Concussion: signs in children and adults, what to do, consequences
All materials on the site are published under the authorship, or edited by professional doctors,
but are not a prescription for treatment. Contact the specialists!
TBI of all types of injuries is perhaps the most common, especially in childhood, when the "adult" proportions have not yet been determined, and the head, when falling, pulls the body down and suffers first. Any blow to the head is perceived as a serious injury, even if at first glance everything is in order. People who are next to the fallen baby immediately begin to look for signs of a concussion in the child, in order to call an ambulance as soon as necessary.
A concussion can also be obtained by landing on the buttocks; therefore, TBI is very often accompanied by other injuries of the body (chest, lower leg, pelvis) and, less often, are isolated. The only question here is which organ needs to be saved in the first place? But the head is always important, therefore:
Even a mild concussion requires a thorough examination in a hospital setting in order to determine the real harm to health and prevent possible consequences.
Concussion is one form of TBI
Usually, people under a concussion of the brain mean any traumatic brain injury and this, of course, cannot be reproached, since all these TBIs are the competence of doctors. In medical circles a concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury, for which focal neurological symptoms are not characteristic, there are no signs of vascular damage, and functional disorders that followed the injury are reversible... However, given the interest of readers not only in this form of pathology, we will try to stop and explain the essence of those head injuries that are popularly considered to be a concussion, since everyone interprets this term in their own way and often confuses it with the concept of a brain injury or the formation of an intracranial hematoma from compression.
Experience shows that each of us can find ourselves in a situation where it becomes very important to determine the degree of damage, since not only a person's life often depends on this, but also its quality in the future. Symptoms of a concussion are both meager and very diverse, it all depends on the strength of the impact or the strength of the head of the person.
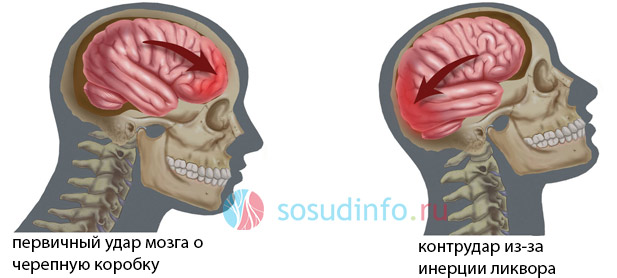
Thus, a concussion of the brain is the result of shaking a soft substance and hitting it against the hard cranium, inside which it is located. In the process of movement of the brain to the bones of the skull, the cells (their processes) stretch and experience some discomfort, which affects their functional abilities, which are temporarily lost.
Doctors still have not come to a consensus on what actually happens in the head at the moment of impact, therefore there are several versions of possible events that knock the work of the central nervous system out of its usual rut:
- Neurons lose communication with each other.
- Disturbances in the nervous tissue of the brain occur at the molecular level.
- A sharp spasm of the vessels of the microvasculature makes it difficult to feed the brain.
- Imbalance in the interaction between the cortex and other structures in the brain.
- Changes in the chemical composition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
- A short-term increase in intracranial pressure due to physicochemical disorders and colloidal imbalance.
- Violation of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, which, upon impact, leaves the cavity of the ventricles of the brain and is sent to the interventricular spaces.
Which of these hypotheses is correct, probably not for us to judge, but what is important is that they all agree on one thing - with SHM, reversible functional disorders occur, but brain structures do not suffer, morphological changes in them are not observed... The veracity of such a statement is also evidenced by the data of computed tomography, which is usually prescribed for head bruises.
Danger can lurk at every turn
In adults, a concussion of the brain often occurs against the background of alcohol intoxication: either he lost his balance, then he got actively involved in a fight, or he got into an accident. Alcohol in such cases becomes a factor aggravating the patient's condition and complicating early diagnosis, since it obscures the clinical signs of the underlying pathology. It is difficult to understand: lethargy and other manifestations are the result of intoxication or indicate the development of symptoms of concussion. True, there are other options when an adult, quite sober person gets a TBI in transport, on the road, at work due to circumstances beyond his control.

Head bruises often haunt children in games and adolescents because of carelessness (slapping a book or a briefcase on the head, other fun) or overestimating opportunities during leisure activities, because you really want to show adult prowess by riding an "iron horse" or jumping on roofs and fences.
