The structure of the human body has long bothered leading scientists and researchers. For thousands of years, a wide variety of theories have been put forward that tried to explain the simple, and at the same time complex issue- how exactly it works human body.
It is important to understand the fact that most of the work of ancient researchers was carried out in secret from everyone. This is due to the fact that the religious canons of that time did not allow a detailed study of the human body.
Avicenna and Paracelsus
Scientists such as Avicenna and Paracelsus made their first conclusions based on the dissection of corpses. This sounds a little unpleasant, but only such material could provide answers to many questions.
Human anatomy is needed for several purposes: first of all, we must know what a healthy and strong organism is.
And treatment can only be carried out if the changes that occur inside organs and systems under the influence of diseases and pathogens are known.
In simple words, you cannot treat diseases without understanding those pathological processes and changes that occur at the level of organ systems, organs, tissues and cells.
The primitive tools of the first scientists were quite meager: they only had a lancet (the world's first scalpel), a clear head for understanding what they saw, and paper and a pen. The data obtained was recorded in diaries, and the first detailed diagrams and drawings appeared several centuries BC.
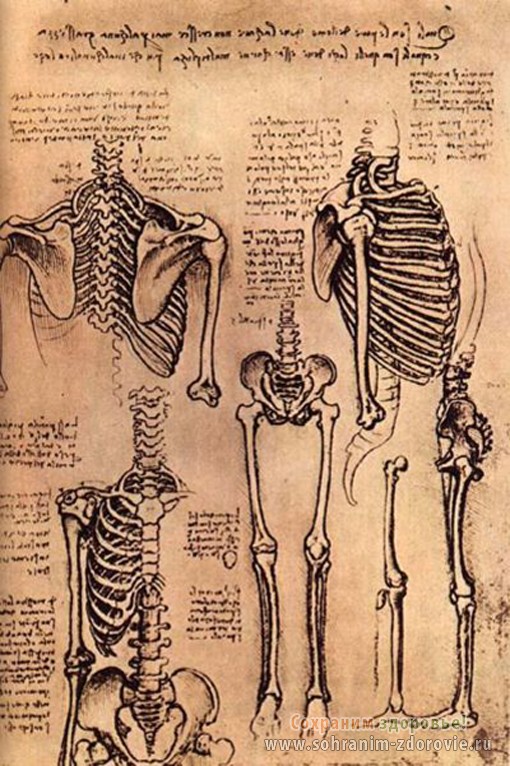
Rice. 1. Human skeleton drawn by Leonardo da Vinci
Research methods were gradually improved, and the information obtained acquired a clearer structure. And communication between leading doctors made it possible to create unified system terms and concepts in medicine.
A new era began in the 18th century scientific discoveries: Scientists are not only actively studying anatomy, but also revealing the secrets of new sciences. Among them is histology, which actively studies the structure and function of tissues, embryology - the science of fetal development in the womb.

After Harvey studied the properties of blood in detail, scientists were left with many unresolved questions.
One of the main secrets concerned the transition of blood from arteries to veins.
Marcello Malpighi fully confirmed the guesses of his colleagues who spoke about the presence of transitional bridges or anastomoses.
With the advent of the microscope, all theories were confirmed. Capillaries were opened, which turned out to be the missing link in anatomical structure circulatory system.
New tools have allowed scientists to delve deeper into the study of this fascinating science.
Organs as an object of study
As you know, our body contains a large number of specialized organs, each of which performs its own function. The stomach is part digestive system and is responsible for digesting the food eaten, the heart is part of the circulatory system, which saturates every cell in the body with nutrients.
A detailed study of each organ allows us to obtain a more in-depth picture of the functioning of the entire organism as a whole. The main task of anatomical research is to understand the functions performed by a particular object of research.
As modern methods Research involves examining the body and autopsy after death. The days of old prejudices are long gone, so scientists can do their work without unnecessary fear. All results obtained during the research process are recorded and recorded in detail.
Based on the data obtained, it is possible to draw conclusions about the functions of the organ, its condition at the time of a person’s life, and establish the exact cause of death.
