pain during eye movement, the patient's pupils will be narrowed or dilated and have different sizes, complaints are received about the inability to focus the gaze and divergence of the eyeballs when reading.
There may be other symptoms - for example, sudden flushing of the face, a feeling of heat, excessive sweating, a systematic sleep disturbance.
| Symptoms | Signs of violations | Origin mechanism |
| Immediately after injury | ||
| Stupor | State of stupor, confusion. The muscles are tense, the expression frozen on the face. | Emotions and body movements are inhibited. This is the result of a violation of the processes of transmission of nerve impulses in the cerebral cortex. |
| Loss of consciousness | A person does not react to stimuli, does not feel anything. This can last from a few seconds to 6 hours depending on the strength of the blow. | Violation of the transmission of impulses along the processes of nerve cells. Thus, the body reacts to the lack of oxygen, which arose due to impaired blood circulation in the brain. |
| Single | The contents of the stomach are ejected through the mouth. At the same time, breathing quickens, saliva and tears are released. Sometimes vomiting can be repeated. | The reason is circulatory disorders in the vomiting center and in the vestibular apparatus. |
| Unpleasant sensations, pressure, heaviness in the epigastric region. | Such sensations are caused by the excitation of the vomiting center. This formation is located in the medulla oblongata. When struck, it becomes irritated. | |
| Dizziness | Occurs at rest and increases with a change in body position. | Caused by impaired blood circulation in the vestibular apparatus. |
| Increased or slow heart rate (less than 60 or more than 90 beats per minute) | It feels like a rapid heartbeat or a feeling of weakness due to the fact that the organs are lacking oxygen. | The phenomenon is associated with an increase in intracranial pressure, compression of the vagus nerve and cerebellum. |
| Paleness, which is replaced by redness of the skin of the face | Redness of the skin of the neck and face is abruptly replaced by pallor. | Violation of the tone of the autonomic nervous system. As a result, small arteries in the skin periodically dilate or narrow. |
| Headache | Throbbing pain in the occiput or at the site of injury. Pressive and bursting pain in the whole head. | Unpleasant sensations are associated with an increase in intracranial pressure and irritation of sensitive receptors on the membrane of the brain. |
| Noise in ears | Sensation of hissing or ringing in the ears. | Due to the increase in pressure in the skull, the greater ear nerve is compressed. This causes a malfunction of the hearing aid. As a result, a person, as it were, hears noises due to irritation of the auditory receptors. |
| Pain on eye movement | Reading or looking away causes discomfort in the eyeballs or temples. | Unpleasant sensations appear due to increased intracranial pressure. |
| Impaired coordination of movements | A person gets the impression that the body does not obey him well, the movements are performed for a long time, as if they are late. | These are the consequences of impaired transmission of nerve impulses from the cerebral cortex along the nerves to the muscles, as well as poor blood circulation in the vestibular apparatus. |
| sweating | Sensation that palms are cold and wet. Droplets of sweat appear on the face and on the body. | The sympathetic nervous system, which controls the work of the internal organs, is too excited. It causes the sweat glands to work actively and release more sweat than usual. |
| In the first hours after injury | ||
| Constriction or dilation of both pupils | The pupils react normally to light, and the person does not feel anything unusual. But the doctor may notice that the reaction of the pupils is incorrect. If the pupils are of different sizes, then this indicates a more serious brain injury than a concussion. | Intracranial pressure has an effect on the centers of the autonomic nervous system, which regulate the contraction of muscles that constrict or expand the pupil. |
| Eye trembling when looking away | When a person looks to the side, his eyes begin to tremble. It is difficult to see objects without turning your head towards them. | This phenomenon is associated with damage to the inner ear, vestibular apparatus and cerebellum. These structures cause the eye muscles to contract rapidly. As a result, the victim cannot focus his eyes. |