Meanwhile, I would like to remind you that a concussion can occur without a stroke. Sudden braking of the vehicle or attempts to maintain balance in winter ice sometimes also end in a known diagnosis.
Everyone knows that there are frequent cases of TBI and injury to other parts of the body among those for whom “sport is life”. Chess does not hone an athletic figure and does not add physical strength, but "a person strives for excellence," therefore he is looking for new types of sports exercises, borrowing them from overseas peers. What it can result in - further.
Signs of a concussion in a child who already knows how to speak and knows his "I" practically do not differ from those in adults. But it can be very difficult even for a health worker to recognize the symptoms of concussion in infants, if he is not a pediatric neurologist, therefore, if this pathology is suspected, it is better for parents not to try to take responsibility and make a diagnosis on their own. The toddler should be immediately shown to a doctor who is able to distinguish the normal behavior of the toddler from the behavior of the sick child.
How to recognize a concussion in young children?
In general, a concussion in infants is a rather rare phenomenon, everything is so soft and elastic in them that the risk of getting a concussion is very small, and, as the saying goes: "A child falls - God is laying straw." However, you do not need to relax unnecessarily, parents should be constantly on the alert and know the basic signs of a concussion in a child:

- Frequent regurgitation, refusal to eat, which, however, can be caused by other reasons (intestinal colic, weather changes, ARVI).
- Increased excitability, anxiety, or, conversely, lethargy and drowsiness also does not say much.
- Twitching of the muscles of the limbs.
- Unnatural pallor or flushing of the face.
You should especially pay attention to the appearance of unusual signs if the child hit his head the day before. More often this happens with children who have learned to roll over, sit and crawl, but have not yet acquired a sense of danger. An eye and an eye are needed behind such a fidget, but he already has more symptoms of concussion than very little ones, for example:
- The child bumped, was silent, and then began to cry bitterly (perhaps he lost consciousness for a few seconds).
- In such "large" children, it is easier to distinguish vomiting from regurgitation and to notice sleep disturbances, since the time spent playing and being awake has lengthened.
In a word, with children who have emerged from a newborn state, one can somehow "agree" and understand the cause of anxiety.
Unfortunately, there are often cases when a visit to a doctor is postponed or canceled altogether, time passes and everything seems to be normalizing, however, the harm to health caused by a seemingly insignificant blow can be significant, and the consequences are not very encouraging:
- Intense headaches following a concussion many years ago can be lifelong.
- Disorder of thinking processes, poor assimilation of the school curriculum.
- Convulsive syndrome.
The clinical picture of mild traumatic brain injury
Signs of TBI are not always present all together and give a vivid clinical picture. In general, the symptoms of a concussion depend on the severity of the condition and are manifested by:

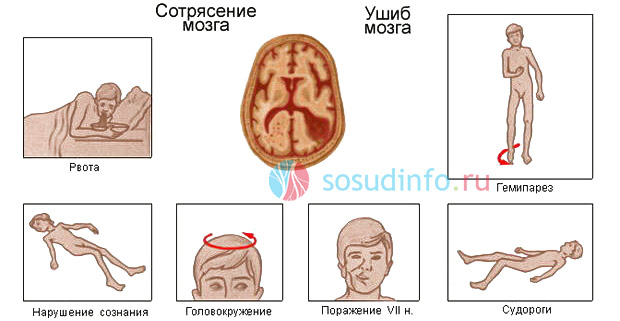
Considering that a diagnosis such as a concussion is in itself the first and mildest degree of serious pathology, united by the general name "craniocerebral trauma", the modern classification does not provide for the division of this form by severity separately. However, we can agree that not all blows and bruises are the same, therefore there are some varieties that allow you to determine and convey (rather, orally) the degree of damage, which is sometimes used by doctors and quite often patients:
- Mild concussion dispenses with loss of consciousness and amnesia, signs of trouble in the head (lethargy, nausea, severe headache) usually disappear in a quarter of an hour.
- At grade 2 loss of consciousness is usually absent, but deafness, loss of memory and other symptoms do occur.
- For severe degree Concussion can be characterized by both memory loss and loss of consciousness in combination with the entire set of objective clinical manifestations of pathology, because the patient can present complaints only upon returning to real life (restoration of consciousness).