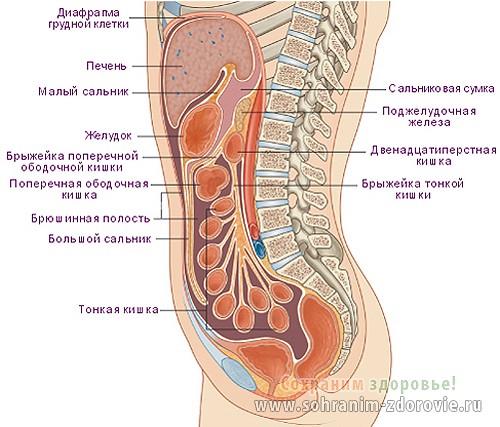
Rice. 2. Sagittal (longitudinal) section of a woman’s body.
Unfortunately, a dead human body cannot provide all the answers. You will not be able to see how cells are saturated with nutrients and absorb oxygen, you cannot see the growth processes in tissues.
Therefore, living and healthy man. In such cases, the main research tools are not a scalpel with knives, but X-ray machines, scanning systems and magnetic resonance imaging scanners.
This amazing device allows you to conduct research in several planes and make so-called “slices”.
The area of research can be very diverse: starting from studying the organ as a whole, and focusing on its functional unit - the cell. For example, for muscles, the basic building unit is a cell called a myocyte; the neuron is the basic building block of our nervous system.
If we consider the lungs, the process of gas exchange occurs in a small sac called the alveoli.
They approach her blood vessels two types: arterioles carry oxygen-enriched blood, and venules (microscopic veins) bring carbon dioxide to the lungs, which is formed during the life of our body.
Human organs as an important element of the whole organism
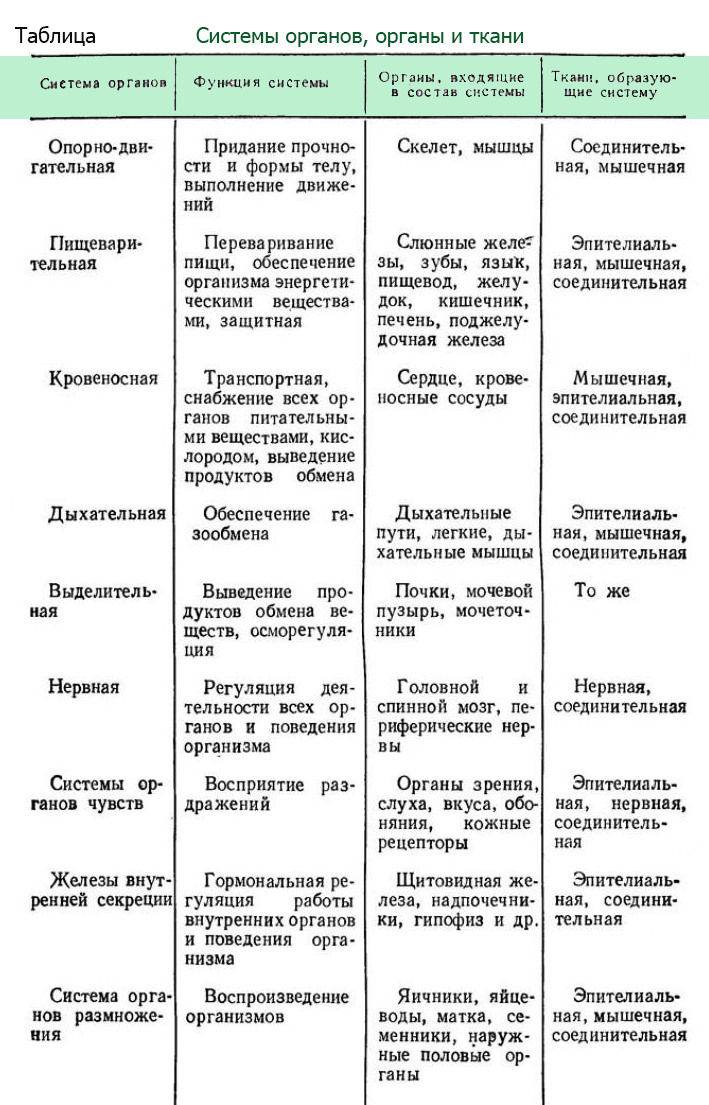
Based on the data obtained on the structure of each cell, conclusions can be drawn about the structure of the whole human body generally. To obtain accurate data, there are five main sections in anatomy. Each of them has a clearly limited range of tasks:
- systematic anatomy deals with the introductory part of this science. There is a study of basic terms and concepts that are unknown to beginners. This section deals with the study of all existing systems in the human body.
