Description of the structure and functions of the nervous and endocrine system, the principle of operation, their meaning and role in the body.
Whereas are building blocks for the human "message system", there are entire networks of neurons that transmit signals between the brain and the body. These organized networks, including more than trillion neurons, create the so-called nervous system. It consists of two parts: Central nervous system (head and spinal cord) and peripheral (nerves and nervous networks throughout the body)
The endocrine system is also an integral part of the body information transmission system. This system uses the glands located throughout the body, which regulate many processes, such as metabolism, digestion, blood pressure and growth. Although endocrine system Not connected directly with nervous, they often work together.
central nervous system
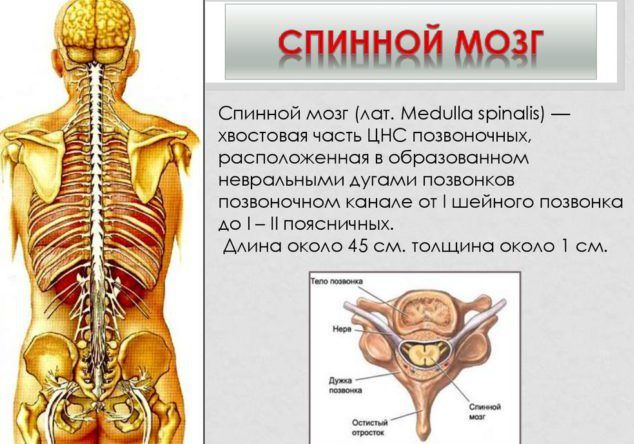
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of a brain and spinal. Primary form Communications in the CNS is neuron. The brain and the spinal cord are vital for the functioning of the body, so there are a number of protective barriers around them: bones (skull and spine), and membrane fabrics ( brain shells). In addition, both structures are in protecting their cerebrospinal fluid.
Why brain and spinal cord are so important? It is worth thinking that these structures are the actual center of our "message system". CNS is able to process all your feelings and think about experience from these sensations. Information about pain, touch, cold, etc. is assembled by receptors throughout the body, and then transmitted to the nervous system. The CNS also sends signals into the body in order to control the movements, actions and reactions to the outside world.
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of nerves propagating the central nervous system. Nerves and nerve networks PNS are actually just bunches of axons leaving nerve cells. The size of the nerves ranges from relatively small, up to sufficiently large, which is easy to see even without a magnifying glass.
PNS can be additionally divided into two different nervous systems: somatic and vegetative.
Somatic nervous system: Sends physical sensations and teams to movements and action. This system consists of afferent (sensitive) neurons delivering information from nerves to the head and spinal cord, and efferent (sometimes some of them are called motor) neurons transmitting information from the CNS to muscle tissues.
Vegetative nervous system: Controls involuntary functions, such as heartbeat, breathing, digestion and blood pressure. This system is also associated with emotional reactions, such as sweating and crying. The vegetative nervous system can be divided further into a sympathetic and parasympathetic system.
Sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system controls the body reaction to stress. When this system works, breathing and heartbeat is rapidly, the digestion slows down or stops, pupils are expanding and strengthening. This system is responsible for the preparation of the body to dangerous situation.
Parasympathetic nervous system: Parasympathetic nervous system acts in counterweight sympathetic system. E system helps to "calm down" the body after the critical situation. Heartbeat and breathing slow down, digestion resumes, pupils narrow and sweating stops.
Endocrine system
As previously noted, the endocrine system is not part of the nervous system, but still needed to transmit information through the body. This system consists of glands that highlight chemical transmitters - hormones. They enroll through blood into special parts of the body, including organs and body tissues. Among the most important endocrine glasses It is possible to note the sishkovoid gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, ovaries and tests. Each of these glands performs certain functions in different areas of the body.
From how the endocrine and nervous systems interact depends on the coherence of the work of the whole organism. Having a complex device, the human body reaches such harmony due to the inseparable interconnection of nervous and endocrine systems. Unifying links in this tandem are hypothalamus and pituitary.
Endocrine system human organism Regulated by the central nervous system (CNS). Their close relationship is due to the fact that information on the state of the body enters the brain through neurons, and the hormones of the endocrine system are intermediaries in the transfer of this information.