The harm to health caused by TBI can be significant and it depends on what kind of injury the person received: a minor concussion in an adult with timely first aid and adequate further treatment can pass and be forgotten. However, it only seems to be. Seizures after a concussion are common and understandable, but the patient himself rarely associates these events with each other, believing that too much time has passed. As for a brain injury, depending on the severity, it can leave the most serious consequences.
What consequences can be expected from TBI?
Why, when taking anamnesis to establish any diagnosis that has nothing to do with the brain, does the doctor never forget to inquire about the history of traumatic brain injury? And all because TBI in any form and degree of severity often gives far-reaching consequences:
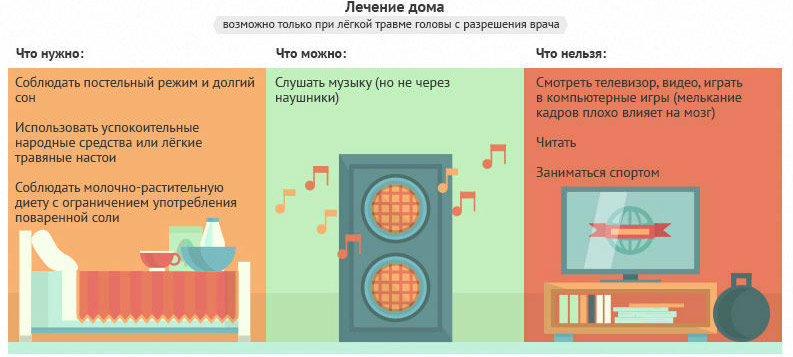
The consequences of any form of TBI, even the mildest, can be very serious, so knowing what to do in case of a concussion and being able to provide first aid will be useful to every person.
Lay down, watch and wait
It is unlikely that a victim in a state of lethargy can quickly navigate and independently assess the situation. It should be noted that the first symptoms of TBI in the case of a concussion and in the case of a brain injury, or may be identical, therefore, first aid in this situation is to observe the behavior of the patient who needs to be put to bed, since excessive activity can bring additional harm to health.

What to do in case of a concussion? For this you need to be sure that it is still a concussion, and not another, more severe, form of TBI, therefore, at the slightest sign of traumatic brain injury (the clinic is described above), a person should be shown to a doctor. If the accident took place at home, the patient did not lose consciousness, the condition did not change for half an hour for the worse and is assessed as quite satisfactory, then you should consult a neurologist at your place of residence. Unfortunately, patients often let everything go “on the brakes” and do not go anywhere, and then wonder where the unreasonable headaches come from? After a concussion, of course, which was not diagnosed in time.
Loss of consciousness or lack of consciousness, nausea and vomiting, worsening of the condition, which initially did not cause much concern - alarming symptoms requiring immediate medical intervention. Such patients need hospitalization, but there is no need to try to transport the patient on their own, if there is no urgent need for this (lack of communication means, remote area). Meanwhile, deciding on independent transportation, if there is no other way out, you need to keep in mind that the victim, in addition to the head, may be damaged other organs (spine, for example), so all actions should be as gentle as possible, but fast.
You should not offer a person medication at his own or (even worse) his discretion, if he is conscious. You just need to put the patient to bed, provide first aid, call an "ambulance" and wait for her arrival.
The actions of a random witness of the incident who happened to be nearby and trying to help somehow should look like this:
- Gently lay down in a horizontal position, but if a person is unconscious, then with a head injury, vomiting cannot be ruled out, so it is better to turn the patient onto the right side, bending the arm and leg on the left side.
- Unbutton the collar, loosen the tie, in general, remove unnecessary accessories and let the victim breathe freely.
- Put cold on the bruised area, treat wounds, make dressings, stop the blood.
- Monitor your heart rate (frequency, filling, tension) and blood pressure, if possible.
- If breathing stops, proceed with the exercise (artificial respiration, chest compressions).

Unfortunately, life is full of surprises, sometimes very unpleasant, and situations in which concussions sometimes occur can be so different….
Diagnosis and treatment is the task of the hospital
As a rule, a neurologist will suspect a mild TBI, that is, a concussion, even for 2-3 signs.

In the hospital, the victim, if everything goes well and will manage only with a concussion, will spend about a week, but this does not mean that all questions are closed, and he can consider himself completely healthy. For another year, he will be monitored by a neurologist, visiting the clinic every quarter and receiving treatment, which is prescribed by the doctor.