- topographic anatomy is a separate field of science that studies the location internal organs. This section is studied by all future doctors, but this knowledge is especially useful for surgeons. Cannot be carried out surgery on the stomach, if the doctor does not know where exactly it is located. In addition, there are pathological options for the placement of internal organs, up to a mirror image (in such people, the heart is on the right, the stomach is shifted to the left, the kidneys also change places, etc.)
- plastic anatomy deals with such important issues, as structural features of the body and external features of a person. This section is studied in detail by practitioners and future plastic surgeons. As you know, these doctors specialize in correction various pathologies. For example, correction of the shape of the nose after injury, breast enlargement, removal of wrinkles and folds on the body. This section studies the internal organs in terms of changes in our appearance under the influence internal factors. An example is the thyroid gland: when an excess amount of hormones is produced, a person loses significant weight, facial features become sharper, and a huge goiter appears on the neck.
As for operations on the mammary glands of women, they cannot be performed without gaps in the field of anatomical knowledge.
- comparative anatomy studies this important point, as the development of the human body under the influence of evolution. According to Darwin's theory, humans have changed significantly over millions of years. The first species were not "homo sapiens" or homo sapiens. In the early stages of evolution, our ancestors learned to walk upright, used primitive tools and learned the basics of hunting. And some organs are vestigial or obsolete. They came to us from the ancestors of animals.
An example is the appendix - this appendix does not participate in the digestive processes of the human body. But in animals it plays one of the key functions. The same applies to the tailbone - humans do not need it, but in animals the tail is attached to this part of the spine.
- anthropological anatomy deals with the study of such issues as racial characteristics, gender and age differences in individuals. Studying this section allows you to understand evolutionary changes and the development features of people of a particular race. For example, people in Africa have black skin for a reason. This reliable protection from scorching sun rays, which with prolonged exposure can lead to burns and sunstroke. Residents of the far north have a characteristic, narrow eye shape. This is due to exposure to powerful winds and snowstorms that often occur in those areas.
If you are interested in human anatomy, internal organs, pictures will help you more clearly imagine the structure of the human body.
Without a visual representation, it is very difficult to understand what exactly is being discussed in a particular case. For these purposes, there are various scientific manuals that demonstrate the structure of internal organs and their location.
Atlases are the most popular: such publications are published every year and are constantly filled with new elements and images. The information received will be of interest to everyone: both students medical universities, and for ordinary people who are interested in science.
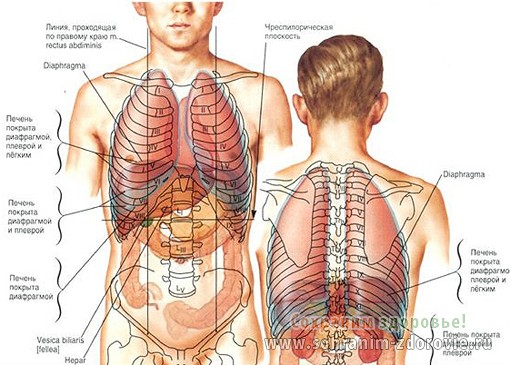
Rice. 3. The location of the internal organs in a man.
As for doctors and medical personnel, then such atlases have long turned into a reference book. Even acquired knowledge must be periodically updated and consolidated. Therefore, it would be useful to open the atlas and flip through a few pages.
