Many times you have probably heard the expression “only a lobotomy will help here,” or something similar. Let's figure out what a lobotomy is.
What is a lobotomy?
Lobotomy is a type of neurosurgical operation, also known in psychosurgery as leucotomy. The essence of the operation is to separate the frontal lobe of the brain from the rest of it, by resection of the white matter of neuronal connections. Thus, the connection between the frontal lobes and other parts of the brain ceases, but they themselves frontal lobes are not affected or damaged. As a result, the influence of the frontal lobes on the central nervous system is stopped, as a result of which the patient loses the ability to make decisions, his will weakens and, often, a person who has undergone a prefrontal lobotomy turns into a vegetable.
This is a starting shot for further testing. After just two patients, Kuhn is euphoric. It was "something completely new, an effect never seen before." The depressed are "usually more lively, the depressive whispers louder and the crying stops." Families talk about 'miracle cure'.
Dosage varies easily
Kuhn plays the entire roster of test opportunities. It is administered three or four tablets of 25 mg per day, with the dose being doubled, and sometimes significantly higher, or the drug is given again suddenly. He is interested in how patients respond to such treatment. He then tries it in combination with morphine. He wants to find out if it is as addictive as an opiate. He compares it to substances chemical formula which was easily changed. To help nurses keep an overview of many of the tablets, they are colored differently.
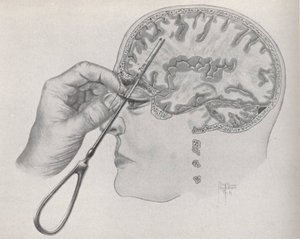
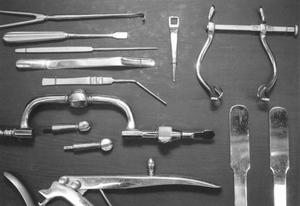
Initially, lobotomy was performed without craniotomy by inserting a surgical instrument into the brain through the eye opening. The first such tool was an ice pick, until Walter Freeman (a famous American psychiatrist who played a significant role in popularizing this method) developed the leukotome and orbitoclast - special knives for performing lobotomies. To cut the white connective tissue, the surgeon placed a knife against the patient's eye socket and struck the knife with a surgical hammer. The knife, separating a thin layer of bone, entered the skull under the frontal lobes, after which the surgeon made several movements with the knife in different sides, destroying the substance of neuronal connections.
No one is finding pharmacologically interesting approaches. Leading psychiatrists openly doubt the antidepressant effect. He states that three-quarters to four-fifths of patients are fed entirely imipramine. For Kuhn, only one question remains: how does the substance affect the unborn child? He later wrote about this experiment: "There was an alarming wait until the birth of a severely depressed mother who had been taking new drug throughout my pregnancy." The mother's consent to the tests was not proven.
"Ready to accept a lot"
Documents show that Kuhn repeated the experiments with other pregnant women. In psychiatry there were bad times, says Asmus Finzen, professor of social psychiatry and former deputy medical director of the University of Basel Psychiatric Clinic. IN serious illnesses was extremely helpless.
The use of this method was fraught with frequent damage to the frontal lobes, so in the second half of the twentieth century, the practice of osteoplastic craniotomy began. The surgeon opened the skull, which revealed necessary review surgical field and allowed for more precise tissue resection without damaging the frontal lobes. After the operation, the skull was sutured, and the patient was given a lifelong diagnosis of Frontal Lobe Syndrome.
International Congress of Psychiatrists. Kun rarely practices side effects. It justifies the patient's suicide as the effect of the drug wanes. A number of other deaths may also have been linked to Kuhn's attempts. Test sheets for imipramine attempts from the mid-fifties, the state archives kept in Thurgau are filled with only very rudimentary: The comment column is mostly empty.
According to these forms, Kuhn tested several substances simultaneously on many patients. The attempts were closely interrelated. This is sometimes called "no entry", "seizure", "electronic strike" or "red". This was noticeable: in some patients, someone had scratched a dead cross directly behind the test date. Sometimes the date of death was recorded. It is amazingly common that there are only a few days between the end of the tests and death. The cause of death is not mentioned in either case.