In this way, treat a concussion on your own, it is not recommended to take any medications, all the more so that often patients, reacting to all external influences (people's voices, light, etc.), become even more irritated, lose the ability to correctly assess their condition. They have a negative attitude towards hospitalization and believe that they themselves know how to best cope with an unexpected problem. This should be taken into account by relatives or people who happened to be nearby by chance.
Brain contusion and other TBI
At the beginning of the article, it was noted that not all TBIs are a concussion, but all concussions are a traumatic brain injury. What does it mean? People often refer to the concept of "concussion" as all injuries, including bruises, compression of the brain, intracranial hematoma. Traumatic brain injury is a collective term. In addition to concussion, TBI can damage the brain structures, cranial nerves, the pathways along which the cerebrospinal fluid moves, as well as the vessels that deliver nutrients and oxygen with the blood. 
In addition, it should be borne in mind that not only the shock itself, when the brain is damaged at the site of application, can be dangerous for the victim, but also the shock coming from the fluctuation of the cerebrospinal fluid or from the impact on the processes of the dura mater. Thus, not only the large hemispheres can be affected, but also the trunk, in which the centers responsible for the activity of many important organs and systems are localized, and metabolic processes are disrupted. To help the reader correctly assess the situation and navigate such diagnoses, if necessary, we will try to briefly dwell on other TBIs:
- Brain contusion which, in contrast to concussion, in addition to general cerebral symptoms, gives local and focal symptoms, depending on the location of the injury. Brain contusion has 3 degrees of severity, patients with mild and moderate severity are sent to neurosurgical departments, and with 3 degrees they are subject to hospitalization in hospitals with intensive care, intensive care and neurosurgery departments.
- Compression of the brain As a rule, it occurs against the background of a severe contusion of GM and is usually a consequence of the formation of an intracranial hematoma. It is manifested by psychomotor agitation, an increase in cerebral symptoms, the development of convulsive syndrome.
- Intracranial hematoma requires urgent surgical intervention in the Department of Neurosurgery. It can manifest itself some time after the injury, why the seeming well-being after TBI does not really give reason for calmness. It is this symptom called bright gap, belong to the important and insidious signs of a hematoma, and underestimation of it is fraught with the development of life-threatening consequences for the victim.
Of course, the therapeutic approach to conditions of this kind differs markedly from the treatment of a concussion:
The victim requires not only emergency hospitalization, but also the immediate start of all measures, including surgery, if an intracranial hematoma is diagnosed, which is capable of “deceiving” others and the doctor of the arriving ambulance team.
Often misleading is the light gap immediately after the injury(the person came to his senses and claims that his state of health is normal). The thing is that post-traumatic intracranial hematoma can proceed at the initial stage without much suffering in the brain, especially if the source of bleeding is venous (when bleeding from an arterial vessel, the light interval lasts minutes). Intensive increase in symptoms of respiratory and vascular disorders, the development of mental disorders, With a decrease in heart rate against the background of an increase in blood pressure increases the suspicion in favor of an intracranial hematoma, therefore, the patient should in no case be left without hospitalization.
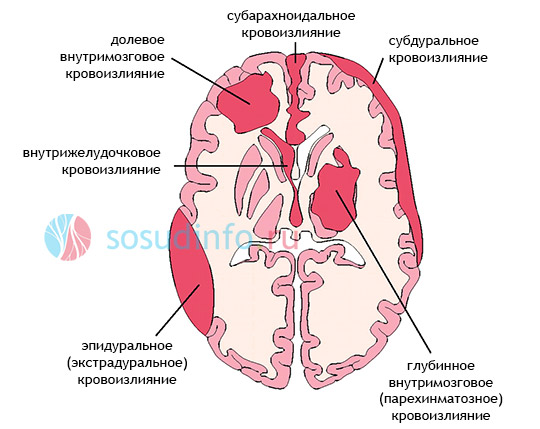
typical areas of hemorrhage and bruising due to head trauma, or
Traumatic brain injury is a frequent phenomenon in our life, because there are so many dangers around. Often it is limited to a mild degree - a concussion, which, however, does not allow you to relax. You always need to keep in mind the possibility of hidden damage and the development of serious complications. Ignorance and underestimation of all the insidiousness of TBI can become a tragic mistake that interrupted someone's life, therefore, in all cases of head injuries, the patient should not be left without attention and help, even if he confidently claims that everything is in order.