There's one more thing interesting direction in the field of studying the structure of the human body, this is...
Pathological anatomy
It is a scientific discipline that studies all pathological processes in organs, tissues and cells that occur during various diseases. Many scientists believe that the founder of this trend is Rudolf Virchow, a famous German scientist.
He was the first to suggest that all changes occur at the cellular level. Until this point, there were many theories, but none of them considered the cell as the main place of struggle between the body and pathogens.
Modern pathological anatomy studies the causes of the disease (the so-called etiology), the main mechanisms of its development (in science the term is known as pathogenesis) and various shapes diseases (among scientists this phenomenon known as pathomorphosis.)
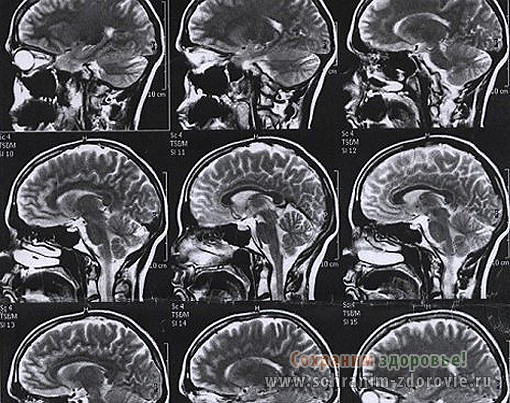
Rice. 4. Results of magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
The main tasks of modern pathological anatomy look like this:
- Identification of the causes of pathological changes and conditions for the development of the disease. The pathogen is called a pathogen and is a leading factor in the development of changes in cells and organs.
- Studying the mechanism of development of certain pathogenic processes. At the same time, in the human body there arise characteristic changes, which allow you to more accurately determine the type of disease.
- The study of such a phenomenon as the general picture of the disease (identification of the main signs at both the macro and micro levels.)
- Pathological anatomy actively studies the outcome of each disease and possible complications for the human body.
- Study of the changes that occur in the human body after taking medicines or procedures performed.
- A detailed study of the diagnosis based on the totality of the data obtained.
- With help various methods All pathological processes are examined. Research is carried out both during the patient’s lifetime and after his death.
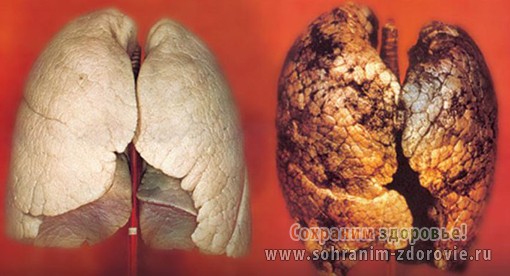
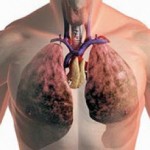
Rice. 5. Pathological changes in the lungs of a smoker.
Human anatomy, internal organs and the structure of the human body is a fascinating science.
Its study is carried out both within the framework school curriculum, and in specialized medical institutions. But it is not at all necessary to enroll in universities to get the information you are interested in.
To do this, it is enough to acquire the relevant literature and an anatomical atlas. We invite you to watch a video about how alcohol affects human internal organs. What happens to them and much more. Take care of yourself and your health!
Sincerely, team of the project “Let's Keep Healthy!
By imagining the structure and location of human internal organs, you can independently determine the source pain and which specialist should be contacted for help first. Each organ of the human body occupies a specific place and has its own unique structure.
In this regard, you should know the location of a person’s internal organs in order to independently diagnose the location of pain and contact the right doctor immediately.
The structure, location and function performed are closely interconnected; the images in the article and the video after will help to facilitate the memorization process. Conditionally human body It is customary to divide into three cavities, inside which all the organs of the human body are located:
- The chest cavity is from the neck to the end of the sternum.
- The abdominal cavity is from the end of the sternum to the hip joint.
- Pelvic cavity (small and large pelvis) – within the boundaries of the hip joints.