Lobotomy is a terrible and inhumane intervention into the human brain. Why do they do a lobotomy then? Many disputes about the ethical and practical side of lobotomy arose from the very beginning of the practice of lobotomy, and on December 9, 1950, Order No. 1003 was issued, which prohibited the use of lobotomy in medicine. Lobotomy was used only in extreme and hopeless cases of schizophrenia, when long and systematic use of other traditional methods Treatment of schizophrenics did not produce results. And when some seriously ill, hopeless patients who had undergone lobotomy found peace and mental stability, it became clear why a lobotomy was needed.
Three years later, a total of 23 dead
At the same time, 23 people participated in the green pill experiment, and four died. He was given not only green pills, but also red ones, that is, imipramine. Unlike other patients, there is no mention of Jacob B. participating in another study. If Kühn had not paid attention to the fact that Yakov B. received twice as much active substance? Was it clarified whether there were deaths?
In the sixties, Kuhn continued his experiments. Gaethje changed the chemical structure several times on behalf of Koons. He wants to find a more tolerable drug. Again, he tests funds from patients of different diagnoses - and can transfer money from patients practicing in the region, including children. He stole money from a family of nurses, bought toys for other children and had sweets for himself.
Lobotomy has been relatively successful in treating paranoid schizophrenia. The patients returned to normal life and work (sometimes), getting rid of psycho-emotional disorders, and healthy members of society felt safe.
Lobotomy is a surgical method of treating mental illnesses, the meaning of which is to disconnect or destroy the connections of one of the parts of the brain of the head with the rest of its parts. As a rule, the concept of “lobotomy” implies the separation of any of the frontal parts with other parts of the brain. This is a neurosurgical operation that this moment is not used, that is, it is already history.
When he reads his papers today, it escapes him: “You stuffed yourself like a goose with medicine.” In Münsterlingen, children such as Walter Emmisberger and Walter Nowak treat Roland Kehn's wife Verena Kuhn. She is a senior physician in child psychiatry. The files suggest that the children had to exorcise the supposed heaviness with medication. They also had to swallow drugs while they were recovering. He said that "he still had a tendency to not concentrate in school, to do too little to the point of using lies," he says in the clinic files.
This method of treatment was developed in those years when there were no effective medications that could be used to cure schizophrenia, disorders mental behavior with hallucinations and delusions when psychiatric patients constituted a significant threat to the lives of others. After the creation of Aminazine (medication class of neuroleptics), lobotomy has become an unpopular method of treatment. But around this concept There are a lot of creepy stories and legends that are still retold today. What kind of terrible method of treatment is this, who created it and used it for the first time, what consequences this operation had, you will find out by reading this article.
"The boy starts to shake so much"
In just two months the boy should start again. Frau Pfarrer reports that she could not give the boy six tablets, but only four: “Otherwise he would have to vomit.” Kuhn, a child psychiatrist, says that he should try this “Chiba remedy”, as he understands it. It is not believed that drugs can be charged. Instead, a twelve-year-old child still needs to swallow higher doses. But the attempt stops: “The boy begins to tremble so much that he can no longer write, which does not apply to school, of course,” notes Verena Kuhn in the dossier.
The history of lobotomy
 The founder of this type of surgical intervention is Dr. Egas Moniz(Mones) from Portugal. In 1934, at a meeting of neurologists, he became very interested in one of the experiments of his colleagues, who cut out the frontal part of a rather irritable and aggressive monkey named Becky. As a result of the removal of this brain part, the monkey became controlled and quiet.
The founder of this type of surgical intervention is Dr. Egas Moniz(Mones) from Portugal. In 1934, at a meeting of neurologists, he became very interested in one of the experiments of his colleagues, who cut out the frontal part of a rather irritable and aggressive monkey named Becky. As a result of the removal of this brain part, the monkey became controlled and quiet.
The patient weighs another 33 kilograms
And: “Children tolerate it much better than imipramine.” As always, Kuhn does not publish numbers. Walter Emmisberger and Walter Nowak landed in another large-scale Kuhn test. Also Valentina O. elderly woman, who has lived in Münsterlingen for decades due to “foot catatonia”, that is, in completely motionless convulsions. Valentina O. weighs only 32.9 kg.