Thyroid And hormones produced by it significantly affect the functioning of the brain. This is expressed in the fact that with the lack of thyroid hormones slows down mental development And cretinism develops.
Overall characteristics of nervous and endocrine systems
The inseparable interrelation of the endocrine and nervous system (NA) provides such vital processes:
- ability to reproduce;
- human growth and development;
- ability to adapt to changing external conditions;
- constancy and stability interior environment Human organism.

The structure of the nervous system includes a spinal and brain, as well as peripheral departments, including vegetative, sensory and motor neurons. They have special processes that affect the target cells. Signals in the form of electrical pulses are transmitted by nervous tissues.
The main element of the endocrine system was the pituitary, as well as it includes:
- sishkovoid;
- thyroid;
- fork and pancreas;
- adrenal glands;
- kidney;
- ovaries and testicles.
Endocrine system organs produce special chemical compounds - Hormones. These are substances governing many vital functions in the body. It is with the help of them the impact on the body. Hormones, standing out in the bloodstream, join the cells of the targets. The interaction of the nervous and endocrine systems ensures the normal activity of the body and form a single neuroendocrine regulation.
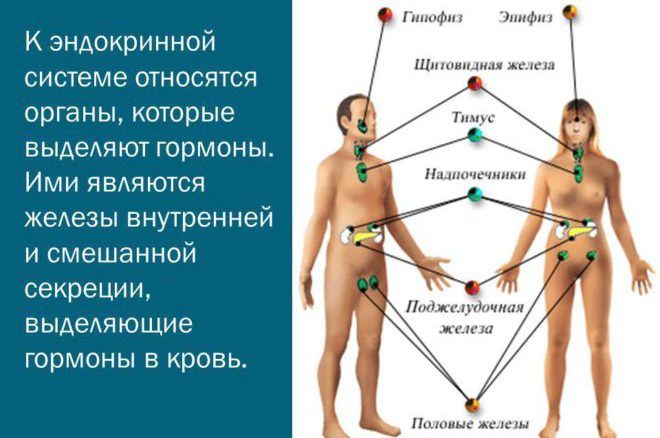
Hormones are regulators of body cell activity. Under their influence there are physical mobility and thinking, the growth and features of the physique, the tone of the voice, behavior, sexual attraction and much more. The endocrine system provides a person to adapt to various changes in the external environment.
What role is the hypothalamus in neuroregulation? The hypothalamus is connected by S. different parts The nervous system and refers to the elements of the intermediate brain. Such a connection is carried out through afferent paths.
The hypothalamus receives signals from the dorsal and medium brain, basal ganglia and Talamus, some parts of large hemispheres. The hypothalamus receives information from all parts of the body through internal and external receptors. These signals and impulses affect the endocrine system by means of pituitary.
Functions of the nervous system
The nervous system, being a complex anatomical formation, ensures the adaptation of a person to the ever-changing conditions of the outside world. The structure of the NA includes:
- nerves;
- spinal and brain;
- nervous plexus and nodes.
NA responds quickly to all sorts of changes by sending electronic signals. This is how work correction is various organs. Adjusting the operation of the endocrine system, it contributes to the preservation of homeostasis.
The main functions of the NA are as follows:
- transmission of all information on the functioning of the body into the brain;
- coordination and regulation of conscious televitations;
- perception of information on the state of the body under the conditions of the external environment;
- coordinates heartbeat arterial pressure, body temperature and breathing.
The main purpose of the NA is to perform vegetative and somatic functions. The vegetative component has sympathetic and parasympathetic departments.
Sympathetic is responsible for the response to stress and prepares the body to a dangerous situation. When this department is working, breathing and heartbeat, digestion stops or slows down, sweating and pupils are expanding.

The parasympathetic department of the NA, on the contrary, is designed to calm the body. When it is activated, breathing and heartbeat slows down, the resumption of digestion, termination reinforced sweating and bringing pupils norm.
The vegetative nervous system is designed to regulate the operation of blood and lymphatic vessels. It provides:
- expansion and narrowing of the glorification of capillaries and arteries;
- normal pulse;
- reducing the smooth muscles of internal organs.