The chest cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by a special muscle - the diaphragm, designed to expand the lungs. Human internal organs: the layout and structural features begin to be studied, as a rule, from top to bottom - from the neck to the pelvic organs. Therefore, the first organ is thyroid, located in the neck area, usually under the Adam's apple.
However, its location is near adult not always . It may increase in size or become smaller, in some cases, prolapse of this organ of the endocrine system is observed.
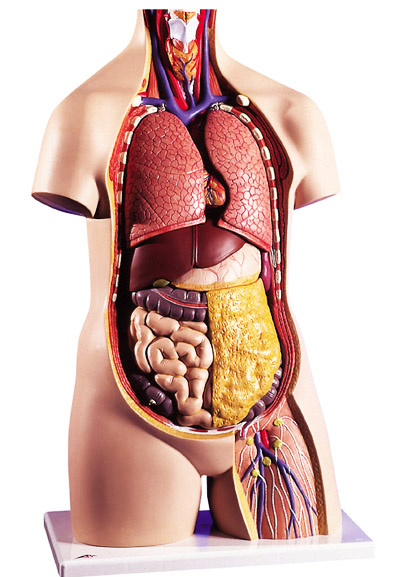
Location of organs in the chest cavity
The location of the photo below shows the internal organs of a person more clearly. Here are the heart, lungs, bronchi and the mysterious thymus, also called thymus.
Heart
An important element of the cardiovascular system, the heart, is responsible for ensuring the movement of blood in the vessels. Its location is rib cage, above the diaphragmatic muscle. To the right and left of it are the lungs.
In this case, the heart is not located with symmetrical precision in the center of our body, but slightly at an angle. Two-thirds of the cardiomuscle is located to the left of the midline, and one-third is located to the right. The shape of the heart is an individual characteristic and depends on age, gender, body constitution, health status, etc.
Lungs
The location of the human internal organs in a picture schematically reflecting the structure chest cavity, continue the most important elements of the respiratory system - the lungs. Their volume is slightly less than that of the cavity, and their sizes themselves depend on the phase of the respiratory cycle: during inhalation they expand, and during exhalation they contract. The shape of the lungs resembles a truncated cone. The base of this cone rests on the dome-shaped diaphragm muscle, and the apex is directed towards the subclavian region.
Bronchi
 Anyone familiar with the device will be able to show the location of human internal organs in the chest cavity bronchial tree– continuation of the trachea beyond the windpipe. Each of the branches of this tree is in a strict hierarchy and has its own name and structural features. Directly from the trachea there are two main bronchi, each of which goes to the corresponding lung. The thin, long and less vertical left main bronchus can be easily distinguished from the right one in the figure.
Anyone familiar with the device will be able to show the location of human internal organs in the chest cavity bronchial tree– continuation of the trachea beyond the windpipe. Each of the branches of this tree is in a strict hierarchy and has its own name and structural features. Directly from the trachea there are two main bronchi, each of which goes to the corresponding lung. The thin, long and less vertical left main bronchus can be easily distinguished from the right one in the figure.
In the lungs of the human internal organs, the location depends on their location: on the surface of the lung or inside it. Therefore, the bronchial branches of the first and second order are called extrapulmonary, and all the rest will be intrapulmonary. Each order has its own name: the first is lobar, the second is segmental, the third is subsegmental, etc. The branching ends with bronchioles, which gradually pass into the alveoli of the lungs.
Thymus
For a long time, why same exactly intended thymus iron for scientists remained a mystery. If you look at the location of the internal organs of a person in the video, you will notice that it is located at the very top of the sternum.
To date, its role has also been studied. It is now known that the thymus gland is the most important element immune system. And the name is identified with appearance: The shape of the gland resembles a two-pronged fork.