| Asymmetry of tendon reflexes | These reflexes are checked by a neurologist. He strikes the tendons with a hammer, in response there is a flexion of the arm at the elbow joint or leg at the knee. | Normally, the right and left limbs bend in the same way. Increased intracranial pressure disrupts the functioning of the brain and nerve fibers that are responsible for performing reflex actions. |
| Symptoms remote in time (appear after 2-5 days) | ||
| Photophobia and hypersensitivity to sound | A person perceives ordinary sounds or a normal level of illumination inadequately. He is annoyed not only by loud, but also by moderate sounds. | Due to the fact that the reflex constriction of the pupils is impaired in a person after an injury, bright light causes discomfort to him. Violation of the nerves that are responsible for the hearing aid, causes irritation from sounds. |
| , moodiness and irritability | Bad mood, unwillingness to move, work and have fun. | Irritability is based on a violation of the connections between nerve cells in the cerebral cortex, which are responsible for emotions. |
| sleep anxiety | Difficulty falling asleep, nocturnal or early awakenings. | Sleep problems are associated with unpleasant emotions that a person experiences, with stress and overexcitation, as well as with impaired blood circulation in the brain. |
| Amnesia | Memory loss. The person cannot remember what happened immediately before the injury. Usually, the stronger the blow, the longer the period falls out of memory. | The process of remembering and reproducing events in memory takes place in several stages. If at the moment of injury this chain is broken, then some events may not be deposited in long-term memory. |
| Lack of concentration | A person cannot concentrate on what he is doing at the moment. He is often distracted, becomes inattentive, switches to other activities. | Poor concentration is caused by a disruption in the connection between the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures. |
All of these symptoms of a concussion of the brain are very conditional - they can be present in a complex, or only one sign of the development of a pathological condition may appear. Doctors say that it all depends on the age of the patient:
- With a concussion in an infant, there is no loss of consciousness, he will have a sudden pallor of the face, the heartbeat becomes rapid, and regurgitation or vomiting will necessarily be present after feeding. Later, parents may notice that the baby has become lethargic, he is overcome by drowsiness, but sleep will be restless.
- If a head injury happened in a preschool child, then with a mild pathological condition, all these symptoms disappear after 2, maximum 3, days.
- Young people and those under the age of 35 are more likely to lose consciousness during a concussion, and all of the above symptoms will have an average intensity - doctors talk about the classic pathology development pattern.
- In old age, the condition in question is most difficult to tolerate - not only will all the symptoms be pronounced, but in the future the patient may become disorientated in time and space.
It is believed that the signs of a concussion disappear after 10-14 days, but doctors warn that the consequences may appear much later. In some cases, regularly occurring severe headaches begin to bother a person even several years after receiving a head injury.
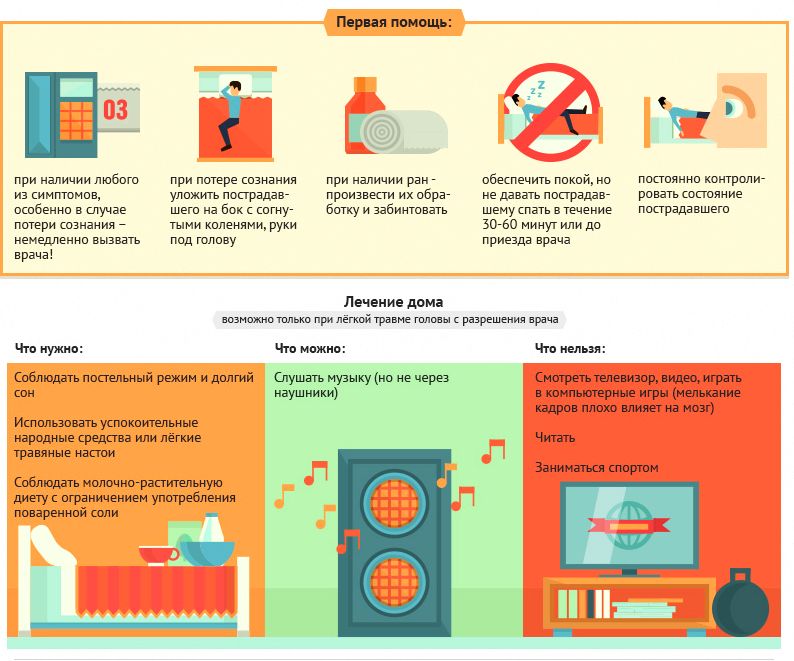
If there is a suspicion of a concussion, you should immediately call the ambulance team - you need to do a full examination and make sure that it is a concussion, and not a bruise or compression. But while waiting for the doctor, you need to do the following:
- lay the patient horizontally with some elevation of the head;
- in no case should you give the victim to drink and eat;
- open the windows - you need to provide the patient with a lot of fresh air;
- something cold should be applied to the head - it can be ice from the freezer, a cloth soaked in cold water;
- the victim must observe absolute rest - he is even forbidden to watch TV or listen to music, talk on the phone, play on a tablet or laptop.