In addition, its tasks include endocrine and exocrine glands of special hormones. And also it regulates the metabolic processes occurring in the body. The vegetative system of autonomous and does not depend on the somatic, which, in turn, is responsible for the perception of various stimuli and the reaction to them.
The functioning of the senses and skeletal muscle organs is under the control of the somatic NA department. The control center is in the brain where information from various senses comes. Changes in behavior and adaptation to the social medium is also under the control of the somatic part of the NA.
Nervous system and adrenal glands
How the nervous system regulates the work of the endocrine can be traced on the functioning of adrenal glands. They are an important part of the endocrine system of the body and in their structure have a cortic and brain layer.
The bark of the adrenal glands performs the functions of the pancreas internal secretionAnd the brain layer is a kind of transitional element between the endocrine and the nervous system. It is in it that the hormones of stress are produced so-called catecholamines, which include norepinephrine and adrenaline. They provide the organism survival in difficult conditions.
In addition, these hormones perform a number of other important functions, in particular, due to them:
- the increase in the heart pulse;
- expansion of pupils;
- strengthening;
- increase the tone of vessels;
- expanding the lumen of the bronchi;

- an increase in blood pressure indicators;
- suppression of motorcycle gasts;
- amplification of myocardial reduction;
- reducing the development of secretion of the digestive glands.
The immediate connection of the adrenal glands and the nervous system is traced in the following: the NC irritation causes stimulation of the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine. In addition, the tissues of the brain layer of the adrenal glands are formed from the primaries, which also underlie the sympathetic NA. Therefore, their further functioning resembles the work of this part of the CNS.
The brain layer of adrenal glands reacts to such factors:
- pain;
- skin irritation;
- muscle work;
- supercooling;

- powerful emotions;
- mental overvoltage;
- reducing blood sugar.
How is the interaction?
The pituitary, not having a direct connection with the outside world of the body, receives information that signals what changes occur in the body. These information, the body receives through the senses and central NA organs.
The pituitary is a key element of the endocrine system. He submits to the hypothalamus, which coordinates all vegetative system. Under his control is both the activities of some brain departments, as well as internal organs. The hypothalamus regulates:
- cardiac frequency;
- body temperature;
- protein, fatty and carbohydrate exchange;
- quantity mineral salts;
- water volume in tissues and blood.
The activity of the hypothalamus is carried out on the basis of nervous connections and blood vessels. It is through them that the guide is guided by the pituitary. The nerve impulses coming from the brain are converted by the hypothalamus into endocrine incentives. They are enhanced or weakened under the influence of humoral signals, which, in turn, enter the hypothalamus from the glands in its subordination.
Through the pituitary gland, the blood enters the hypothalamus and is saturated there with special neurogormons. These substances having a peptide nature of origin are part of the protein molecules. There are 7 such neurogormons, otherwise they are called liberins. Their main purpose is to synthesize trop hormones affecting many vital important functions organism. These tropins perform certain functions. To their number, among other things, are as follows:
- stimulation of immunity activity;
- regulation of lipid metabolism;
- improving the sensitivity of the germ;
- parental instinct stimulation;
- suspension and differentiation of cells;
- conversion short-term memory in long-term.
Along with Lebber, hormones are distinguished - overwhelming statins. Their function is to suppress the production of trop hormones. These include somatostatin, prolactostatin and melanostatin. The endocrine system operates on the principle of feedback.
If some iron internal secretion produces hormones in excessive amounts, then a slowdown in the synthesis of its own pituitary hormones, which regulate the operation of this gland.
Conversely, the lack of relevant hormones causes reinforced production. This difficult process The interaction is processed throughout the evolution, so it is very reliable. But when there is a failure in it, the entire chain of connections is reacting, which is expressed in the development of endocrine pathologies.
What you need to know about how the endocrine system of our kids works and works? The nervous and endocrine system of the body is very important elements.
1 54810
Photo Gallery: Nervous and Endocrine Body System
Our body can be compared with the megalopolis. Cells, its inhabitants, sometimes live by "families", forming organs, and sometimes, getting lost among others, are accumulated (such as cells of the immune system). Some - Domases and never leave their refuge, others - travelers and do not sit in one place. All of them are different, each with their needs, character and regime. Between cells pass small and large transport highways - blood and lymphatic vessels. Every second in our body there are millions of events: someone or something violates the peaceful life of cells or some of them forget about their duties or, on the contrary, too much. And, as in any metropolis, a competent administration is required to maintain order here. We know that our main manager is a nervous system. And her right hand is an endocrine system (ES).