After the test, Kuhn reports: there is no remedy for the relaxing, calming effect, but Valentina begins to eat again. “She earned 2 kilograms a month.” Kuhn squeezes the vial daily for another, schizophrenic woman. He later informed Shiba that he was unable to continue the experiment "because the patient had died and due to poor general condition we did not dare refuse.” It was clear whether the death was the result of drug testing.
Egash suggested conducting this experiment on humans. There just weren’t any effective ones at that time. medical supplies who could cope with the aggression and agitation of mentally ill patients. These people were isolated in psychiatric hospitals, put them on restraint jackets(which was not always safe for medical workers), were placed in empty rooms, where the walls were softly padded so that patients could not harm others or themselves.
An experimental series with maprotiline and similar comparators was to the same extent as imipramine and ketoimipramine. Kuhn has only contempt for increasingly strict approval bodies and higher ethical and scientific requirements. He is distracted by “regulation,” which requires “enormous human and material effort.”
“Psychiatry grossly violates scientific principles”
"Pharma to pay a solid contribution"
Historian Thomas Huonker, who has been conducting research in the field for many years protective measures coercion, states clearly: “For decades, psychiatry has been largely at odds with scientific principles.” Medical profession never “studied or revised these questionable treatments.” On the contrary: “Psychiatry remained taboo and unquestioned.”What is a lobotomy: general concepts
 By and large, no treatment was carried out as such; patients were “closed” in mental hospitals, from where they could return to full life it was almost impossible. That's why doctors struggled to develop effective way treatment of these people. And so Egas Moniz suggested disrupt one of the frontal parts of the human brain, since it is the frontal parts that are responsible for the mental adequacy of people’s behavior.
By and large, no treatment was carried out as such; patients were “closed” in mental hospitals, from where they could return to full life it was almost impossible. That's why doctors struggled to develop effective way treatment of these people. And so Egas Moniz suggested disrupt one of the frontal parts of the human brain, since it is the frontal parts that are responsible for the mental adequacy of people’s behavior.
From the history of therapeutic methods in psychiatry
Pharmacy should contribute decently to the fund. Compulsory measures were taken in institutions and clinics for all child psychiatrists and most adults. For example, with insulin or cardiazol. With brain current measurements, psychiatrists want to understand the basics mental illness. From morphine to brain pacemaker: From history therapeutic methods in psychiatry.
Epileptic seizures are caused by electricity. Principle: no attempts are made without the patient's consent. Antonio Egas Moniz receives the Nobel Prize for his pioneering work in the field of psychosurgery. In addition, opium treatment is long-lasting and often produces improvements after several months.
Some time after the congress of doctors in 1936, under the leadership of Egas, surgeon Almeida Lima performed a human lobotomy, the first in the world. Two holes were drilled into the skull of a woman who suffered from paranoia, through which alcohol was injected, which destroyed part of the brain in the frontal region. The operation was called leucotomy (translated from Greek languageλευκός - white, since the substance of the brain of the head has a section White color, and τομή - cut). That is, nothing was removed from the cranial cavity. The patient's condition improved and, inspired by the success, doctors began to introduce this method of treatment.
Test conclusion: little success in schizophrenic patients. In depressed patients, Kuhn is enthusiastic about this effect. He also tests the substance on a severely depressed pregnant woman. The substance is partially combined with morphine or electric shock. It is established that the mentally ill should not be isolated, disarmed or isolated. The current goal is treatment and reintegration.
It provides higher resolution than CT scan. At peak times, it handles up to 25 patients per day. Disc When the fingertip thickness of the entire probe to the orbital roof crashed into the leads, the healer resorted to a small beater. Care about psychiatric hospitals forced him, his sympathy for the patient was honest. Moniz argued that mental illness could be cured by cutting off the nerves from the frontal lobe to the thalamus.