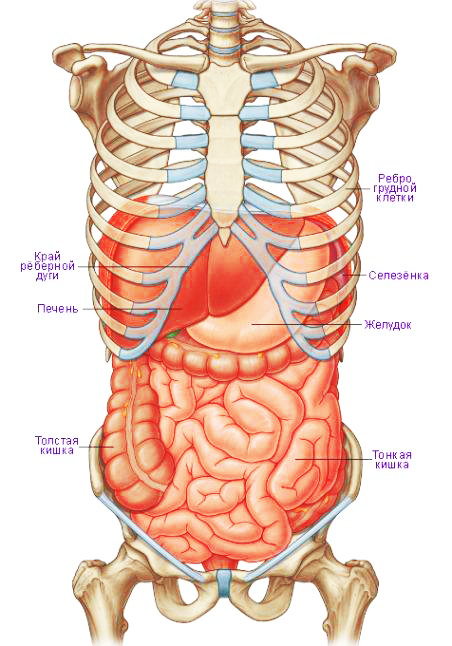
Location of organs in the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is the center of almost all elements gastrointestinal tract, digestive glands and organs of the excretory system. The incoming “food bolus” begins to be digested in the stomach, then it enters the intestines, from where the ducts of the pancreas and gall bladder open, collecting liver secretions.
The absorption process is completed in the large intestine, and filtration continues in the kidneys and spleen. The adrenal glands are also present here, controlling many processes in our body. The drawing will help you better understand the location of the internal organs of a person.
Stomach
The abdominal cavity is separated from the chest cavity by the diaphragm, so immediately below it, to the left of the midline, is the stomach - a sac-like outgrowth of the digestive canal. Its main function is the primary reservoir for food and the first stage of breakdown of incoming complex nutrients to simpler elements.
The fullness of the stomach determines its size. Food from the esophagus enters the stomach, where, with the participation of gastric juice biological oxidation processes begin.
Pancreas
The location of human internal organs in the peritoneum is subject to their role in metabolic processes. Therefore, immediately under the stomach, closer to the spine, is the permanent location of the pancreas. This is one of the largest secretory organs of the human body, performing a dual function.
The pancreatic juice it produces is saturated with digestive enzymes and is a waste product of the exocrine gland. At the same time, the pancreas secretes a whole complex of hormones that regulate the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as befits endocrine glands.
Liver
Describing the internal organs of a person, the arrangement of which is limited to the abdominal region, one cannot help but dwell on the liver - one of the vital important elements our body. The liver is located along right side from the stomach under the dome of the diaphragm and is an organ of cleansing.
It consists of two unequal lobes: the small left and large right, occupying the upper right position under the diaphragm. She is in charge of a whole range of physiological programs, the slightest failure in the implementation of which is detrimental to the body:
- neutralization medicines and other unsafe substances into substances that are less toxic in composition;
- removal of excess hormones and other substances;
- control of saturation and blood glucose levels;
- regulation of fat metabolism, cholesterol and lipid production;
- participation in the hematopoietic processes of the embryo, etc.
Gallbladder
The main function of this organ is the accumulation of bile (a greenish viscous liquid) synthesized by the liver and its excretion in the 12 duodenum through the bile and cystic ducts. It is located in the lower part of the liver, on the border of its lobes. By shape gallbladder resembles a longitudinal shaped pouch with very thin walls.
In this peculiar sac, bile produced by the liver is collected, which is then released in portions into the area duodenum to regulate the process of digestion of fats received from food. The location of the photo will only help to identify some internal organs, for example, the gallbladder is localized in the lower third of the liver can be seen in the pictures at the end of the article.
Spleen
Looking at the location of the human internal organs in the pictures in the area of the peritoneum, at the top left you can see the spleen in shape resembling a flattened hemisphere. In shape it is represented by a hemisphere, which is flattened. In both a child and an adult, this organ performs hematopoietic and immune function, through the formation of lymphocytes.
The spleen also filters the flow of platelets and red blood cells if their structure is damaged. If we continue the conversation about filtration, we can note that the spleen also prevents the passage of protozoa, foreign particles and bacteria. It is also worth noting that this organ takes an active part in the exchange of food products.
Functions of the spleen
The spleen is actively involved in both the hematopoietic and immune processes of our body, namely:
- formation of lymphocytes and filtration of microorganisms;
- participation in metabolic reactions and filtration of damaged blood cells;
- accumulation of platelets and the platelet organ and hematopoietic organ at the initial stage of embryonic development.