In order
ES is one of the most complex and mysterious systems of the body. Complicated because it consists of many glands, each of which can produce from one to dozens of different hormones, and regulates the work of a huge number of organs, including the endocrine glands themselves. Inside the system there is a special hierarchy that allows it to strictly control its operation. The mysteriousness of the ES is associated with the complexity of the mechanisms of regulation and composition of hormones. To explore her work, super-modern technology is required. The role of many hormones is still unclear. And we only guess the existence of some, despite the fact that it is impossible to determine their composition and cells that are not allowed. That is why endocrinology is a science studying hormones and organs that produce them - they consider one of the most complex among medical specialties And the most promising. Understanding the exact purpose and mechanisms of the work of certain substances, we will be able to influence the processes flowing into our organism. After all, thanks to hormones, we appear on the light, it is they who create a sense of attraction between future parents, determine the time of the formation of genital cells and the moment of fertilization. They change our lives, affecting the mood and character. Today we know that the processes of aging are also managed by ES.
Characters...
The organs that make up the ES (thyroid gland, adrenal glands, etc.), are groups of cells located in other organs or tissues, and individual cells scattered in different places. The difference between endocrine glands from others (they are called exocrine) lies in the fact that the first allocate their products - hormones - directly in blood or lymph. For this they are called the glands of internal secretion. And exocrine - in the clearance of a particular organ (the largest largest ecocrine iron - The liver - allocates its secret - bile - in the clearance of the gallbladder and further into the intestines) or outward (example - lacrimal glands). Ecocrine glands Called iron outer secretion. Hormones are substances that can influence cell sensitive to them (they are called target cells), changing the speed of metabolic processes. The selection of hormones directly into the blood gives ES a huge advantage. To achieve the effect, it requires a few seconds. The hormones fall directly in the bloodstream, which serves by transport and allows you to very quickly deliver the desired substance to all tissues, unlike the nervous signal, which extends through the nerve fibers and due to their rupture or damage may not reach their goal. In the case of hormones, this will not happen: liquid blood Easily finds workarounds if one or more vessels are blocked. In order for the organs and cells to be destined by ES, they received it, they are receptors that perceive a particular hormone. The feature of the work of the endocrine system is its ability to "feel" the concentration of different hormones and adjust it. And their quantity depends on age, gender, time of day and year, age, mental and physical condition man and even our habits. So ES sets the rhythm and the speed of our exchange processes.
... and performers
Guipophy - the main one endocrine Organ. It highlights hormones that stimulate or braking the rest of the rest. But the pituitary is not the vertex ES, it only performs the role of the manager. Hypotalamus - superior instance. This is a brain department consisting of cell clusters that combine the properties of nerve and endocrine. They allocate substances that regulate the work of the pituitary gland and endocrine glands. Under the leadership of the hypothalamus, hypophies produces hormones that affect the tissue sensitive to them. So, the thyrotropic hormone regulates the work thyroid gland, Corticotropic - the work of the adrenal cortex. Somatotropic hormone (or growth hormone) does not affect some concrete Organ. Its action applies to many tissues and organs. Such a difference in the action of hormones is caused by the difference in their significance for the body and the number of tasks they provide. Feature of this work complex system is the principle of feedback. Es can be called the very democratic exaggeration. And, although it has "leading" bodies (hypothalamus and pituitary gland), subordinates also affect the work of the superior glands. In the hypothalamus, hypophysies have receptors that react to the concentration of different hormones in the blood. If it is high, the signals from the receptors will block their development "at all levels. This is the principle of feedback in action. The thyroid gland received its name for the form. She closes the neck, surrounding the trachea. It includes iodine, and its lack can lead to violations of the body. Hormones gland provide a balance between the formation of adipose tissue and the use of fats stored in it. They are needed for the development of a skeleton and well-being bone tissue, And even reinforce the effect of other hormones (for example, insulin, accelerating carbohydrate exchange). These substances play a critical role in the development of the nervous system. The lack of hormones of the gland in kids leads to the underdevelopment of the brain, and later - to a decrease in the intellect. Therefore, all newborns examine on the level of these substances (such a test is included in the program of screening newborns). Together with adrenaline, the thyroid hormones affect the work of the heart and regulate blood pressure.