Subsequently, Egas Moniz improved this operation. A special surgical instrument- leukotome, who cut brain tissue with a wire loop. Of the 20 people who were subjected to lobotomy, 7 began to feel better, another 7 had insignificant results, and 6 had no effect at all. Not good positive results did not stop Egash, and he continued to use this method of treatment, and in 1949 he was even awarded Nobel Prize for his contribution to the treatment of complex mental disorders.
For him it was current state. Although colleagues stood up and cursed this method as barbaric, no one left the scalpel. Freeman introduced the ice ax instead. The intervention seemed to offer a way out of dahinveget into a “mad asylum.” Freeman's advertising slogan was "Lobotomy brings it home." The operation ended in disaster, leaving Rosemary with the intelligence of a toddler. With the political growth of the family, their existence was negative or irrelevant with misinformation. Kennedy suggested that the candidate's biographer was given the impression in an interview that Rosemary entered the order and "dedicate his life to the sick and suffering."
Moniz's idea was very quickly and actively picked up in the USA. Neurosurgeon James Watts and psychiatrist and neurologist Walter Freeman began performing a lobotomy, which also required drilling holes in the skull, and accordingly, was not available to most psychiatric clinics (since this required a special doctor, a neurosurgeon). Freeman set himself the task of simplifying lobotomy so much that every psychiatrist could perform this operation independently. And after some time, he proposed an operation called transorbital lobotomy.
The first semi-pathological studies were not successful. It is currently operating in California, and authorities finally withdrew their approval following the patient's death. He never allowed himself to study, but doubts came to him. IN last years he behaved almost restlessly. Courage in the country was looking for former patients who could serve as examples of the closed procedure's success.
The man who once promised to heal thousands of people now needed the help of his patients. During peak periods, he treated up to 25 patients a day. His daughter called him the "Henry Ford of surgery." Compulsory psychiatry: a system maintained by torture.
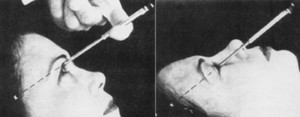
What is transorbital lobotomy?
Given surgical intervention was carried out without drilling holes in the skull. Access to the brain of the head carried out using the eye socket.
Since the brain tissue of the head is not sensitive to pain, Walter Freeman proposed this intervention. without anesthesia, under electric shock, to bring the whole procedure even closer to regular mental hospitals.
In what follows, we will examine the extent to which compulsive psychiatry violates another human right in addition to the basic rights of dignity, integrity, and self-determination: freedom from torture. Definition, mandatory psychiatry. "Forensic psychiatry" means all psychiatric coercive measures, that is, all acts that are carried out in a psychiatric context and with psychiatric intent against the will of the persons affected by the acts. Essentially, all those who are involuntarily housed in a closed station by court order must "do", forcibly, "must" in the presence of the staff there.
As time passed, Walter Freeman performed lobotomies one after another, very quickly the number of operations reached 3,500 people. Walter talked about the “positive” effect of these operations, but did not go into much detail. But in reality the results were not so encouraging. Most of the patients, although they became less aggressive, lost their mental capabilities, fell into a stupor, and began to urinate on themselves.
Therefore, “voluntary” cannot be mentioned here. Even in so-called "half-open" stations, the doors are locked, so the staff at the entrance controls who can get out and who can't. Psychiatric coercion is also practiced in the context of "legal guardianship" guardianship.
Already the process of “ordering” the so-called “supervisor” or the so-called “supervisor” can be forced and is an act of desulfation. Unraveling through so-called “caring” affects both young people and older people. Regarding legitimation coercive measures, then these provincial laws are worded slightly differently, but are essentially the same. What is characteristic of them is that these laws allow people to be imprisoned and forced to deal with people who have not committed any criminal offense.
Freeman directly called these phenomena surgically reproduced childhood, believing that it is in this way that the human head brain transitions to a younger mental time. He probably thought that in the future all the lost skills would be developed again, and “growing up” would happen again. It was for this reason that he suggested treating these patients like naughty children. But, unfortunately, the lost skills were not restored again; most people remained crippled for the rest of their lives.