Intestines
It is quite simple to imagine the location of the human internal organs below the stomach, since all this space is occupied by the compactly packed intestines. Starting immediately from the stomach, a long tangled tube is small intestine, which on the right transforms into colon. The latter describes a kind of circle, the end point of which is the anus.
Smooth functioning of the intestines is the key to the health of the human body. Two thirds of all cells that provide immunity are localized in this area of the human internal organs: the location is so large quantity immunocytes are the best proof of the importance of this organ. A glass drunk on an empty stomach triggers peristalsis warm water, while cleansing the entire body of accumulated toxins.
Kidneys
One of the few organs represented by a pair. One of the few organs represented by a pair. The kidneys are paired bean-shaped elements of the urinary system. They are located to the right and left of spinal column in area lumbar region. Their sizes do not exceed 10-12 cm, while right kidney slightly smaller than the left one. By studying the location of human internal organs in the video, you can understand the main function kidneys, consisting of maintaining consistency in the internal environment and in urine formation. This is the main organ of the genitourinary system.
The localization of the kidneys in the body is the lumbar region, behind the intestines, and, accordingly, the parietal abdominal layer. Without pathology, this organ weighs from 110 to 190 grams. The main functions of the kidneys are secretion and filtration of urine, regulation of chemical homeostasis.
The kidneys are divided into cortex and medulla. On its side there is the renal pelvis, in which there is an opening for the renal vein, artery, and also for the ureter. On top, this organ is covered with a fibrous membrane.
Adrenal glands
Localized at the apex of the kidney cortex from the outside. These are paired, like the kidneys, glands internal secretion. Like the kidneys, they consist of a cortex (outer) and medulla (inner). The parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems regulate the activity of the adrenal glands.
They, in turn, regulate metabolism and also help the body adapt to changes. external environment. The latter function is due to the fact that the adrenal glands synthesize norepinephrine, adrenaline, corticosteroid hormones and androgens, which are the main hormones of the reproductive system of the human body.
On upper parts In the kidneys, paired endocrine glands are localized - the adrenal glands, consisting of the medulla and cortex. Their main function is to regulate metabolic processes, especially during stressful situations and adaptation period.
How are the organs of the large and
Between hip joints the location of the internal organs of a person in the figure fits into the following sequence: if the body is female, then the ovaries and uterus are localized here, if the body is male, the testicles and prostate. This is the location of the bladder.
Ovaries
These are the glands of the reproductive system, represented by a pair and performing endocrine function. They synthesize female sex hormones (steroids, estrogen, and partially androgens), and also the maturation and excretion of cells of the reproductive system.
Localized on both sides of the uterine walls. As already mentioned, a pair of female reproductive glands, the ovaries, not only produce hormones (estrogen, steroids and weak androgens), but also serve as a site for the development and maturation of eggs.
Uterus
The uterus is a hollow organ made of smooth muscle, the purpose of which is to bear the fetus during pregnancy. The pelvis is a relatively small cavity, so the location of the human internal organs in this area is described relative to each other. So, the uterus is located in front of the rectum directly behind bladder.
The rounded lower part ends with the cervix. The size of this organ depends on the presence/absence of pregnancy and the stage of embryonic development. During gestation, the uterus enlarges along with the fertilized egg, and after childbirth it returns to its normal size, not exceeding 10 cm.
Bladder
In the lower third of the pelvis there is a hollow smooth muscle element of the excretory organ system - bladder. Its functionality is associated with the reservation of urine secreted by the kidneys and its subsequent removal during urination. IN male body The prostate gland is located below it, and in the female behind it is the vagina.
By imagining the location of the internal organs in your body, you can quickly identify the suffering organ and have a constructive conversation with the doctor. And this, in turn, will lead to a more accurate diagnosis and the appointment of timely and effective treatment, which will have a positive effect on the speed of recovery.
Location of internal organs: table and pictures
 |
 |
 |
Video: Anatomy through human eyes