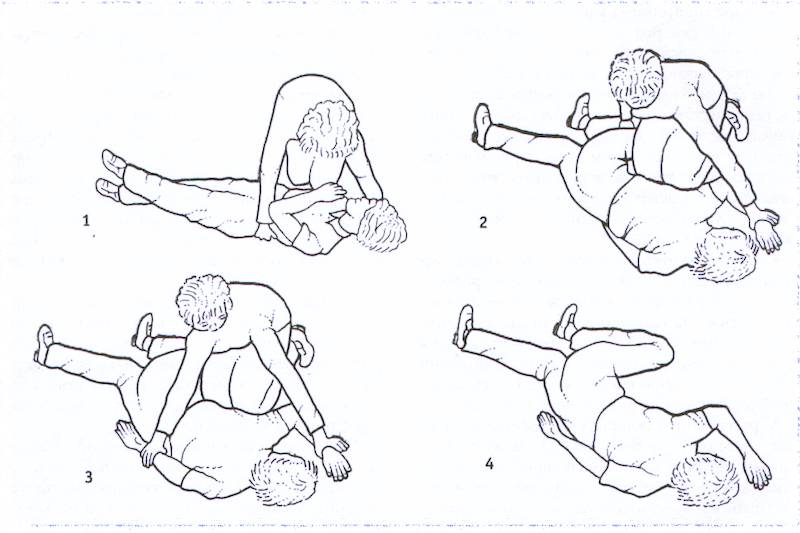
If the victim is unconscious, then it is strictly forbidden to move him, and even more so to transport him! It is necessary to lay him on his right side (albeit on the floor), bend his left leg at the knee and his left arm at the elbow, and turn his head to his right side and press his chin to his chest. In this position, the air will flow to the patient into the lungs without hindrance, breathing will not be suspended, and he will not choke on vomit.
Treatment of a concussion is carried out only after an examination; only a doctor can prescribe any medications. If there is no opportunity to seek medical help, then the following recommendations should be followed during the rehabilitation period of the patient:
- in the room where the victim is located, absolute peace must be observed - he cannot listen to music, watch TV and read books;
- no drugs with an analgesic effect can not be taken;
- alcohol tinctures and alcoholic beverages are prohibited;
In any case, even if no symptoms are observed after 2 weeks, it is necessary to undergo an examination in a medical institution - this will prevent the development of complications.
There are several traditional medicines that can be of real benefit during the treatment of a concussion. But they can and should be used only after examination and obtaining permission for such therapy from a doctor.
The following folk remedies can be used during the rehabilitation period:

Note:shepherd's purse can cause uterine bleeding, so you need to find out from a woman who is recovering from a concussion if she has a predisposition to bleeding from the uterus.
- Take a tablespoon of dry black thyme and pour two cups of boiling water, then, with a slight heat, the product is brought to a boil and cools. Take a decoction of black thyme should be three times a day before meals in the amount of ½ cup. The course of treatment with this particular drug is long - at least 3 months in a row.
Bee pollen will help speed up the recovery of the brain after the condition under consideration - it is recommended to use it three times a day at a dose of half a teaspoon. The duration of such treatment is at least 30 days, then you need to take a break in therapy and after 10-15 days you can repeat taking the remedy. As a rule, if the concussion passed without complications, then only 2 such courses of bee pollen treatment will be needed for a full recovery.
Note:some healers recommend using alcohol tinctures and motherwort as a treatment for concussion - official medicine categorically does not allow this. The fact is that no one can determine the real level of brain damage in the condition under consideration, and the body's reaction to alcohol tinctures can be absolutely unpredictable.
Possible complications after a concussion
If the concussion is severe, there is a hematoma and compression of the tissues of the organ, then the complications can be very serious - from partial speech impairment to confusion, loss of acquired skills, and so on. But in the case of a mild concussion of the course, only headaches can be distinguished from the possible complications. And it is only at first glance that such a complication is accepted as insignificant! In fact, patients with a history of concussion may experience intense, prolonged headaches after several years.