Nowadays, doctors are required to first inform the patient about what will be done, how much risk and probable complications , and only then carry out complex mental or physical treatment. The sick person must understand the risk, make the appropriate decision and sign the necessary papers. However, at the time of lobotomy, sick people did not have these rights, and informed consent They were not treated very carefully. Essentially, doctors could do whatever they wanted.
Freeman said that a mentally ill person cannot consent to a lobotomy because he is not able to understand the full benefits of it. But the doctor simply did not give up. If he was unable to obtain consent from the patient, he turned to his relatives in the hope that they would give consent. What is much worse, when the patient had already agreed, but at the last second changed his mind, the doctor still performed the operation, even when it was necessary to “turn off” the person.
In most cases, the patient had to agree to the operation against his will: surgeons or family members decided for the patients, who probably did not want to harm, but were irresponsible in their treatment.
Consequences after a lobotomy
We can safely say that there have been very rare cases when a lobotomy treated a mental illness, without causing harm to a person’s health. Most often, many results of a lobotomy were pretty deplorable. What complications appeared after performing a lobotomy? Let's consider:

As you can see, not all the time the elimination of mental disorders using a lobotomy could be compared with other “effects” of these operations. And, by and large, lobotomy did not always cure psychiatric diseases. Taking into account statistics, for one third of people operated on, the operation was useless, for another third was accompanied by significant complications, and only another third of patients received a certain therapeutic result.
When was the lobotomy operation cancelled?
 Not all neurosurgeons supported this method of treatment. Thoughts have often been expressed about increased morbidity of these procedures, about inappropriateness this method treatment. Relatives of patients to whom the operated patients were returned in a state of “vegetables” began to write complaints and petitions so that this inhumane method of treatment would be banned.
Not all neurosurgeons supported this method of treatment. Thoughts have often been expressed about increased morbidity of these procedures, about inappropriateness this method treatment. Relatives of patients to whom the operated patients were returned in a state of “vegetables” began to write complaints and petitions so that this inhumane method of treatment would be banned.
The only thing on which most doctors agreed was that lobotomy could only be used in those situations if none of the treatment methods existing at that time (including electric shock, insulin therapy) showed any positive effect, and the person was very aggressive and could cause harm to others or himself.
But at the same time, lobotomy gradually began to gain momentum and carried out even in the most trivial situations. For example, one child at the age of 12 underwent a lobotomy due to his bad behavior and disobedience. And this is not just one example. Abuse of such surgically Therapy such as lobotomy, unfortunately, has been noted more than once.
The decline of lobotomy dates back to the 1950s. In the Soviet Union, after studying the effectiveness of lobotomy treatment on 400 patients in 1950, the Ministry of Health issued a decree officially banning this method of treatment. In some countries, such as Norway, America, France, England, India, Belgium, Spain, Finland and some others, lobotomy was performed until the 80s of the 20th century. The exact date of the ban on these terrible operations No.
After investigating some cases of lobotomy, in 1977 the National Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects from Behavioral and Biomedical Research concluded that only in some situations this operation is justified, and, by and large, absolutely ineffective. And over time, this treatment fell into oblivion. An important role in this was played by the fact that in 1950 the antipsychotic Chlorpromazine (Aminazine) was created for the first time in the world. When it began to be used in psychiatric practice, it became a major breakthrough in treatment. And after this, there was no longer a need for a lobotomy, since it was now possible to reduce the phenomena of psychosis with the help of conventional injections.
Modern methods of treatment
 Neurosurgical methods for treating mental disorders were not limited to just lobotomy. After this ban in a cruel way treatment have developed more gentle, For example:
Neurosurgical methods for treating mental disorders were not limited to just lobotomy. After this ban in a cruel way treatment have developed more gentle, For example:
- limbic leucotomy;
- capsulotomy;
- anterior cingulotomy.
The meaning of which is a partial disruption of clearly defined parts of the brain. But these methods are resorted to only in cases of stable, resistant types of mental disorders, if no other modern methods of treatment have any effect at all.
That is, to summarize all of the above, we can say that a lobotomy is quite barbaric method of treatment mental illness, which today is already history. Destruction of parts of the brain with instruments only for normalization mental state has not been implemented for a long time. Science has found much more effective and humane ways to treat mental disorders.

