Topic: General overview of the human body
Lesson: Organ systems in the body. Levels of organization
Our body. This definition seems so familiar and understandable that we rarely think about its essence. And to the question: “What is this anyway?” many may find it difficult to answer.
Organism- is a certain complex or system that reacts as a whole to various changes external environment. This system is relatively stable, despite the fact that it consists of many organs. Organs, in turn, consist of tissues, tissues of cells, cells of molecules.
Molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems - all these floors, or different levels living things, are combined in the human body into a single and inseparable whole.
Living organisms are built from special chemical compounds - organic matter(proteins, fats, carbohydrates, nucleic acids). They are part of any living cell. These large molecules act as building blocks that create complex complexes. Cell substances are not randomly located, but form ordered structures - organelles, which ensure the vital processes of the cell. The human body is a multicellular state. The cells of the human body are not the same and differ in their specialization. Cells of the same specialty are combined into groups. Together with the intercellular substance they form tissues. Organs are made up of several tissues. Organs that perform a single function and have overall plan structure and development, will unite into organ systems. All organ systems are interconnected and make up single organism.
There are 10 major organ systems in the human body.
Integumentary system- consists of skin and mucous membranes lining cavities internal organs, respiratory tract, digestive tract. The function of this system is to protect the body from mechanical damage, drying out, temperature fluctuations, penetration of pathogenic bacteria.
1. Kolesov D.V., Mash R.D., Belyaev I.N. Biology 8 M.: Bustard - p. 49, tasks and question 1.
2. What is included in the urinary system?
3. What is included in the digestive system?
4. Prepare an essay about one of the organ systems.
The purpose of the lesson:
- to form in students a concept about the human body, levels of organization human body, structure of the body.
Lesson objectives:
- introduce the concepts of “organism”, “tissues”, “organs”, “organ systems”, develop thinking based on the lesson material.
Lesson plan:
1.Organizational part.
2.Updating background knowledge students.
3.Learning new material.
4. Consolidation of knowledge.
5.Homework.
During the classes:
Organizational moment - on the board the date, month, topic of the lesson.
Updating basic knowledge:
The human body is divided into musculoskeletal, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, excretory, reproductive, endocrine, nervous and sensory systems.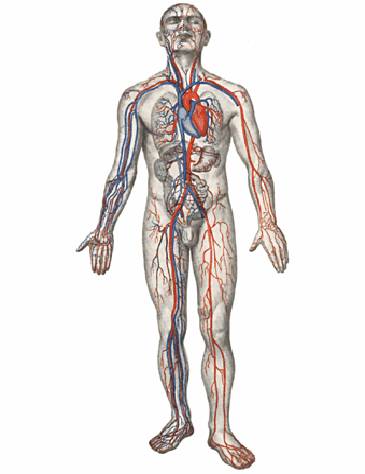
Fig. No. 4. Human circulatory system.
Organ systems are closely interconnected, their coordinated activity ensures the vital activity of the entire organism. All organisms are characterized by the distribution of functions between its cells, organs and physiological systems.
A functional system is a mutually coordinated combination of the activities of different organs or physiological systems, which is aimed at achieving a beneficial adaptation to the environment for the organism. To ensure vital processes, coordinated activity of organs or physiological systems is necessary. Thus, for the supply of oxygen to cells and the removal of carbon dioxide from them, the joint work of the respiratory and circulatory systems is necessary. To ensure movement, the joint work of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems is necessary. 
Rice. No. 5. An example of a functional system.
The human body reacts to changes in the internal and external environment. For normal functioning an important condition is to maintain constancy internal environment(temperature, chemical composition blood, etc.). To achieve this goal, the activity of physiological systems and processes is constantly regulated. Thus, if necessary, the activity of certain organs and systems is enhanced or slowed down, and this is ensured by the mechanisms of humoral, nervous and immune regulation.
Humoral regulation of the body occurs with the participation of biological active substances, in particular, hormones. They are carried throughout the body through the bloodstream and act slowly but for a long time.
Nervous system perceives the influence of the external and changes in the internal environment, analyzes information and influences activities individual organs or systems. Nervous regulation It acts quickly enough, but not for long, is addressed to a specific organ and is strictly dosed. The activity of the nervous system occurs through reflexes. The nervous system closely interacts with the endocrine system and forms a single unit with it functional system neuro humoral regulation. Chemical elements, circulating in the blood, affect the functioning of the nervous system. The formation of these substances is regulated by the nervous system.
It also plays an important role in regulating the body’s vital functions. the immune system, which controls the constancy of the body’s defenses throughout a person’s life.
Consolidation of knowledge:
1. Describe the concept of “organism”.
2. Name the levels of structure of the body known to you.
3. What is necessary for the normal functioning of the body? What regulates the body's activity?
Homework:
Prepare for a conversation on the following questions:
1. Define the concept of “organism”.
2. Name the structures of the body.
3 Define the concepts “cell” and “tissue”.
4. Describe the concept of “organ”. Name the human organs you know.
5. The relationship between the structure and functions of organs.
6. Name the ones you know physiological systems, define this concept.
7. The concept of “functional system”.
8. Mechanisms for regulating the body’s activities.
General acquaintance with the human body (organs and organ systems). The human body consists of cells and intercellular substances that form tissues, organs and organ systems. All these components are combined into a single organism, which functions under the control of the nervous and endocrine systems.
Participates in the humoral regulation of the body's vital processes vascular system. The nervous system not only coordinates the activities of all systems of the human body, but also establishes relationships with environment. Structural features of an organism, its form and functions are determined by the genotype formed in the process of phylo- and ontogenetic development.
An organ is a system of tissues connected by common development and origin; it has a specific shape, topography and function. Each organ consists of various tissues that are structurally and functionally interconnected. However, in each organ one type of tissue predominates. For example, the heart contains all types of tissues (epithelial, muscle, connective, nervous), but muscle tissue predominates in it, nervous tissue in the brain, and epithelial tissue in the skin.
During development in humans and higher animals, many organs functionally complement each other. Thus, the formation of organ systems aimed at fulfilling general function. However, the identification of organ systems in the whole organism is conditional, since they are all functionally interconnected. The body functions as a single whole. The organs that form this or that system develop from a common rudiment, perform one function and are topographically interconnected. There are nine organ systems in the human body. Such systems in the human body are: the system of movement organs (movement apparatus, musculoskeletal system), digestive, lymphatic, genitourinary system, glands internal secretion, endocrine system, sensory system; respiratory system, cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Brief information about the structure and functions of tissues. In the process of evolution of animals and humans, specialization of the cells of a multicellular organism and division of functions between them occurred.
Tissue is a phylogenetically formed structure of cells, which has its own morphofunctional properties, high specialization, inherent only this species fabrics. Each tissue is built from cells that are characterized by a certain shape and size. The organic morphofunctional unity of the body is achieved only through the interaction of all tissues.
Biologists disagree about the number of tissue types. Most authors distinguish four types of tissues in animals: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous.