Parashydovoid glands
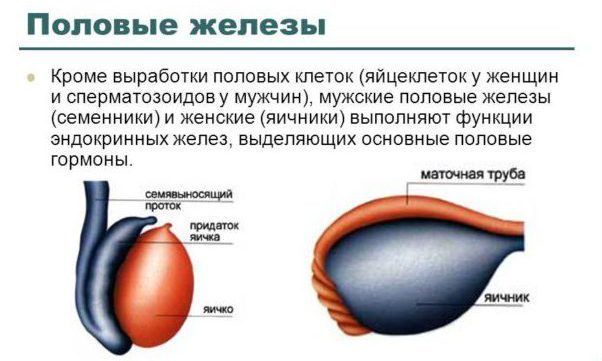
Parashydovoid glands - These are 4 glands located in the thickness of the fatty tissue behind the thyroid, for which they received their name. The glands produce 2 hormones: parathyroid and calcitonin. Both ensure the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Unlike most endocrine glands, the work of the parathyroidism regulates oscillations mineral Makeup Blood and vitamin D. Pancreas controls the exchange of carbohydrates in the body, and also participates in digestion and produces enzymes that ensure the splitting of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Therefore, it is located in the area of \u200b\u200bthe gastric transition in small intestine. Iron highlights 2 hormones: insulin and glucagon. The first reduces blood sugar levels, forcing the cells actively absorb it and use it. The second, on the contrary, increases the amount of sugar, forcing the liver cells and muscle tissue to give it. The most common disease associated with disorders in the work of the pancreas is diabetes mellitus 1 -th (or insulin-dependent). It develops due to the destruction of cells producing insulin, cells of the immune system. Most babies in patients diabetes, There are genome features that are likely to predetermine the development of the disease. But infection is most often launched or transferred stress. The adrenal glands received their name for the location. A person cannot live without adrenal glands and hormone produced, and these organs belong to vital. The program of examination of all newborns includes a test for a violation of their work - there are so dangerous consequences of such problems. The adrenal glands produce a record number of hormones. The most famous of them is adrenaline. It helps the body to prepare and cope with possible dangers. This hormone makes the heart beat faster and pump more blood to the movement organs (if you need to flee), increases the respiratory rate to ensure the organism with oxygen, reduces the sensitivity to pain. It increases pressure, providing a maximum blood flow to the brain and another important organs. Norainerenalin has similar effect. The second most important hormone of the adrenal glands is cortisol. It is difficult to name a process in the body to which he would not have influence. It causes the fabric to highlight stored substances in the blood so that all cells are provided nutrient substances. The role of cortisol is increasing when inflammation. It stimulates the development of protective substances and the work of the cells of the immune system necessary to combat inflammation, and if the latter are too active (including against its own cells), cortisol suppresses their diligence. In stress, it blocks cell division so that the body does not waste forces on this work, and engaged in guidance the immune system I would not miss "defective" samples. Hormone aldosterone regulates the concentration in the body of the main mineral salts - sodium and potassium. Sex glands - testicles in boys and ovaries in girls. The hormones they produce are capable of changing metabolic processes. Thus, testosterone (the main men's hormone) helps the growth of muscle tissue, bone system. It enhances appetite and makes boys more aggressive. And, although testosterone is considered a male hormone, it stands out in women, but in a lesser concentration.
To the doctor!
Most often at the reception to children's endocrinologist kids having excess weightAnd those kids that are seriously lagging behind the peers in growth. Parents rather draw attention to the fact that the child stands out among the peers, and begin to find out the cause. Most other endocrine diseases have no characteristic signs, and the problem of parents and doctors often recognize when the violation has already seriously changed the work of some organ or the whole body. Close to the baby: physique. Little children head and torso with relatively total body length will be more. From 9-10 years, the child begins to stretch, and the proportions of his body approach adults.

